|
P21
p21Cip1 (alternatively p21Waf1), also known as cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1 or CDK-interacting protein 1, is a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor (CKI) that is capable of inhibiting all cyclin/CDK complexes, though is primarily associated with inhibition of CDK2. p21 represents a major target of p53 activity and thus is associated with linking DNA damage to cell cycle arrest.Waldman, Todd, Kenneth W. Kinzler, and Bert Vogelstein. "p21 is necessary for the p53-mediated G1 arrest in human cancer cells." Cancer research 55.22 (1995): 5187-5190. This protein is encoded by the ''CDKN1A'' gene located on chromosome 6 (6p21.2) in humans. Function CDK inhibition p21 is a potent cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor (CKI). The p21 (CIP1/WAF1) protein binds to and inhibits the activity of cyclin-CDK2, -CDK1, and - CDK4 /6 complexes, and thus functions as a regulator of cell cycle progression at G1 and S phase. The binding of p21 to CDK complexes occurs through p21's N-terminal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
P27 (gene)
Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1B (p27Kip1) is an enzyme inhibitor that in humans is encoded by the CDKN1B gene. It encodes a protein which belongs to the ''Cip/Kip'' family of cyclin dependent kinase (Cdk) inhibitor proteins. The encoded protein binds to and prevents the activation of cyclin E-CDK2 or cyclin D-CDK4 complexes, and thus controls the cell cycle progression at G1. It is often referred to as a cell cycle inhibitor protein because its major function is to stop or slow down the cell division cycle. Function The p27Kip1 gene has a DNA sequence similar to other members of the "Cip/Kip" family which include the p21Cip1/Waf1 and p57Kip2 genes. In addition to this structural similarity the "Cip/Kip" proteins share the functional characteristic of being able to bind several different classes of Cyclin and Cdk molecules. For example, p27Kip1 binds to cyclin D either alone, or when complexed to its catalytic subunit CDK4. In doing so p27Kip1 inhibits the catalytic activ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclin-dependent Kinase 2
Cyclin-dependent kinase 2, also known as cell division protein kinase 2, or Cdk2, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''CDK2'' gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the cyclin-dependent kinase family of Ser/Thr protein kinases. This protein kinase is highly similar to the gene products of ''S. cerevisiae'' cdc28, and ''S. pombe'' cdc2, also known as Cdk1 in humans. It is a catalytic subunit of the cyclin-dependent kinase complex, whose activity is restricted to the G1-S phase of the cell cycle, where cells make proteins necessary for mitosis and replicate their DNA. This protein associates with and is regulated by the regulatory subunits of the complex including cyclin E or A. Cyclin E binds G1 phase Cdk2, which is required for the transition from G1 to S phase while binding with Cyclin A is required to progress through the S phase. Its activity is also regulated by phosphorylation. Multiple alternatively spliced variants and multiple transcription initi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CDK2
Cyclin-dependent kinase 2, also known as cell division protein kinase 2, or Cdk2, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''CDK2'' gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the cyclin-dependent kinase family of Ser/Thr protein kinases. This protein kinase is highly similar to the gene products of ''S. cerevisiae'' cdc28, and ''S. pombe'' cdc2, also known as Cdk1 in humans. It is a catalytic subunit of the cyclin-dependent kinase complex, whose activity is restricted to the G1-S phase of the cell cycle, where cells make proteins necessary for mitosis and replicate their DNA. This protein associates with and is regulated by the regulatory subunits of the complex including cyclin E or A. Cyclin E binds G1 phase Cdk2, which is required for the transition from G1 to S phase while binding with Cyclin A is required to progress through the S phase. Its activity is also regulated by phosphorylation. Multiple alternatively spliced variants and multiple transcription initi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PCNA
Proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) is a DNA clamp that acts as a processivity factor for DNA polymerase δ in eukaryotic cells and is essential for replication. PCNA is a homotrimer and achieves its processivity by encircling the DNA, where it acts as a scaffold to recruit proteins involved in DNA replication, DNA repair, chromatin remodeling and epigenetics. Many proteins interact with PCNA via the two known PCNA-interacting motifs PCNA-interacting peptide (PIP) box and AlkB homologue 2 PCNA interacting motif (APIM). Proteins binding to PCNA via the PIP-box are mainly involved in DNA replication whereas proteins binding to PCNA via APIM are mainly important in the context of genotoxic stress. Function The protein encoded by this gene is found in the nucleus and is a cofactor of DNA polymerase delta. The encoded protein acts as a homotrimer and helps increase the processivity of leading strand synthesis during DNA replication. In response to DNA damage, this protein is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromosome 6
Chromosome 6 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 6 spans more than 170 million base pairs (the building material of DNA) and represents between 5.5 and 6% of the total DNA in cells. It contains the major histocompatibility complex, which contains over 100 genes related to the immune response, and plays a vital role in organ transplantation. Genes The human leukocyte antigen lies on chromosome 6, with the exception of the gene for β2-microglobulin (which is located on chromosome 15), and encodes cell-surface antigen-presenting proteins among other functions. Number of genes In 2003, the entirety of chromosome 6 was manually annotated for proteins, resulting in the identification of 1,557 genes, and 633 pseudogenes. The following are some of the newer gene count estimates. Because researchers use different approaches to genome annotation their predictions of the number of genes on each chromosome var ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
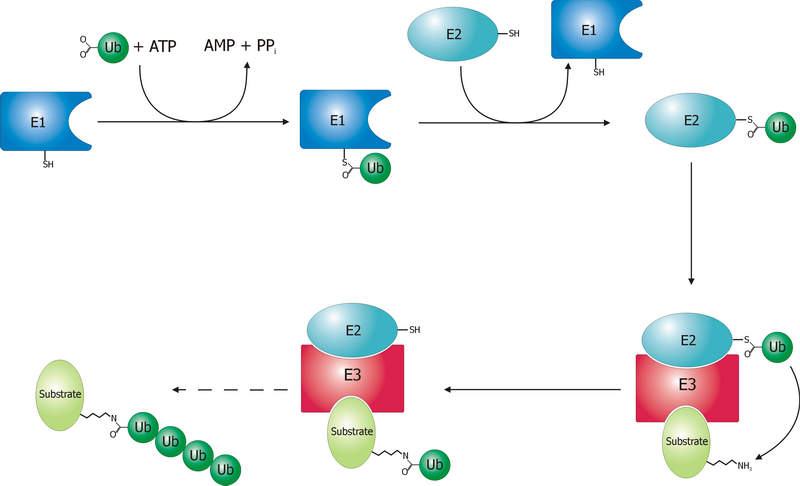
Ubiquitin Ligases
A ubiquitin ligase (also called an E3 ubiquitin ligase) is a protein that recruits an E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme that has been loaded with ubiquitin, recognizes a protein substrate, and assists or directly catalyzes the transfer of ubiquitin from the E2 to the protein substrate. In simple and more general terms, the ligase enables movement of ubiquitin from a ubiquitin carrier to another thing (the substrate) by some mechanism. The ubiquitin, once it reaches its destination, ends up being attached by an isopeptide bond to a lysine residue, which is part of the target protein. E3 ligases interact with both the target protein and the E2 enzyme, and so impart substrate specificity to the E2. Commonly, E3s polyubiquitinate their substrate with Lys48-linked chains of ubiquitin, targeting the substrate for destruction by the proteasome. However, many other types of linkages are possible and alter a protein's activity, interactions, or localization. Ubiquitination by E3 ligases r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caspase
Caspases (cysteine-aspartic proteases, cysteine aspartases or cysteine-dependent aspartate-directed proteases) are a family of protease enzymes playing essential roles in programmed cell death. They are named caspases due to their specific cysteine protease activity – a cysteine in its active site nucleophilically attacks and cleaves a target protein only after an aspartic acid residue. As of 2009, there are 12 confirmed caspases in humans and 10 in mice, carrying out a variety of cellular functions. The role of these enzymes in programmed cell death was first identified in 1993, with their functions in apoptosis well characterised. This is a form of programmed cell death, occurring widely during development, and throughout life to maintain cell homeostasis. Activation of caspases ensures that the cellular components are degraded in a controlled manner, carrying out cell death with minimal effect on surrounding tissues. Caspases have other identified roles in programmed cell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apoptosis
Apoptosis (from grc, ἀπόπτωσις, apóptōsis, 'falling off') is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (morphology) and death. These changes include blebbing, cell shrinkage, nuclear fragmentation, chromatin condensation, DNA fragmentation, and mRNA decay. The average adult human loses between 50 and 70 billion cells each day due to apoptosis. For an average human child between eight and fourteen years old, approximately twenty to thirty billion cells die per day. In contrast to necrosis, which is a form of traumatic cell death that results from acute cellular injury, apoptosis is a highly regulated and controlled process that confers advantages during an organism's life cycle. For example, the separation of fingers and toes in a developing human embryo occurs because cells between the digits undergo apoptosis. Unlike necrosis, apoptosis produces cell fragments called apoptotic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclin E
Cyclin E is a member of the cyclin family. Cyclin E binds to G1 phase Cdk2, which is required for the transition from G1 to S phase of the cell cycle that determines initiation of DNA duplication. The Cyclin E/CDK2 complex phosphorylates p27Kip1 (an inhibitor of Cyclin D), tagging it for degradation, thus promoting expression of Cyclin A, allowing progression to S phase. Functions of Cyclin E Like all cyclin family members, cyclin E forms a complex with cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK2). Cyclin E/CDK2 regulates multiple cellular processes by phosphorylating numerous downstream proteins. Cyclin E/CDK2 plays a critical role in the G1 phase and in the G1-S phase transition. Cyclin E/CDK2 phosphorylates retinoblastoma protein (Rb) to promote G1 progression. Hyper-phosphorylated Rb will no longer interact with E2F transcriptional factor, thus release it to promote expression of genes that drive cells to S phase through G1 phase. Cyclin E/CDK2 also phosphorylates p27 and p21 during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclin-dependent Kinase Inhibitor
A cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor protein is a protein which inhibits the enzyme cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK). Several function as tumor suppressor proteins. Cell cycle progression is delayed or stopped by cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors, abbreviated CDIs, CKIs or CDKIs. CDIs are involved in cell cycle arrest An arrest is the act of apprehending and taking a person into custody (legal protection or control), usually because the person has been suspected of or observed committing a crime. After being taken into custody, the person can be questi ... at the G1 phase. Seven cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor proteins have thus far been identified. They are named by the small letter "p" followed by their molecular weight in kilodaltons. They are p15, p16, p18, p19, p21, p27, and p57. Associated gene and target References External links * Protein domains {{protein-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SCF Complex
Skp, Cullin, F-box containing complex (or SCF complex) is a multi-protein E3 ubiquitin ligase complex that catalyzes the ubiquitination of proteins destined for 26S proteasomal degradation. Along with the anaphase-promoting complex, SCF has important roles in the ubiquitination of proteins involved in the cell cycle. The SCF complex also marks various other cellular proteins for destruction. Core components SCF contains a variable F-box protein and three core subunits: *F-box protein (FBP) – FBP contributes to the substrate specificity of the SCF complex by first aggregating to target proteins independently of the complex. Each FBP (e.g. Skp2) may recognize several different substrates in a manner that is dependent on post-translational modifications such as phosphorylation or glycosylation. FBP then binds to Skp1 of the SCF complex using an F-box motif, bringing the target protein into proximity with the functional E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme. FBP is also essential in reg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CASP3
Caspase-3 is a caspase protein that interacts with caspase-8 and caspase-9. It is encoded by the ''CASP3'' gene. ''CASP3'' orthologs have been identified in numerous mammals for which complete genome data are available. Unique orthologs are also present in birds, lizards, lissamphibians, and teleosts. The CASP3 protein is a member of the cysteine-aspartic acid protease (caspase) family. Sequential activation of caspases plays a central role in the execution-phase of cell apoptosis. Caspases exist as inactive proenzymes that undergo proteolytic processing at conserved aspartic residues to produce two subunits, large and small, that dimerize to form the active enzyme. This protein cleaves and activates caspases 6 and 7; and the protein itself is processed and activated by caspases 8, 9, and 10. It is the predominant caspase involved in the cleavage of amyloid-beta 4A precursor protein, which is associated with neuronal death in Alzheimer's disease. Alternative splicing of this g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |