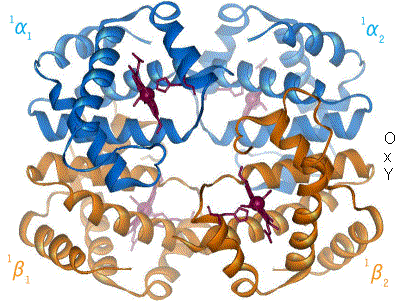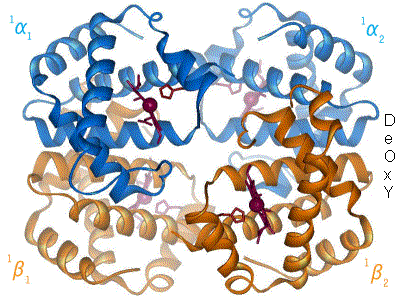
|
PyMOL
PyMOL is an open source but proprietary molecular visualization system created by Warren Lyford DeLano. It was commercialized initially by DeLano Scientific LLC, which was a private software company dedicated to creating useful tools that become universally accessible to scientific and educational communities. It is currently commercialized by Schrödinger, Inc. As the original software license was a permissive licence, they were able to remove it; new versions are no longer released under the Python license, but under a custom license (granting broad use, redistribution, and modification rights, but assigning copyright to any version to Schrodinger, LLC.), and some of the source code is no longer released. PyMOL can produce high-quality 3D images of small molecules and biological macromolecules, such as proteins. According to the original author, by 2009, almost a quarter of all published images of 3D protein structures in the scientific literature were made using PyMOL. PyMOL ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warren Lyford DeLano
Warren Lyford DeLano (June 21, 1972 – November 3, 2009) was an advocate for the increased adoption of open source practices in the sciences, and especially drug discovery, where advances which save time and resources can also potentially save lives. Biography Born in Philadelphia on June 21, 1972, DeLano was educated at Yale University, where he helped produce campus humor magazine ''The Yale Record''. In 2000, he launched the PyMOL open-source molecular viewer in an attempt to demonstrate the practical impact open source might have on discovery of new medicines. Since then, PyMOL has been widely adopted for molecular structure visualization within the pharmaceutical industry and at public sector research institutions. In 2003, DeLano founded DeLano Scientific LLC to commercialize PyMOL and conduct an experiment in the "laboratory of the market" regarding the commercial viability of an open source software company. His hypothesis was that open source software is intrinsically ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permissive Licence
A permissive software license, sometimes also called BSD-like or BSD-style license, is a free-software license which instead of copyleft protections, carries only minimal restrictions on how the software can be used, modified, and redistributed, usually including a warranty disclaimer. Examples include the GNU All-permissive License, MIT License, BSD licenses, Apple Public Source License and Apache license. the most popular free-software license is the permissive MIT license. Example The following is the full text of the simple GNU All-permissive License: Definitions The Open Source Initiative defines a permissive software license as a "non-copyleft license that guarantees the freedoms to use, modify and redistribute". GitHub's ''choosealicense'' website describes the permissive MIT license as "ettingpeople do anything they want with your code as long as they provide attribution back to you and don’t hold you liable." California Western School of Law's newmediarights ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aqua (user Interface)
Aqua is the graphical user interface, design language and Theme (computing), visual theme of Apple Inc., Apple's macOS operating system. It was originally based on the theme of water, with droplet-like components and a liberal use of reflection effects and translucency. Its goal is to "incorporate color, depth, translucence, and complex textures into a visually appealing interface" in macOS applications. At its introduction, Steve Jobs noted that "... it's liquid, one of the design goals was when you saw it you wanted to lick it". Aqua was first introduced at the 2000 Macworld Conference & Expo in San Francisco. Its first appearance in a commercial product was in the July 2000 release of iMovie 2, followed by Mac OS X 10.0 the following year. Aqua is the successor to Appearance Manager, Platinum, which was used in Mac OS 8, Mac OS 9 and macOS Server, Mac OS X Server 1.2. The appearance of Aqua has changed frequently over the years, most recently and drastically with the release ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Widget (GUI)
A graphical widget (also graphical control element or control) in a graphical user interface is an element of interaction, such as a button or a scroll bar. Controls are software components that a computer user interacts with through direct manipulation to read or edit information about an application. User interface libraries such as Windows Presentation Foundation, Qt, GTK, and Cocoa, contain a collection of controls and the logic to render these. Each widget facilitates a specific type of user-computer interaction, and appears as a visible part of the application's GUI as defined by the theme and rendered by the rendering engine. The theme makes all widgets adhere to a unified aesthetic design and creates a sense of overall cohesion. Some widgets support interaction with the user, for example labels, buttons, and check boxes. Others act as containers that group the widgets added to them, for example windows, panels, and tabs. Structuring a user interface with widget to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tk (software)
Tk is a free and open-source, cross-platform widget toolkit that provides a library of basic elements of GUI widgets for building a graphical user interface (GUI) in many programming languages. Tk provides a number of widgets commonly needed to develop desktop applications, such as button, menu, canvas, text, frame, label, etc. Tk has been ported to run on most flavors of Linux, Mac OS, Unix, and Microsoft Windows. Like Tcl, Tk supports Unicode within the Basic Multilingual Plane, but it has not yet been extended to handle the current extended full Unicode (e.g., UTF-16 from UCS-2 that Tk supports). Tk was designed to be extended, and a wide range of extensions are available that offer new widgets or other capabilities. Since Tcl/Tk 8, it offers "native look and feel" (for instance, menus and buttons are displayed in the manner of "native" software for any given platform). Highlights of version 8.5 include a new theming engine, originally called Tk Tile, but it is now general ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poisson–Boltzmann Equation
The Poisson–Boltzmann equation is a useful equation in many settings, whether it be to understand physiological interfaces, polymer science, electron interactions in a semiconductor, or more. It aims to describe the distribution of the electric potential in solution in the direction normal to a charged surface. This distribution is important to determine how the electrostatic interactions will affect the molecules in solution. The Poisson–Boltzmann equation is derived via mean-field assumptions. From the Poisson–Boltzmann equation many other equations have been derived with a number of different assumptions. Origins Background and derivation The Poisson–Boltzmann equation describes a model proposed independently by Louis Georges Gouy and David Leonard Chapman in 1910 and 1913, respectively. In the Gouy-Chapman model, a charged solid comes into contact with an ionic solution, creating a layer of surface charges and counter-ions or double layer. Due to thermal motio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FreeGLUT
FreeGLUT is an open-source alternative to the OpenGL Utility Toolkit (GLUT) library. GLUT (and hence FreeGLUT) allows the user to create and manage windows containing OpenGL contexts on a wide range of platforms and also read the mouse, keyboard and joystick functions. FreeGLUT is intended to be a full replacement for GLUT, and has only a few differences. Since GLUT has gone into stagnation, FreeGLUT is in development to improve the toolkit. It is released under the MIT License. History FreeGLUT was originally written by Paweł W. Olszta with contributions from Andreas Umbach and Steve Baker. Since Paweł ceased working in 3D graphics, he passed the baton to Steve Baker. The current maintainers of FreeGLUT are John F. Fay, John Tsiombikas, and Diederick C. Niehorster. Paweł started FreeGLUT development on December 1, 1999. The project is now virtually a 100% replacement for the original GLUT with only a few departures (such as the abandonment of SGI-specific features such as th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OpenGL Extension Wrangler Library
OpenGL (Open Graphics Library) is a cross-language, cross-platform application programming interface (API) for rendering 2D and 3D vector graphics. The API is typically used to interact with a graphics processing unit (GPU), to achieve hardware-accelerated rendering. Silicon Graphics, Inc. (SGI) began developing OpenGL in 1991 and released it on June 30, 1992; applications use it extensively in the fields of computer-aided design (CAD), virtual reality, scientific visualization, information visualization, flight simulation, and video games. Since 2006, OpenGL has been managed by the non-profit technology consortium Khronos Group. Design The OpenGL specification describes an abstract API for drawing 2D and 3D graphics. Although it is possible for the API to be implemented entirely in software, it is designed to be implemented mostly or entirely in hardware. The API is defined as a set of functions which may be called by the client program, alongside a set of named int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software
Software is a set of computer programs and associated documentation and data. This is in contrast to hardware, from which the system is built and which actually performs the work. At the lowest programming level, executable code consists of machine language instructions supported by an individual processor—typically a central processing unit (CPU) or a graphics processing unit (GPU). Machine language consists of groups of binary values signifying processor instructions that change the state of the computer from its preceding state. For example, an instruction may change the value stored in a particular storage location in the computer—an effect that is not directly observable to the user. An instruction may also invoke one of many input or output operations, for example displaying some text on a computer screen; causing state changes which should be visible to the user. The processor executes the instructions in the order they are provided, unless it is instructed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structural Biology
Structural biology is a field that is many centuries old which, and as defined by the Journal of Structural Biology, deals with structural analysis of living material (formed, composed of, and/or maintained and refined by living cells) at every level of organization. Early structural biologists throughout the 19th and early 20th centuries were primarily only able to study structures to the limit of the naked eye's visual acuity and through magnifying glasses and light microscopes. In the 20th century, a variety of experimental techniques were developed to examine the 3D structures of biological molecules. The most prominent techniques are X-ray crystallography, nuclear magnetic resonance, and electron microscopy. Through the discovery of X-rays and its applications to protein crystals, structural biology was revolutionized, as now scientists could obtain the three-dimensional structures of biological molecules in atomic detail. Likewise, NMR spectroscopy allowed information about p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open-source Model
Open source is source code that is made freely available for possible modification and redistribution. Products include permission to use the source code, design documents, or content of the product. The open-source model is a decentralized software development model that encourages open collaboration. A main principle of open-source software development is peer production, with products such as source code, blueprints, and documentation freely available to the public. The open-source movement in software began as a response to the limitations of proprietary code. The model is used for projects such as in open-source appropriate technology, and open-source drug discovery. Open source promotes universal access via an open-source or free license to a product's design or blueprint, and universal redistribution of that design or blueprint. Before the phrase ''open source'' became widely adopted, developers and producers have used a variety of other terms. ''Open source'' gained ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |