|
Purposive Behaviorism
Purposive behaviorism is a branch of psychology that was introduced by Edward Tolman. It combines the study of behavior while also considering the purpose or goal of behavior.Schultz, D.P. & Schultz, S.E. (2012). ''A history of modern psychology.'' (10). Belmont, CA: Wadsworth, Cengage Learning. Tolman thought that learning developed from knowledge about the environment and how the organism relates to its environment. Tolman's goal was to identify the complex cognitive mechanisms and purposes that guided behavior.Eichenenbaum, H. (2001). The hippocampus and declarative memory: Cognitive mechanisms and neural codes. ''Behavioural Brain Research 127(1)'', 199–207. His theories on learning went against the traditionally accepted stimulus-response connections (see classical conditioning) at his time that had been proposed by other psychologists such as Edward Thorndike. Tolman disagreed with John B.Watson's behaviorism, so he initiated his own behaviorism, which became known as purp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychology
Psychology is the scientific study of mind and behavior. Psychology includes the study of conscious and unconscious phenomena, including feelings and thoughts. It is an academic discipline of immense scope, crossing the boundaries between the natural and social sciences. Psychologists seek an understanding of the emergent properties of brains, linking the discipline to neuroscience. As social scientists, psychologists aim to understand the behavior of individuals and groups.Fernald LD (2008)''Psychology: Six perspectives'' (pp.12–15). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications.Hockenbury & Hockenbury. Psychology. Worth Publishers, 2010. Ψ (''psi''), the first letter of the Greek word ''psyche'' from which the term psychology is derived (see below), is commonly associated with the science. A professional practitioner or researcher involved in the discipline is called a psychologist. Some psychologists can also be classified as behavioral or cognitive scientists. Some psyc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognitive Map
A cognitive map is a type of mental representation which serves an individual to acquire, code, store, recall, and decode information about the relative locations and attributes of phenomena in their everyday or metaphorical spatial environment. The concept was introduced by Edward Tolman in 1948. He tried to explain the behavior of rats that appeared to learn the spatial layout of a maze, and subsequently the concept was applied to other animals, including humans. The term was later generalized by some researchers, especially in the field of operations research, to refer to a kind of semantic network representing an individual's personal knowledge or schemas. Overview Cognitive maps have been studied in various fields, such as psychology, education, archaeology, planning, geography, cartography, architecture, landscape architecture, urban planning, management and history. Because of the broad use and study of cognitive maps, it has become a colloquialism for just about any ment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognitive Psychology
Cognitive psychology is the scientific study of mental processes such as attention, language use, memory, perception, problem solving, creativity, and reasoning. Cognitive psychology originated in the 1960s in a break from behaviorism, which held from the 1920s to 1950s that unobservable mental processes were outside the realm of empirical science. This break came as researchers in linguistics and cybernetics, as well as applied psychology, used models of mental processing to explain human behavior. Work derived from cognitive psychology was integrated into other branches of psychology and various other modern disciplines like cognitive science, linguistics, and economics. The domain of cognitive psychology overlaps with that of cognitive science, which takes a more interdisciplinary approach and includes studies of non-human subjects and artificial intelligence. History Philosophically, ruminations on the human mind and its processes have been around since the times of the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consciousness
Consciousness, at its simplest, is sentience and awareness of internal and external existence. However, the lack of definitions has led to millennia of analyses, explanations and debates by philosophers, theologians, linguisticians, and scientists. Opinions differ about what exactly needs to be studied or even considered consciousness. In some explanations, it is synonymous with the mind, and at other times, an aspect of mind. In the past, it was one's "inner life", the world of introspection, of private thought, imagination and volition. Today, it often includes any kind of cognition, experience, feeling or perception. It may be awareness, awareness of awareness, or self-awareness either continuously changing or not. The disparate range of research, notions and speculations raises a curiosity about whether the right questions are being asked. Examples of the range of descriptions, definitions or explanations are: simple wakefulness, one's sense of selfhood or sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
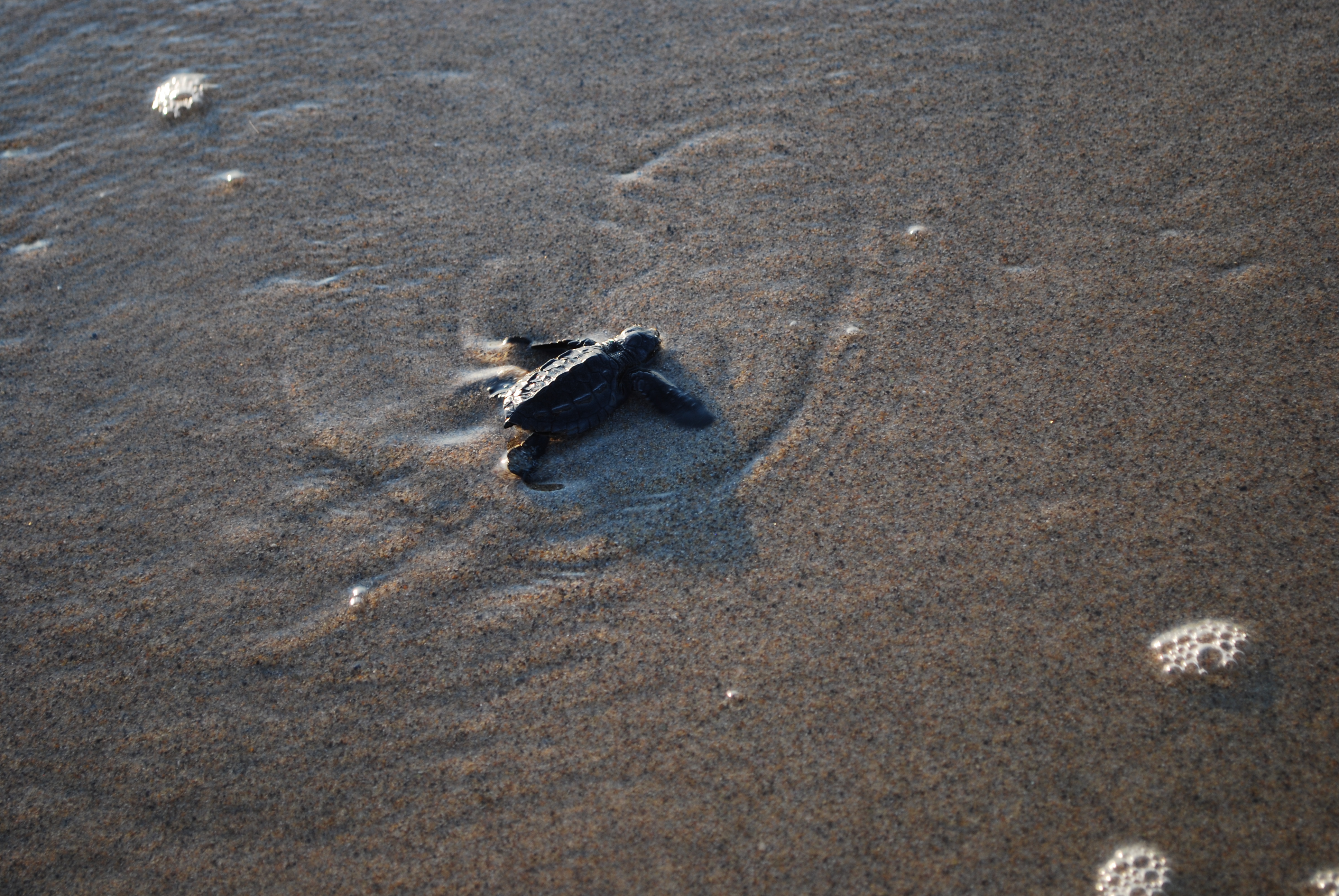
Instinct
Instinct is the inherent inclination of a living organism towards a particular complex behaviour, containing both innate (inborn) and learned elements. The simplest example of an instinctive behaviour is a fixed action pattern (FAP), in which a very short to medium length sequence of actions, without variation, are carried out in response to a corresponding clearly defined stimulus. Any behaviour is instinctive if it is performed without being based upon prior experience (that is, in the absence of learning), and is therefore an expression of innate biological factors. Sea turtles, newly hatched on a beach, will instinctively move toward the ocean. A marsupial climbs into its mother's pouch upon being born. Other examples include animal fighting, animal courtship behaviour, internal escape functions, and the building of nests. Though an instinct is defined by its invariant innate characteristics, details of its performance can be changed by experience; for example, a dog can imp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychological Review
''Psychological Review'' is a bimonthly peer-reviewed academic journal that covers psychological theory. It was established by James Mark Baldwin (Princeton University) and James McKeen Cattell (Columbia University) in 1894 as a publication vehicle for psychologists not connected with the laboratory of G. Stanley Hall (Clark University), who often published in his ''American Journal of Psychology''. ''Psychological Review'' soon became the most prominent and influential psychology journal in North America, publishing important articles by William James, John Dewey, James Rowland Angell, and many others. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor of 8.934. The journal has implemented the Transparency and Openness Promotion guidelines that provide structure to research planning and reporting and aim to make research more transparent, accessible, and reproducible. History In the early years of the 20th century, Baldwin purchased Cattell's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Problem Solving
Problem solving is the process of achieving a goal by overcoming obstacles, a frequent part of most activities. Problems in need of solutions range from simple personal tasks (e.g. how to turn on an appliance) to complex issues in business and technical fields. The former is an example of simple problem solving (SPS) addressing one issue, whereas the latter is complex problem solving (CPS) with multiple interrelated obstacles. Another classification is into well-defined problems with specific obstacles and goals, and ill-defined problems in which the current situation is troublesome but it is not clear what kind of resolution to aim for. Similarly, one may distinguish formal or fact-based problems requiring psychometric intelligence, versus socio-emotional problems which depend on the changeable emotions of individuals or groups, such as tactful behavior, fashion, or gift choices. Solutions require sufficient resources and knowledge to attain the goal. Professionals such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognitive Maps
A cognitive map is a type of mental representation which serves an individual to acquire, code, store, recall, and decode information about the relative locations and attributes of phenomena in their everyday or metaphorical spatial environment. The concept was introduced by Edward Tolman in 1948. He tried to explain the behavior of rats that appeared to learn the spatial layout of a maze, and subsequently the concept was applied to other animals, including humans. The term was later generalized by some researchers, especially in the field of operations research, to refer to a kind of semantic network representing an individual's personal knowledge or schemas. Overview Cognitive maps have been studied in various fields, such as psychology, education, archaeology, planning, geography, cartography, architecture, landscape architecture, urban planning, management and history. Because of the broad use and study of cognitive maps, it has become a colloquialism for just about any men ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latent Learning
Latent learning is the subconscious retention of information without reinforcement or motivation. In latent learning, one changes behavior only when there is sufficient motivation later than when they subconsciously retained the information. Latent learning is when the observation of something, rather than experiencing something directly, can affect later behavior. Observational learning can be many things. A human observes a behavior, and later repeats that behavior at another time (not direct imitation) even though no one is rewarding them to do that behavior. In the social learning theory, humans observe others receiving rewards or punishments, which invokes feelings in the observer and motivates them to change their behavior. In latent learning particularly, there is no observation of a reward or punishment. Latent learning is simply animals observing their surroundings with no particular motivation to learn the geography of it; however, at a later date, they are able to expl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Tolman
Edward Chace Tolman (April 14, 1886 – November 19, 1959) was an American psychologist and a professor of psychology at the University of California, Berkeley. Through Tolman's theories and works, he founded what is now a branch of psychology known as purposive behaviorism. Tolman also promoted the concept known as latent learning first coined by Blodgett (1929). A ''Review of General Psychology'' survey, published in 2002, ranked Tolman as the 45th most cited psychologist of the 20th century. Tolman was one of the leading figures in protecting academic freedom during the McCarthy era in early 1950s. In recognition of Tolman's contributions to both the development of psychology and academic freedom, the Education and Psychology building on Berkeley campus, the "Tolman Hall", was named after him. Early life Born in West Newton, Massachusetts, brother of Caltech physicist Richard Chace Tolman, Edward C. Tolman studied at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, receiving B.S. i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
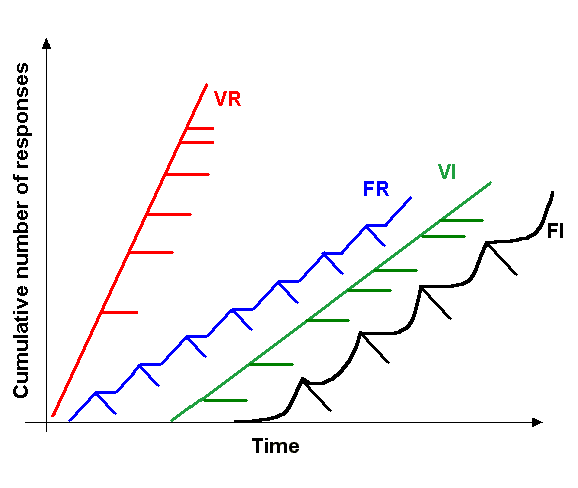
Reinforcement
In behavioral psychology, reinforcement is a consequence applied that will strengthen an organism's future behavior whenever that behavior is preceded by a specific antecedent stimulus. This strengthening effect may be measured as a higher frequency of behavior (e.g., pulling a lever more frequently), longer duration (e.g., pulling a lever for longer periods of time), greater magnitude (e.g., pulling a lever with greater force), or shorter latency (e.g., pulling a lever more quickly following the antecedent stimulus). The model of self-regulation has three main aspects of human behavior, which are self-awareness, self-reflection, and self-regulation. Reinforcements traditionally align with self-regulation. The behavior can be influenced by the consequence but behavior also needs antecedents. There are four types of reinforcement: positive reinforcement, negative reinforcement, extinction, and punishment. Positive reinforcement is the application of a positive reinforcer. Negati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Behaviourism
Behaviorism is a systematic approach to understanding the behavior of humans and animals. It assumes that behavior is either a reflex evoked by the pairing of certain antecedent stimuli in the environment, or a consequence of that individual's history, including especially reinforcement and punishment contingencies, together with the individual's current motivational state and controlling stimuli. Although behaviorists generally accept the important role of heredity in determining behavior, they focus primarily on environmental events. Behaviorism emerged in the early 1900s as a reaction to depth psychology and other traditional forms of psychology, which often had difficulty making predictions that could be tested experimentally, but derived from earlier research in the late nineteenth century, such as when Edward Thorndike pioneered the law of effect, a procedure that involved the use of consequences to strengthen or weaken behavior. With a 1924 publication, John B. W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |