|
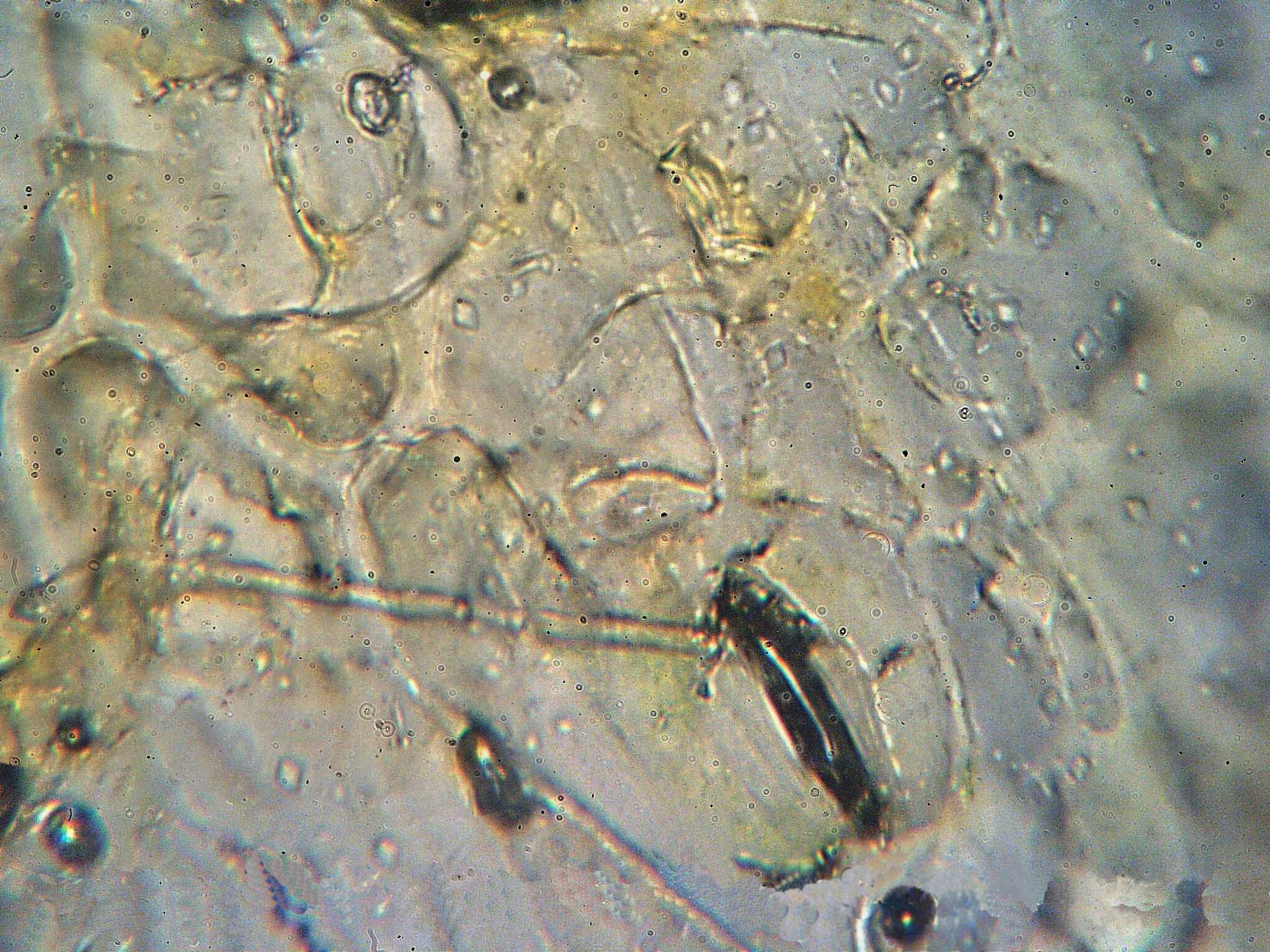
Pucciniastrum Epilobii
''Pucciniastrum epilobii'' is a plant pathogen Plant pathology (also phytopathology) is the scientific study of diseases in plants caused by pathogens (infectious organisms) and environmental conditions (physiological factors). Organisms that cause infectious disease include fungi, oomyc ... infecting fuchsias. References External links USDA ARS Fungal Database Fungal plant pathogens and diseases Ornamental plant pathogens and diseases Pucciniales Fungi described in 1861 Fungus species {{Teliomycotina-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fuchsia
''Fuchsia'' () is a genus of flowering plants that consists mostly of shrubs or small trees. The first to be scientifically described, '' Fuchsia triphylla'', was discovered on the Caribbean island of Hispaniola (Haiti and the Dominican Republic) about 1696–1697 by the French Minim monk and botanist, Charles Plumier, during his third expedition to the Greater Antilles. He named the new genus after German botanist Leonhart Fuchs (1501–1566). Taxonomy The fuchsias are most closely related to the northern hemisphere genus '' Circaea'', the two lineages having diverged around 41 million years ago. Description Almost 110 species of ''Fuchsia'' are recognized; the vast majority are native to South America, but a few occur north through Central America to Mexico, and also several from New Zealand to Tahiti. One species, '' F. magellanica'', extends as far as the southern tip of South America, occurring on Tierra del Fuego in the cool temperate zone, but the majority are tro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plant Pathogen
Plant pathology (also phytopathology) is the scientific study of diseases in plants caused by pathogens (infectious organisms) and environmental conditions (physiological factors). Organisms that cause infectious disease include fungi, oomycetes, bacteria, viruses, viroids, virus-like organisms, phytoplasmas, protozoa, nematodes and parasitic plants. Not included are ectoparasites like insects, mites, vertebrate, or other pests that affect plant health by eating plant tissues. Plant pathology also involves the study of pathogen identification, disease etiology, disease cycles, economic impact, plant disease epidemiology, plant disease resistance, how plant diseases affect humans and animals, pathosystem genetics, and management of plant diseases. Overview Control of plant diseases is crucial to the reliable production of food, and it provides significant problems in agricultural use of land, water, fuel and other inputs. Plants in both natural and cultivated populat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fuchsia
''Fuchsia'' () is a genus of flowering plants that consists mostly of shrubs or small trees. The first to be scientifically described, '' Fuchsia triphylla'', was discovered on the Caribbean island of Hispaniola (Haiti and the Dominican Republic) about 1696–1697 by the French Minim monk and botanist, Charles Plumier, during his third expedition to the Greater Antilles. He named the new genus after German botanist Leonhart Fuchs (1501–1566). Taxonomy The fuchsias are most closely related to the northern hemisphere genus '' Circaea'', the two lineages having diverged around 41 million years ago. Description Almost 110 species of ''Fuchsia'' are recognized; the vast majority are native to South America, but a few occur north through Central America to Mexico, and also several from New Zealand to Tahiti. One species, '' F. magellanica'', extends as far as the southern tip of South America, occurring on Tierra del Fuego in the cool temperate zone, but the majority are tro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungal Plant Pathogens And Diseases
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''true f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ornamental Plant Pathogens And Diseases
Ornamental may refer to: *Ornamental grass, a type of grass grown as a decoration *Ornamental iron, mild steel that has been formed into decorative shapes, similar to wrought iron work *Ornamental plant, a plant that is grown for its ornamental qualities *Ornament (architecture), a decorative detail used to embellish parts of a building or interior furnishing *Ornament (art) *Ornament (music), musical flourishes that are not necessary to the overall melodic (or harmonic) line Music *Ornamental, a music group formed as a side project of Strawberry Switchblade vocalist Rose McDowall See also *Ornament (other) {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pucciniales
Rusts are plant diseases caused by pathogenic fungi of the order Pucciniales (previously known as Uredinales). An estimated 168 rust genera and approximately 7,000 species, more than half of which belong to the genus ''Puccinia'', are currently accepted. Rust fungi are highly specialized plant pathogens with several unique features. Taken as a group, rust fungi are diverse and affect many kinds of plants. However, each species has a very narrow range of hosts and cannot be transmitted to non-host plants. In addition, most rust fungi cannot be grown easily in pure culture. A single species of rust fungi may be able to infect two different plant hosts in different stages of its life cycle, and may produce up to five morphologically and cytologically distinct spore-producing structures viz., spermogonia, aecia, uredinia, telia, and basidia in successive stages of reproduction. Each spore type is very host specific, and can typically infect only one kind of plant. Rust fungi are o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungi Described In 1861
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''true fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |