|
Public Law (United States)
An Act of Congress is a statute enacted by the United States Congress. Acts may apply only to individual entities (called private laws), or to the general public ( public laws). For a bill to become an act, the text must pass through both houses with a majority, then be either signed into law by the president of the United States, be left unsigned for ten days (excluding Sundays) while Congress remains in session, or, if vetoed by the president, receive a congressional override from of both houses. Public law, private law, designation In the United States, Acts of Congress are designated as either public laws, relating to the general public, or private laws, relating to specific institutions or individuals. Since 1957, all Acts of Congress have been designated as "Public Law X–Y" or "Private Law X–Y", where X is the number of the Congress and Y refers to the sequential order of the bill (when it was enacted). For example, P. L. 111–5 (American Recovery and Reinvestmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statute
A statute is a formal written enactment of a legislative authority that governs the legal entities of a city, state, or country by way of consent. Typically, statutes command or prohibit something, or declare policy. Statutes are rules made by legislative bodies; they are distinguished from case law or precedent, which is decided by courts, and regulations issued by government agencies. Publication and organization In virtually all countries, newly enacted statutes are published and distributed so that everyone can look up the statutory law. This can be done in the form of a government gazette which may include other kinds of legal notices released by the government, or in the form of a series of books whose content is limited to legislative acts. In either form, statutes are traditionally published in chronological order based on date of enactment. A universal problem encountered by lawmakers throughout human history is how to organize published statutes. Such publications h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Promulgation
Promulgation is the formal proclamation or the declaration that a new statutory or administrative law is enacted after its final approval. In some jurisdictions, this additional step is necessary before the law can take effect. After a new law is approved, it is announced to the public through the publication of government gazettes and/or on official government websites. National laws of extraordinary importance to the public may be announced by the head of state on national broadcast. Local laws are usually announced in local newspapers and published in bulletins or compendia of municipal regulations. Jurisdiction-specific details Armenia Bills are enacted by the President of Armenia and published in the '' Official Gazette of the Republic of Armenia''. Belgium Statutes are promulgated by the King of the Belgians and published in the '' Belgian Official Journal''. Decrees and Ordinances are promulgated by the different Regional and Community governments and published in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
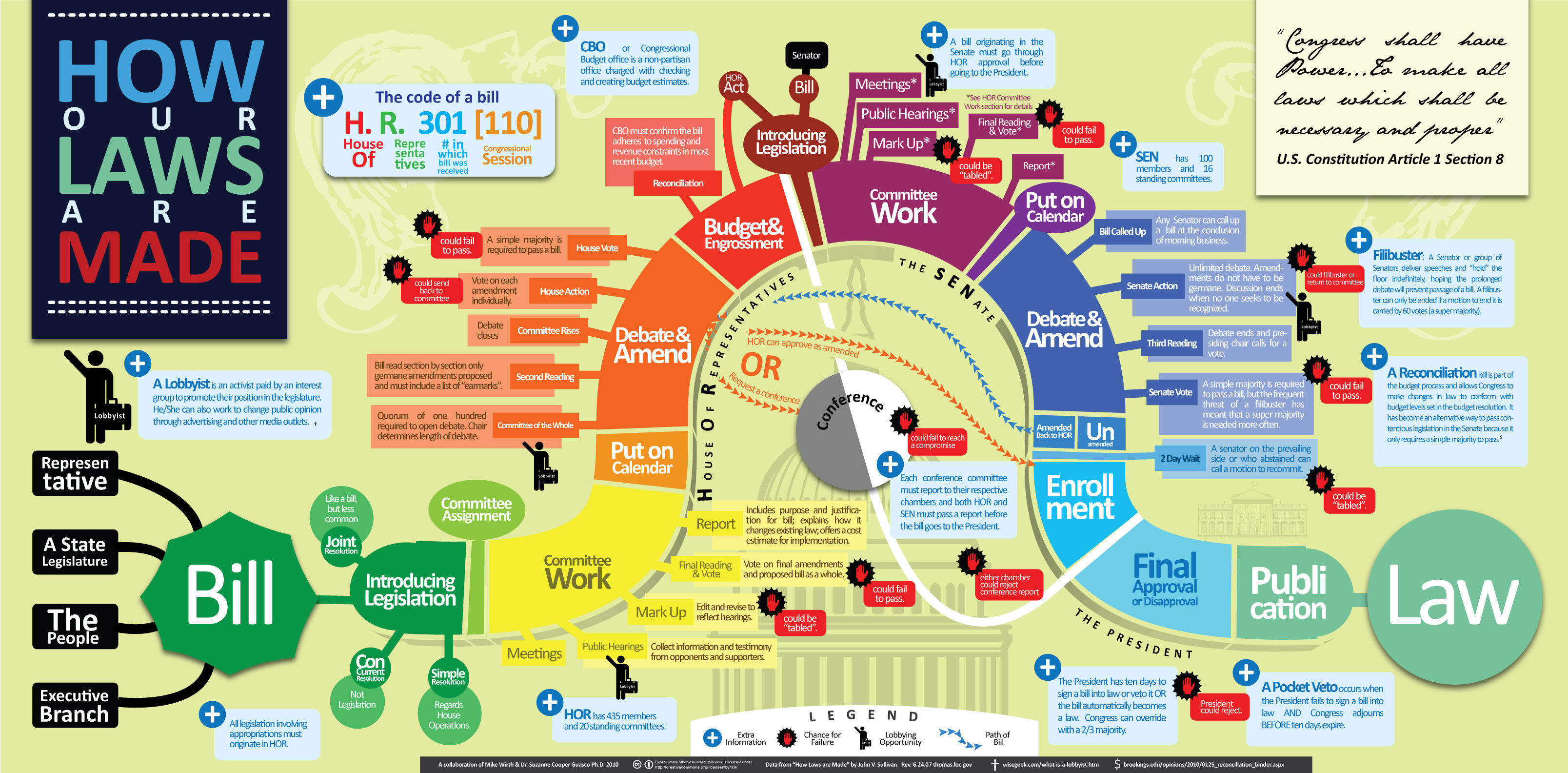
Enactment
Enactment may refer to: Law * Enactment of a bill, when a bill becomes law * Enacting formula, formulaic words in a bill or act which introduce its provisions * Enactment (British legal term), a piece of legislation or a legal instrument made under a piece of legislation Other *Enactment (psychology), in relational psychoanalysis, a playing out of a mental scenario *Enactment effect, in linguistics, in which verb phrases are better memorized if a learner performs the described action while learning the phrase See also *Other steps after enactment of a bill **Promulgation, the formal proclamation that a new law is enacted after its final approval **Coming into force In law, coming into force or entry into force (also called commencement) is the process by which legislation, regulations, treaties and other legal instruments come to have legal force and effect. The term is closely related to the date of this t ..., the process by which legal instruments come to have legal for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coming Into Force
In law, coming into force or entry into force (also called commencement) is the process by which legislation, regulations, treaties and other legal instruments come to have legal force and effect. The term is closely related to the date of this transition. The point at which such instrument comes into effect may be set out in the instrument itself, or after the lapse of a certain period, or upon the happening of a certain event, such as a proclamation or an objective event, such as the birth, marriage, reaching a particular age or death of a certain person. On rare occasions, the effective date of a law may be backdated to a date before the enactment. To come into force, a treaty or Act first needs to receive the required number of votes or ratifications. Although it is common practice to stipulate this number as a requirement in the body of the treaty itself, it can also be set out in a superior law or legal framework, such as a constitution or the standing orders of the legisla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Act Of Parliament
Acts of Parliament, sometimes referred to as primary legislation, are texts of law passed by the Legislature, legislative body of a jurisdiction (often a parliament or council). In most countries with a parliamentary system of government, acts of parliament begin as a Bill (law), bill, which the legislature votes on. Depending on the structure of government, this text may then be subject to assent or approval from the Executive (government), executive branch. Bills A draft act of parliament is known as a Bill (proposed law), bill. In other words, a bill is a proposed law that needs to be discussed in the parliament before it can become a law. In territories with a Westminster system, most bills that have any possibility of becoming law are introduced into parliament by the government. This will usually happen following the publication of a "white paper", setting out the issues and the way in which the proposed new law is intended to deal with them. A bill may also be introduced in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Procedures Of The United States Congress
Procedures of the United States Congress are established ways of doing legislative business. Congress has two-year terms with one session each year. There are rules and procedures, often complex, which guide how it converts ideas for legislation into laws. Sessions A term of Congress is divided into two " sessions", one for each year; Congress has occasionally also been called into an extra, (or special) session (the Constitution requires Congress to meet at least once each year). A new session commences each year on January 3, unless Congress chooses another date. Before the Twentieth Amendment, Congress met from the first Monday in December to April or May in the first session of their term (the "long session"); and from December to March 4 in the second "short session". (The new Congress would then meet for some days, for the inauguration, swearing in new members, and organization.) The Constitution forbids either house from meeting any place outside the United States Cap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of United States Federal Legislation
This is a chronological, but still incomplete, list of United States federal legislation. Congress has enacted approximately 200–600 statutes during each of its 115 biennial terms so that more than 30,000 statutes have been enacted since 1789. At the federal level in the United States, legislation (i.e., "statutes" or "statutory law") consists exclusively of Acts passed by the Congress of the United States and its predecessor, the Continental Congress, that were either signed into law by the President or passed by Congress after a presidential veto. Legislation is not the only source of regulations with the force of law. However, most executive branch and judicial branch regulations must originate in a congressional grant of power. ''See also'': Executive orders issued by the President; ''Code of Federal Regulations'' for rules issued by executive branch departments and administrative agencies; and the Federal Rules of Civil Procedure of the federal courts. Publication of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legislation
Legislation is the process or result of enrolled bill, enrolling, enactment of a bill, enacting, or promulgation, promulgating laws by a legislature, parliament, or analogous Government, governing body. Before an item of legislation becomes law it may be known as a bill (proposed law), bill, and may be broadly referred to as "legislation" while it remains under consideration to distinguish it from other business. Legislation can have many purposes: to regulate, to authorize, to outlaw, to provide (funds), to sanction, to grant, to declare, or to restrict. It may be contrasted with a non-legislative act by an Executive (government), executive or administrative body under the authority of a legislative act. Overview Legislation is usually proposed by a member of the legislature (e.g. a member of Congress or Parliament), or by the executive, whereupon it is debated by members of the legislature and is often amended before passage (legislature), passage. Most large legislatures enact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Judicial Review In The United States
In the United States, judicial review is the legal power of a court to determine if a statute, treaty, or administrative regulation contradicts or violates the provisions of existing law, a State Constitution, or ultimately the United States Constitution. While the U.S. Constitution does not explicitly define the power of judicial review, the authority for judicial review in the United States has been inferred from the structure, provisions, and history of the Constitution. Two landmark decisions by the U.S. Supreme Court served to confirm the inferred constitutional authority for judicial review in the United States. In 1796, '' Hylton v. United States'' was the first case decided by the Supreme Court involving a direct challenge to the constitutionality of an act of Congress, the Carriage Act of 1794 which imposed a "carriage tax". The Court performed judicial review of the plaintiff's claim that the carriage tax was unconstitutional. After review, the Supreme Court decided ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Statutes At Large
The ''United States Statutes at Large'', commonly referred to as the ''Statutes at Large'' and abbreviated Stat., are an official record of Acts of Congress and concurrent resolutions passed by the United States Congress. Each act and resolution of Congress is originally published as a slip law, which is classified as either public law (abbreviated Pub.L.) or private law (Pvt.L.), and designated and numbered accordingly. At the end of a Congressional session, the statutes enacted during that session are compiled into bound books, known as "session law" publications. The session law publication for U.S. Federal statutes is called the ''United States Statutes at Large''. In that publication, the public laws and private laws are numbered and organized in chronological order. U.S. Federal statutes are published in a three-part process, consisting of slip laws, session laws (''Statutes at Large''), and codification ('' United States Code''). Codification Large portions of public l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slip Law
In the United States, a slip law is an individual Act of Congress which is either a public law (Pub.L.) or a private law (Pvt.L.). They are part of a three-part model for publication of federal statutes consisting of slip laws, session laws, and codification. Session laws are compiled into the '' Statutes at Large'' (Stat.), and codification results in the United States Code (U.S.C.). Public and private laws are prepared and published by the Office of the Federal Register (OFR) of the National Archives and Records Administration (NARA). At the end of a Congressional session, slip laws are compiled into the '' Statutes at Large'', which are called "session laws", published by the Government Printing Office (GPO). Today, most of the public laws, but not private laws, are drafted as amendments to the United States Code. See also * ''United States Statutes at Large'' * '' United States Code'' References {{reflist Further reading "Slip Laws"from ''Federal Statutes: A Beginner's G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archivist Of The United States
The Archivist of the United States is the head and chief administrator of the National Archives and Records Administration (NARA) of the United States. The Archivist is responsible for the supervision and direction of the National Archives. The first Archivist, R.D.W. Connor, began serving in 1934, when the National Archives was established as an independent federal agency by Congress. The Archivists served as subordinate officials of the General Services Administration from 1949 until the National Archives and Records Administration became an independent agency again on April 1, 1985. The position was most recently held by David Ferriero, who left office on April 30, 2022. President Joe Biden has named Colleen Joy Shogan as Archivist. Her nomination is currently pending before the Senate. Background The Archivist is appointed by the President with the advice and consent of the Senate and is responsible for safeguarding and making available for study all the permanently va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |