|
Psychoanalytic Sociology
Psychoanalytic sociology is the research field that analyzes society using the same methods that psychoanalysis applied to analyze an individual. 'Psychoanalytic sociology embraces work from divergent sociological traditions and political perspectives': its common 'emphasis on unconscious mental processes and behavior renders psychoanalytic sociology a controversial subfield within the broader sociological discipline' (as with psychoanalysis in academic psychology). Similarly, sociatry applies psychiatry to society itself. History Freud 'The desire to establish a link between psychoanalysis and sociology appears very early on in Freud's work. The articles "Obsessive Actions and Religious Practices" (1907b) and " 'Civilized' Sexual Morality and Modern Nervous Illness" (1908d) are evidence of this'. Though the latter article was 'the earliest of Freud's full-length discussions of the antagonism between civilization and instinctual life, his convictions on the subject went back mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Society
A society is a group of individuals involved in persistent social interaction, or a large social group sharing the same spatial or social territory, typically subject to the same political authority and dominant cultural expectations. Societies are characterized by patterns of relationships (social relations) between individuals who share a distinctive culture and institutions; a given society may be described as the sum total of such relationships among its constituent of members. In the social sciences, a larger society often exhibits stratification or dominance patterns in subgroups. Societies construct patterns of behavior by deeming certain actions or concepts as acceptable or unacceptable. These patterns of behavior within a given society are known as societal norms. Societies, and their norms, undergo gradual and perpetual changes. Insofar as it is collaborative, a society can enable its members to benefit in ways that would otherwise be difficult on an individua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacques Lacan
Jacques Marie Émile Lacan (, , ; 13 April 1901 – 9 September 1981) was a French psychoanalyst and psychiatrist. Described as "the most controversial psycho-analyst since Freud", Lacan gave yearly seminars in Paris from 1953 to 1981, and published papers that were later collected in the book ''Écrits''. His work made a significant impact on continental philosophy and cultural theory in areas such as post-structuralism, critical theory, feminist theory and film theory, as well as on the practice of psychoanalysis itself. Lacan took up and discussed the whole range of Freudian concepts, emphasizing the philosophical dimension of Freud's thought and applying concepts derived from structuralism in linguistics and anthropology to its development in his own work, which he would further augment by employing formulae from predicate logic and topology. Taking this new direction, and introducing controversial innovations in clinical practice, led to expulsion for Lacan and his foll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nancy Chodorow
Nancy Julia Chodorow (born January 20, 1944) is an American sociologist and professor. She began her career as a professor of Women's studies at Wellesley College in 1973, and from 1974 on taught at the University of California, Santa Cruz, until 1986. She then was a professor in the departments of sociology and clinical psychology at the University of California, Berkeley until she resigned in 1986, after which she taught psychiatry at Harvard Medical School/Cambridge Health Alliance. Chodorow is often described as a leader in feminist thought, especially in the realms of psychoanalysis and psychology. Chodorow has written a number of influential books in contemporary feminist writing, including ''The Reproduction of Mothering: Psychoanalysis and the Sociology of Gender'' (1978);The Reproduction of Mothering [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duane Rousselle
Duane Rousselle (born April 28, 1982) is a Canadian sociological theorist, Lacanian psychoanalyst, and professor of sociology. He works in several academic fields including Social Movement Studies, Lacanian Psychoanalysis, Cultural Sociology, Gender and Sexuality Studies, Anarchist Studies, and Aesthetics. His work attempts to introduce an alternative to scholarly discourses that aim to produce consistent and coherent bodies of knowledge (e.g., "University Discourse"). It also offers a counterpoint to what Jacques Lacan has called "capitalist discourse." He helped to contribute to the emergence of a new field of scholarly investigation known as " post-anarchism." He founded and edits the journal ''Anarchist Developments in Cultural Studies.'' Biography Duane was born in Miramichi, New Brunswick to Catholic parents. He attended the New Brunswick Community College and graduated with a diploma in Electronic Game Design. After participating in a hunger strike for admittance, he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Repressive Desublimation
Repressive desublimation is a term, first coined by Frankfurt School philosopher and sociologist Herbert Marcuse in his 1964 work '' One-Dimensional Man'', that refers to the way in which, in advanced industrial society (capitalism), "the progress of technological rationality is liquidating the oppositional and transcending elements in the “ higher culture.” In other words, where art was previously a way to represent "that which is" from "that which is not," capitalist society causes the "flattening out" of art into a commodity incorporated into society itself. As Marcuse put it in '' One-Dimensional Man'', "The music of the soul is also the music of salesmanship." By offering instantaneous, rather than mediated, gratifications, repressive desublimation was considered by Marcuse to remove the energies otherwise available for a social critique; and thus to function as a conservative force ''under the guise of'' liberation. Origins and influence The roots of Marcuse's concept ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herbert Marcuse
Herbert Marcuse (; ; July 19, 1898 – July 29, 1979) was a German-American philosopher, social critic, and political theorist, associated with the Frankfurt School of critical theory. Born in Berlin, Marcuse studied at the Humboldt University of Berlin and then at Freiburg, where he received his PhD. He was a prominent figure in the Frankfurt-based Institute for Social Research – what later became known as the Frankfurt School. He was married to Sophie Wertheim (1924–1951), Inge Neumann (1955–1973), and Erica Sherover (1976–1979). In his written works, he criticized capitalism, modern technology, Soviet Communism and popular culture, arguing that they represent new forms of social control. Between 1943 and 1950, Marcuse worked in US government service for the Office of Strategic Services (predecessor of the Central Intelligence Agency) where he criticized the ideology of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union in the book '' Soviet Marxism: A Critical Analysis'' (195 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norman O
Norman or Normans may refer to: Ethnic and cultural identity * The Normans, a people partly descended from Norse Vikings who settled in the territory of Normandy in France in the 10th and 11th centuries ** People or things connected with the Norman conquest of southern Italy in the 11th and 12th centuries ** Norman dynasty, a series of monarchs in England and Normandy ** Norman architecture, romanesque architecture in England and elsewhere ** Norman language, spoken in Normandy ** People or things connected with the French region of Normandy Arts and entertainment * ''Norman'' (film), a 2010 drama film * '' Norman: The Moderate Rise and Tragic Fall of a New York Fixer'', a 2016 film * ''Norman'' (TV series), a 1970 British sitcom starring Norman Wisdom * ''The Normans'' (TV series), a documentary * "Norman" (song), a 1962 song written by John D. Loudermilk and recorded by Sue Thompson * "Norman (He's a Rebel)", a song by Mo-dettes from ''The Story So Far'', 1980 Businesses * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parental Alienation
Parental alienation is a theorized process through which a child becomes estranged from one parent as the result of the psychological manipulation of another parent. The child's estrangement may manifest itself as fear, disrespect or hostility toward the distant parent, and may extend to additional relatives or parties. The child's estrangement is disproportionate to any acts or conduct attributable to the alienated parent. Parental alienation can occur in any family unit, but is claimed to occur most often within the context of family separation, particularly when legal proceedings are involved, although the participation of professionals such as lawyers, judges and psychologists may also contribute to conflict. Proponents of the concept of parental alienation assert that it is primarily motivated by one parent's desire to exclude the other parent from their child's life. Some assert that parental alienation should be diagnosable in children as a mental disorder. Some propose that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sartre
Jean-Paul Charles Aymard Sartre (, ; ; 21 June 1905 – 15 April 1980) was one of the key figures in the philosophy of existentialism (and phenomenology), a French playwright, novelist, screenwriter, political activist, biographer, and literary critic, as well as a leading figure in 20th-century French philosophy and Marxism. His work has influenced sociology, critical theory, post-colonial theory, and literary studies, and continues to do so. He was awarded the 1964 Nobel Prize in Literature despite attempting to refuse it, saying that he always declined official honors and that "a writer should not allow himself to be turned into an institution." Sartre held an open relationship with prominent feminist and fellow existentialist philosopher Simone de Beauvoir. Together, Sartre and de Beauvoir challenged the cultural and social assumptions and expectations of their upbringings, which they considered bourgeois, in both lifestyles and thought. The conflict between oppressive, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Cooper (psychiatrist)
David Graham Cooper (1931 in Cape Town, South Africa – 29 July 1986 in Paris, France) was a South African-born psychiatrist and theorist who was prominent in the anti-psychiatry movement. Cooper graduated from the University of Cape Town in 1955. R.D. Laing claimed that Cooper underwent Soviet training to prepare him as an Anti Apartheid communist revolutionary, but after completing his course he never returned to South Africa out of fear that B.O.S.S. would eliminate him. He moved to London, where he worked at several hospitals. From 1961 to 1965 he ran an experimental unit for young people with schizophrenia called ''Villa 21'', which he saw as a revolutionary 'anti-hospital' and a prototype for the later Kingsley Hall Community. In 1965, he was involved with Laing and others in establishing the Philadelphia Association. An "existential Marxist" he left the Philadelphia Association in the 1970s in a disagreement over its lack of political orientation. Cooper coined the term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
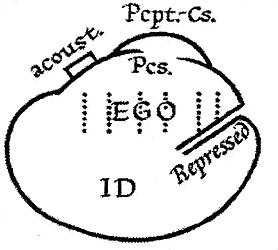
Superego
The id, ego, and super-ego are a set of three concepts in psychoanalytic theory describing distinct, interacting agents in the psychic apparatus (defined in Sigmund Freud's structural model of the psyche). The three agents are theoretical constructs that describe the activities and interactions of the mental life of a person. In the ego psychology model of the psyche, the id is the set of uncoordinated instinctual desires; the super-ego plays the critical and moralizing role; and the ego is the organized, realistic agent that mediates between the instinctual desires of the id and the critical super-ego; Freud explained that: The functional importance of the ego is manifested in the fact that, normally, control over the approaches to motility devolves upon it. Thus, in its relation to the id, he egois like a man on horseback, who has to hold in check the superior strength of the horse; with this difference, that the rider tries to do so with his own strength, while the ego uses b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Post-Lacanian
Lacanianism or Lacanian psychoanalysis is a theoretical system that explains the mind, behaviour, and culture through a structuralist and post-structuralist extension of classical psychoanalysis, initiated by the work of Jacques Lacan from the 1950s to the 1980s. Lacanian perspectives contend that the world of language, the Symbolic, structures the human mind, and stress the importance of desire, which is conceived of as endless and impossible to satisfy. Contemporary Lacanianism is characterised by a broad range of thought and extensive debate between Lacanians. Lacanianism has been particularly influential in post-structuralism, literary theory and feminist theory, as well as in various branches of critical theory, including queer theory. Equally, it has been criticised by the post-structuralists Deleuze and Guattari and by various feminist theorists. Its clinical relevance is limited and outside France it has had no influence on psychiatry. There is a Lacanian strand in left ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |