|
Pseudomyrmex Gracilis
''Pseudomyrmex gracilis'', also known as the graceful twig ant, Mexican twig ant, slender twig ant, or elongated twig ant, is a large, slender species native to Mexico and arid parts of the United States, US. The workers are about in length and generally wasp, wasp-like in appearance and style of movement. Worker ants are bi-colored; the head and gaster (insect anatomy), gaster are dark, while the Antenna (biology), antennae, Insect mouthparts, mouthparts, Thorax (insect anatomy), thorax and legs are dull orange with dark shading. They often may be seen on vegetation, foraging for live insects or collecting Honeydew (secretion), honeydew from sap, sap-sucking insects. If the colony ever finds themselves without a queen, the worker ants form dominance hierarchies by boxing with their antennae. This leads to a couple high ranking individuals to lay eggs until a new queen returns. Photos File:Pseudomyrmex gracilis colony chamber - Mount Dora, Florida, USA - Joseph Stansbury Rosin. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motility, able to move, can Sexual reproduction, reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in which their body consists of a hollow sphere of Cell (biology), cells, the blastula, during Embryogenesis, embryonic development. Over 1.5 million Extant taxon, living animal species have been Species description, described—of which around 1 million are Insecta, insects—but it has been estimated there are over 7 million animal species in total. Animals range in length from to . They have Ecology, complex interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology. Most living animal species are in Bilateria, a clade whose members have a Symmetry in biology#Bilate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaster (insect Anatomy)
The gaster is the bulbous posterior portion of the metasoma found in hymenopterans of the suborder Apocrita ( bees, wasps and ants). This begins with abdominal segment III on most ants, but some make a constricted postpetiole out of segment III, in which case the gaster begins with abdominal segment IV. Certain ants in the genus '' Cataglyphis'', specifically ''Cataglyphis bicolor'' and ''Cataglyphis fortis'', have a cubiform petiole that allows them to decrease their inertia Inertia is the idea that an object will continue its current motion until some force causes its speed or direction to change. The term is properly understood as shorthand for "the principle of inertia" as described by Newton in his first law ... (and therefore increase their speed) by raising their gaster into an upright position. References Insect anatomy {{insect-anatomy-stub de:Gaster ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sabal Palmetto
''Sabal palmetto'' (, '' SAY-bəl''), also known as cabbage palm, cabbage palmetto, sabal palm, blue palmetto, Carolina palmetto, common palmetto, Garfield's tree, and swamp cabbage, is one of 15 species of palmetto palm. It is native to the Southern United States and the West Indies. Description ''Sabal palmetto'' grows up to tall. Starting at half to two-thirds the height, the tree develops into a rounded, costapalmate fan of numerous leaflets. A costapalmate leaf has a definite costa (midrib) unlike the typical palmate or fan leaf, but the leaflets are arranged radially like in a palmate leaf. All costapalmate leaves are about across, produced in large compound panicles up to in radius, extending out beyond the leaves. The fruit is a black drupe about long containing a single seed. It is extremely salt-tolerant and is often seen growing near both the Atlantic Ocean coast and the Gulf of Mexico coast. Sabal palmetto00.jpg, ''Sabal palmetto'' from Carl Friedrich Philipp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Honeydew (secretion)
Honeydew is a sugar-rich sticky liquid, secreted by aphids and some scale insects as they feed on plant sap. When their mouthpart penetrates the phloem, the sugary, high-pressure liquid is forced out of the anus of the aphid. Honeydew is particularly common as a secretion in hemipteran insects and is often the basis for trophobiosis. Some caterpillars of Lycaenidae butterflies and some moths also produce honeydew. Honeydew producing insects, like cicadas, pierce phloem ducts to access the sugar rich sap. The sap continues to bleed after the insects have moved on, leaving a white sugar crust called manna. Ants may collect, or "milk", honeydew directly from aphids and other honeydew producers, which benefit from their presence due to their driving away predators such as lady beetles or parasitic wasps—see ''Crematogaster peringueyi''. Animals and plants in a mutually symbiotic arrangement with ants are called Myrmecophiles. In Madagascar, some gecko species in the genera ''Ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vegetation
Vegetation is an assemblage of plant species and the ground cover they provide. It is a general term, without specific reference to particular taxa, life forms, structure, spatial extent, or any other specific botanical or geographic characteristics. It is broader than the term ''flora'' which refers to species composition. Perhaps the closest synonym is plant community, but ''vegetation'' can, and often does, refer to a wider range of spatial scales than that term does, including scales as large as the global. Primeval redwood forests, coastal mangrove stands, sphagnum bogs, desert soil crusts, roadside weed patches, wheat fields, cultivated gardens and lawns; all are encompassed by the term ''vegetation''. The vegetation type is defined by characteristic dominant species, or a common aspect of the assemblage, such as an elevation range or environmental commonality. The contemporary use of ''vegetation'' approximates that of ecologist Frederic Clements' term earth cover, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thorax (insect Anatomy)
The thorax is the midsection ( tagma) of the hexapod body (insects and entognathans). It holds the head, legs, wings and abdomen. It is also called mesosoma or cephalothorax in other arthropods. It is formed by the prothorax, mesothorax and metathorax and comprises the scutellum; the cervix, a membrane that separates the head from the thorax; and the pleuron, a lateral sclerite of the thorax. In dragonflies and damselflies the mesothorax and metathorax are fused together to form the synthorax. In some insect pupae, like the mosquitoes', the head and thorax can be fused in a cephalothorax. Members of suborder Apocrita (wasps, ants and bees) in the order Hymenoptera have the first segment of the abdomen fused with the thorax, which is called the propodeum. The head is connected to the thorax by the occipital foramen, enabling a wide range of motion for the head. In most flying insects, the thorax allows for the use of asynchronous muscles Asynchronous muscles are muscles in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
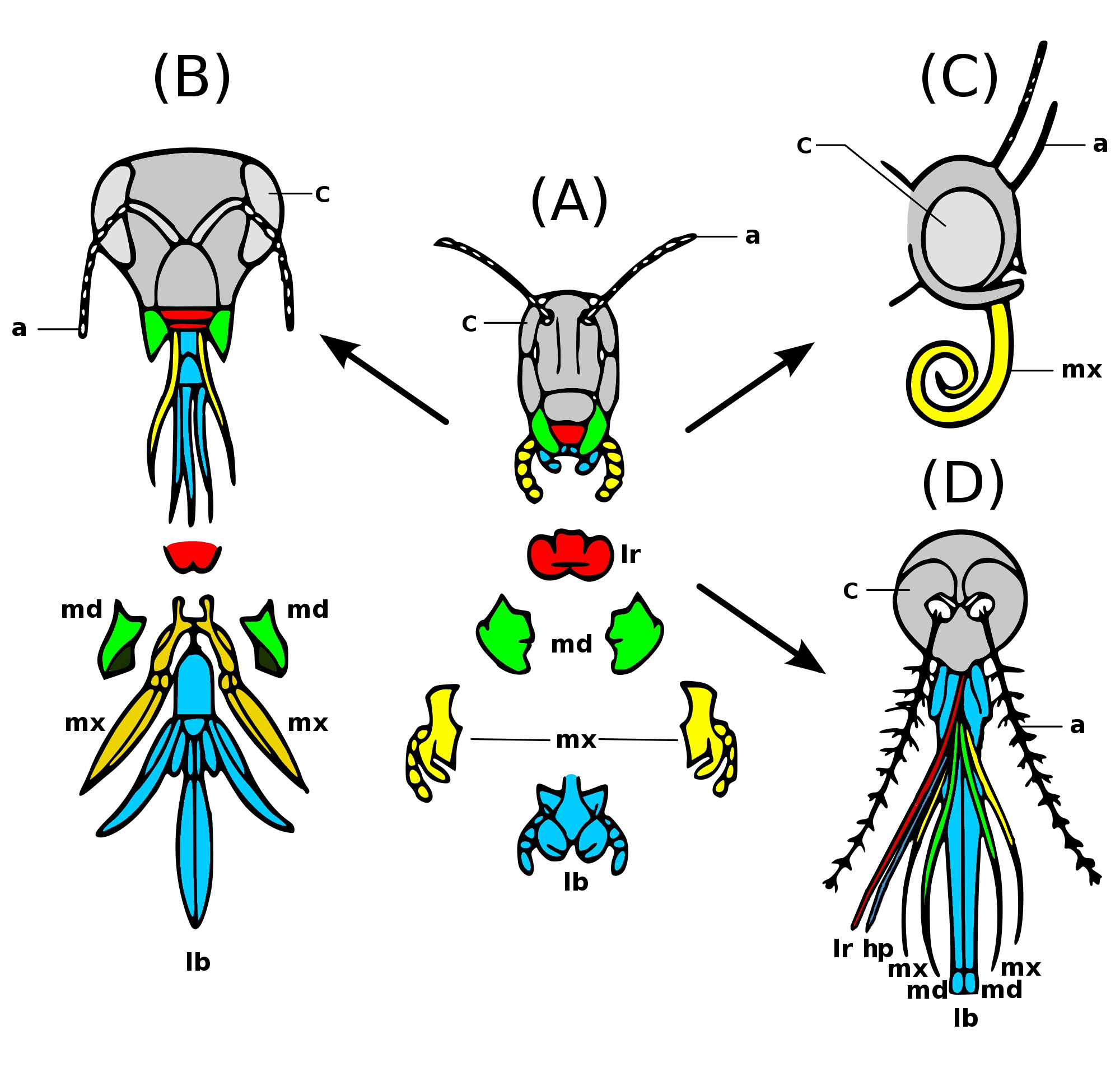
Insect Mouthparts
Insects have mouthparts that may vary greatly across insect species, as they are adapted to particular modes of feeding. The earliest insects had chewing mouthparts. Most specialisation of mouthparts are for piercing and sucking, and this mode of feeding has evolved a number of times idependently. For example, mosquitoes and aphids (which are true bugs) both pierce and suck, however female mosquitoes feed on animal blood whereas aphids feed on plant fluids. Evolution Like most external features of arthropods, the mouthparts of Hexapoda are highly derived. Insect mouthparts show a multitude of different functional mechanisms across the wide diversity of insect species. It is common for significant homology to be conserved, with matching structures forming from matching primordia, and having the same evolutionary origin. However, even if structures are almost physically and functionally identical, they may not be homologous; their analogous functions and appearance might be the pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antenna (biology)
Antennae ( antenna), sometimes referred to as "feelers", are paired appendages used for sensing in arthropods. Antennae are connected to the first one or two segments of the arthropod head. They vary widely in form but are always made of one or more jointed segments. While they are typically sensory organs, the exact nature of what they sense and how they sense it is not the same in all groups. Functions may variously include sensing touch, air motion, heat, vibration (sound), and especially smell or taste. Antennae are sometimes modified for other purposes, such as mating, brooding, swimming, and even anchoring the arthropod to a substrate. Larval arthropods have antennae that differ from those of the adult. Many crustaceans, for example, have free-swimming larvae that use their antennae for swimming. Antennae can also locate other group members if the insect lives in a group, like the ant. The common ancestor of all arthropods likely had one pair of uniramous (unbranched ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wasp
A wasp is any insect of the narrow-waisted suborder Apocrita of the order Hymenoptera which is neither a bee nor an ant; this excludes the broad-waisted sawflies (Symphyta), which look somewhat like wasps, but are in a separate suborder. The wasps do not constitute a clade, a complete natural group with a single ancestor, as bees and ants are deeply nested within the wasps, having evolved from wasp ancestors. Wasps that are members of the clade Aculeata can Stinger, sting their prey. The most commonly known wasps, such as yellowjackets and hornets, are in the family Vespidae and are Eusociality, eusocial, living together in a nest with an egg-laying queen and non-reproducing workers. Eusociality is favoured by the unusual haplodiploid system of sex-determination system, sex determination in Hymenoptera, as it makes sisters exceptionally closely related to each other. However, the majority of wasp species are solitary, with each adult female living and breeding independently ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthropod
Arthropods (, (gen. ποδός)) are invertebrate animals with an exoskeleton, a Segmentation (biology), segmented body, and paired jointed appendages. Arthropods form the phylum Arthropoda. They are distinguished by their jointed limbs and Arthropod cuticle, cuticle made of chitin, often Mineralization (biology), mineralised with calcium carbonate. The arthropod body plan consists of segments, each with a pair of appendages. Arthropods are bilaterally symmetrical and their body possesses an exoskeleton, external skeleton. In order to keep growing, they must go through stages of moulting, a process by which they shed their exoskeleton to reveal a new one. Some species have wings. They are an extremely diverse group, with up to 10 million species. The haemocoel, an arthropod's internal cavity, through which its haemolymph – analogue of blood – circulates, accommodates its interior Organ (anatomy), organs; it has an open circulatory system. Like their exteriors, the internal or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Indian reservations. The United States is also in free association with three Pacific Island sovereign states: the Federated States of Micronesia, the Marshall Islands, and the Republic of Palau. It is the world's third-largest country by both land and total area. It shares land borders with Canada to its north and with Mexico to its south and has maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, Russia, and other nations. With a population of over 333 million, it is the most populous country in the Americas and the third most populous in the world. The national capital of the United States is Washington, D.C. and its most populous city and principal financial center is New York City. Paleo-Americ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mexico
Mexico (Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatemala, Belize, and the Caribbean Sea; and to the east by the Gulf of Mexico. Mexico covers ,Mexico ''''. . making it the world's 13th-largest country by are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |