|
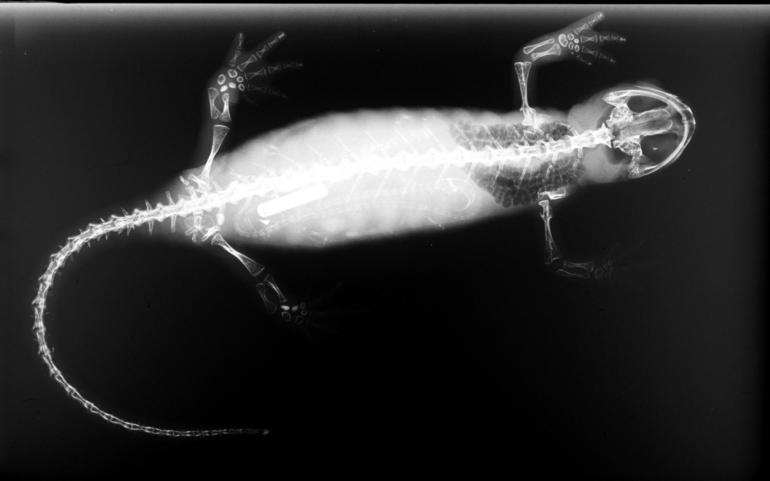
Pseudobranchus Axanthus
The southern dwarf siren, (''Pseudobranchus axanthus'') is a perennibranch salamander lacking hind legs. Found exclusively in Florida, it is one of two currently recognized species of dwarf sirens. Two subspecies are currently recognized; ''P. a. axanthus'', the narrow-striped dwarf siren, and ''P. a. belli'', the Everglades dwarf siren. Physical description Southern dwarf sirens are thin, slimy salamanders that are frequently mistaken for eels. They have long bodies with bushy gills and small, three-toed fore legs. Coloration is generally brown, black, or gray, with yellow or tan stripes on their backs and sides. Adults reach a length of to . Southern dwarf sirens can easily be distinguished from amphiumas by size and the presence of hind legs, and from ''Siren'' spp. salamanders by the presence of three toes on each foot. Distinguishing between ''P. axanthus'' and ''P. striatus'' is more difficult, requiring comparison of patterns with a field guide, known distribution, or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perennibranchiate
Perennibranchiate, in zoology, is the condition of an organism retaining branchae, or gills, through life. This condition is generally said of certain amphibia, such as the mudpuppy. The term is opposed to caducibranchiate. In some cases only a small proportion of a given amphibian population is perennibranchiate, but in other instances a preponderance of the individuals have an adult gill retention. For example, in the case of the Rough-skinned Newt in the Cascade Mountains populations, approximately ninety percent of the adult population is perennibranchiate.C. Michael Hogan, 2008 See also * Neoteny Neoteny (), also called juvenilization,Montagu, A. (1989). Growing Young. Bergin & Garvey: CT. is the delaying or slowing of the physiological, or somatic, development of an organism, typically an animal. Neoteny is found in modern humans compared ... References * William Benjamin Carpenter (1854) ''Principles of Comparative Physiology'', Published by Blanchard and Lea, 752 pages * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salamander
Salamanders are a group of amphibians typically characterized by their lizard-like appearance, with slender bodies, blunt snouts, short limbs projecting at right angles to the body, and the presence of a tail in both larvae and adults. All ten extant salamander families are grouped together under the order Urodela. Salamander diversity is highest in eastern North America, especially in the Appalachian Mountains; most species are found in the Holarctic realm, with some species present in the Neotropical realm. Salamanders rarely have more than four toes on their front legs and five on their rear legs, but some species have fewer digits and others lack hind limbs. Their permeable skin usually makes them reliant on habitats in or near water or other cool, damp places. Some salamander species are fully aquatic throughout their lives, some take to the water intermittently, and others are entirely terrestrial as adults. This group of amphibians is capable of regenerating lost lim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, and to the south by the Straits of Florida and Cuba; it is the only state that borders both the Gulf of Mexico and the Atlantic Ocean. Spanning , Florida ranks 22nd in area among the 50 states, and with a population of over 21 million, it is the third-most populous. The state capital is Tallahassee, and the most populous city is Jacksonville. The Miami metropolitan area, with a population of almost 6.2 million, is the most populous urban area in Florida and the ninth-most populous in the United States; other urban conurbations with over one million people are Tampa Bay, Orlando, and Jacksonville. Various Native American groups have inhabited Florida for at least 14,000 years. In 1513, Spanish explorer Juan Ponce de León became the first k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subspecies
In biological classification, subspecies is a rank below species, used for populations that live in different areas and vary in size, shape, or other physical characteristics (morphology), but that can successfully interbreed. Not all species have subspecies, but for those that do there must be at least two. Subspecies is abbreviated subsp. or ssp. and the singular and plural forms are the same ("the subspecies is" or "the subspecies are"). In zoology, under the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature, the subspecies is the only taxonomic rank below that of species that can receive a name. In botany and mycology, under the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants, other infraspecific ranks, such as variety, may be named. In bacteriology and virology, under standard bacterial nomenclature and virus nomenclature, there are recommendations but not strict requirements for recognizing other important infraspecific ranks. A taxonomist decides whether ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eels
Eels are ray-finned fish belonging to the order Anguilliformes (), which consists of eight suborders, 19 families, 111 genera, and about 800 species. Eels undergo considerable development from the early larval stage to the eventual adult stage and are usually predators. The term "eel" is also used for some other eel-shaped fish, such as electric eels (genus ''Electrophorus''), spiny eels (family Mastacembelidae), swamp eels (family Synbranchidae), and deep-sea spiny eels (family Notacanthidae). However, these other clades evolved their eel-like shapes independently from the true eels. Eels live both in salt and fresh water, and some species are catadromous. Description Eels are elongated fish, ranging in length from in the one-jawed eel (''Monognathus ahlstromi'') to in the slender giant moray. Adults range in weight from to well over . They possess no pelvic fins, and many species also lack pectoral fins. The dorsal and anal fins are fused with the caudal fin, formin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gill
A gill () is a respiratory organ that many aquatic organisms use to extract dissolved oxygen from water and to excrete carbon dioxide. The gills of some species, such as hermit crabs, have adapted to allow respiration on land provided they are kept moist. The microscopic structure of a gill presents a large surface area to the external environment. Branchia (pl. branchiae) is the zoologists' name for gills (from Ancient Greek ). With the exception of some aquatic insects, the filaments and lamellae (folds) contain blood or coelomic fluid, from which gases are exchanged through the thin walls. The blood carries oxygen to other parts of the body. Carbon dioxide passes from the blood through the thin gill tissue into the water. Gills or gill-like organs, located in different parts of the body, are found in various groups of aquatic animals, including mollusks, crustaceans, insects, fish, and amphibians. Semiterrestrial marine animals such as crabs and mudskippers have gill cham ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphiuma
''Amphiuma'' is a genus of aquatic salamanders from the United States, the only extant genus within the family Amphiumidae . They are colloquially known as amphiumas. They are also known to fishermen as "conger eels" or "Congo snakes", which are zoologically incorrect designations or misnomers, since amphiumas are actually salamanders (and thus amphibians), and not fish, nor reptiles and are not from Congo. ''Amphiuma'' exhibits one of the largest complements of DNA in the living world, around 25 times more than a human. Taxonomy Numerous phylogenetic studies have indicated that amphiumas form a clade with the families Rhyacotritonidae (torrent salamanders) and Plethodontidae (lungless salamanders), with an especially close relationship to Plethodontidae. Despite this possible relationship, the two families must have still diverged very early on. The genus ''Proamphiuma'' from the Cretaceous is the earliest known member of the family, and closely resembles the modern species ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daphnia Magna
''Daphnia magna'' is a small planktonic crustacean (adult length 1.5–5.0 mm) that belongs to the subclass Phyllopoda. Description ''D. magna'' is a typical water flea of the genus ''Daphnia''. The females reach up to 5 mm in size, the males about 2 mm, thus they are among the largest species in the genus. The body is protected by a translucent carapace made of chitin, a transparent polysaccharide. It has a ventral opening and five pairs of thoracic limbs, used to help the filtering process. Spike rows run along the back of the carapace. The intestine is hook-shaped and has two digestive ceca. The head has two antennae and a large compound eye. Adult females can be distinguished from those of otherwise similar species such as '' D. pulex'' by the absence of a comb on the abdominal claw and the presence of two distinct combs on the abdomen. The males are smaller than the females and have larger first antennas, a diagnostic feature that distinguishes them from s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnegie Museum Of Natural History
The Carnegie Museum of Natural History (abbreviated as CMNH) is a natural history museum in the Oakland neighborhood of Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. It was founded by Pittsburgh-based industrialist Andrew Carnegie in 1896. Housing some 22 million specimens, the museum features one of the finest paleontological collections in the world. Description and history The museum consists of organized into 20 galleries as well as research, library, and office space. It holds some 22 million specimens, of which about 10,000 are on view at any given time and about 1 million are cataloged in online databases. In 2008 it hosted 386,300 admissions and 63,000 school group visits. Museum education staff also actively engage in outreach by traveling to schools all around western Pennsylvania. The museum gained prominence in 1899 when its scientists unearthed the fossils of ''Diplodocus carnegii''. Notable dinosaur specimens include one of the world's very few fossils of a juvenile ''Apatosauru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sirenoidea
Sirenidae, the sirens, are a family of neotenic aquatic salamanders. Family members have very small fore limbs and lack hind limbs altogether. In one species, the skeleton in their fore limbs is made of only cartilage. In contrast to most other salamanders, they have external gills bunched together on the neck in both larval and adult states. Sirens are found only in the Southeastern United States and northern Mexico. Although they are primarily carnivorous, they are the only salamanders observed eating plant material.Hill, R. L., Mendelson, J. R. & Stabile, J. L. 2015. Direct observation and review of herbivory in Sirenidae (Amphibia: Caudata). Southeastern Naturalist 14, N5-N9. Description Sirens are quite distinct from other salamanders, and in some classifications they form their own suborder, Sirenoidea, or as a completely distinct order (Meantes or Trachystomata). Genetic analysis variously places them as the sister to other Salamandroidea or as sister to all other salama ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphibians Described In 1942
Amphibians are tetrapod, four-limbed and ectothermic vertebrates of the Class (biology), class Amphibia. All living amphibians belong to the group Lissamphibia. They inhabit a wide variety of habitats, with most species living within terrestrial animal, terrestrial, fossorial, arboreal or freshwater aquatic ecosystems. Thus amphibians typically start out as larvae living in water, but some species have developed behavioural adaptations to bypass this. The young generally undergo metamorphosis from larva with gills to an adult air-breathing form with lungs. Amphibians use their skin as a secondary respiratory surface and some small terrestrial salamanders and frogs lack lungs and rely entirely on their skin. They are superficially similar to reptiles like lizards but, along with mammals and birds, reptiles are amniotes and do not require water bodies in which to breed. With their complex reproductive needs and permeable skins, amphibians are often ecological indicators; in re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxa Named By M
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; plural taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and given a particular ranking, especially if and when it is accepted or becomes established. It is very common, however, for taxonomists to remain at odds over what belongs to a taxon and the criteria used for inclusion. If a taxon is given a formal scientific name, its use is then governed by one of the nomenclature codes specifying which scientific name is correct for a particular grouping. Initial attempts at classifying and ordering organisms (plants and animals) were set forth in Carl Linnaeus's system in ''Systema Naturae'', 10th edition (1758), as well as an unpublished work by Bernard and Antoine Laurent de Jussieu. The idea of a unit-based system of biological classification was first made widely available in 1805 in the intro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.png)
