|
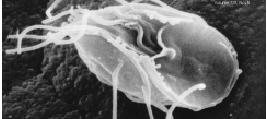
Protostelium Apiculatum
''Protostelium'' is a genus of protosteloid amoebozoans, i.e., amoebae capable of forming simple fruiting bodies composed of a stalk and a ball of spores. It contains numerous species, including '' P. aurantium'', which was initially classified in a different genus ''Planoprotostelium''. Phylogenetic analyses revealed that ''Planoprotostelium'' branches from within the genus ''Protostelium'', making them synonyms. The genus is placed in the family Protosteliidae within the monotypic order Protosteliida, which is part of a larger group of amoebozoans known as Variosea. Classification Many species from the genus ''Protostelium'' have been transferred over time to other protosteloid genera. The following species remain: * '' Protostelium apiculatum'' * ''Protostelium aurantium'' (=''Planoprotostelium aurantium'' ) * ''Protostelium mycophaga ''Protostelium'' is a genus of protosteloid amoebozoans, i.e., amoebae capable of forming simple fruiting bodies composed of a stalk and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protostelium Mycophaga
''Protostelium'' is a genus of protosteloid amoebozoans, i.e., amoebae capable of forming simple fruiting bodies composed of a stalk and a ball of spores. It contains numerous species, including '' P. aurantium'', which was initially classified in a different genus ''Planoprotostelium''. Phylogenetic analyses revealed that ''Planoprotostelium'' branches from within the genus ''Protostelium'', making them synonyms. The genus is placed in the family Protosteliidae within the monotypic order Protosteliida, which is part of a larger group of amoebozoans known as Variosea. Classification Many species from the genus ''Protostelium'' have been transferred over time to other protosteloid genera. The following species remain: * '' Protostelium apiculatum'' * ''Protostelium aurantium ''Protostelium'' is a genus of protosteloid amoebozoans, i.e., amoebae capable of forming simple fruiting bodies composed of a stalk and a ball of spores. It contains numerous species, including '' P. au ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family (taxonomy), family as used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. ''Panthera leo'' (lion) and ''Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomy (biology), taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants of an ancestral taxon are grouped together (i.e. Phylogeneti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protosteloid
The protosteloid amoebae, or protosteloids (formerly known as protostelids), are a group of terrestrial amoebae capable of developing a tiny fruiting body or sporocarp consisting of a stalk supporting one or more spores. They do not form a natural group; instead, they have gained the sporocarp-forming ability independently from each other during evolution. Description Protosteloid amoebae are capable of making simple fruiting bodies consisting of a cellular stalk topped by one or a few spores. These are known as sporocarps. All species are microscopic and are typically found on dead plant matter where they consume bacteria, yeasts, and fungal spores. Since protostelids are amoebae that make spores, they are considered to be slime molds. Protosteloid amoebae are terrestrial, typically found on dead plant matter, including stems and leaves of herbaceous plants, stems and leaves of grasses, bark of living trees, decaying wood and other types of dead plant matter. Some speci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amoebozoa
Amoebozoa is a major Taxonomy (biology), taxonomic group containing about 2,400 described species of Amoeba, amoeboid protists, often possessing blunt, fingerlike, Pseudopod#Morphology, lobose pseudopods and tubular mitochondrial cristae. In traditional classification schemes, Amoebozoa is usually ranked as a phylum within either the kingdom (biology), kingdom Protista or the kingdom Protozoa. In the classification favored by the International Society of Protistologists, it is retained as an unranked "supergroup (biology), supergroup" within Eukaryota. Molecular genetics, Molecular genetic analysis supports Amoebozoa as a monophyletic clade. Modern studies of eukaryotic phylogenetic trees identify it as the sister group to Opisthokonta, another major clade which contains both fungi and animals as well as several other clades comprising some 300 species of unicellular eukaryotes. Amoebozoa and Opisthokonta are sometimes grouped together in a high-level taxon, named Amorphea. Amoeboz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planoprotostelium Aurantium
''Planoprotostelium aurantium'' is a mycetozoa Mycetozoa is a polyphyletic grouping of slime molds. It was originally thought to be a monophyletic clade, but in 2010 it was discovered that protostelia are a polyphyletic group within Conosa. Classification It can be divided into dictyoste ...n species. References Mycetozoa Protists described in 1971 Dictyostelid species {{Amoebozoa-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phylogenetic Analyses
In biology, phylogenetics () is the study of the evolutionary history of life using observable characteristics of organisms (or genes), which is known as Computational phylogenetics, phylogenetic inference. It infers the relationship among organisms based on empirical data and observed heritable traits of DNA sequences, protein amino acid sequences, and Morphology (biology), morphology. The results are a phylogenetic tree—a diagram depicting the hypothesis, hypothetical relationships among the organisms, reflecting their inferred evolutionary history. The tips of a phylogenetic tree represent the observed entities, which can be living Taxon, taxa or fossils. A phylogenetic diagram can be rooted or unrooted. A rooted tree diagram indicates the hypothetical common ancestor of the taxa represented on the tree. An unrooted tree diagram (a network) makes no assumption about directionality of character state transformation, and does not show the origin or "root" of the taxa in questi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synonym (biology)
In taxonomy, the scientific classification of living organisms, a synonym is an alternative scientific name for the accepted scientific name of a taxon. The botanical and zoological codes of nomenclature treat the concept of synonymy differently. * In botanical nomenclature, a synonym is a scientific name that applies to a taxon that now goes by a different scientific name. For example, Linnaeus was the first to give a scientific name (under the currently used system of scientific nomenclature) to the Norway spruce, which he called '' Pinus abies''. This name is no longer in use, so it is now a synonym of the current scientific name, ''Picea abies''. * In zoology, moving a species from one genus to another results in a different binomen, but the name is considered an alternative combination rather than a synonym. The concept of synonymy in zoology is reserved for two names at the same rank that refers to a taxon at that rank – for example, the name ''Papilio prorsa'' Linnaeus, 17 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Variosea
Conosa is a grouping of Amoebozoa. It is subdivided into three groups: Archamoeba, Variosea and Mycetozoa. In some classifications, the mycetozoan Myxogastria and Dictyostelia are united in Macromycetozoa (= Eumycetozoa). Conosa includes the species ''Dictyostelium discoideum,'' a social amoeba, and ''Entamoeba histolytica'', a human pathogen, among others. Conosa are morphologically defined by a conical microtubular structure, and have been found to be monophyletic. Characteristics The Conosa group was first proposed by Thomas Cavalier-Smith in 1998 as a subphylum of Amoebozoa. Cavalier-Smith originally separated this group into two infraphyla: Archamoebae and Mycetozoa. Notable characteristics of these two groups are that Mycetozoa are free living, while Archamoebae are amitochondrial. This clade is morphologically defined by their complex microtubular skeleton that forms a partial or complete cone. They have a monolayer of microtubules that surround at least some of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protostelium Apiculatum
''Protostelium'' is a genus of protosteloid amoebozoans, i.e., amoebae capable of forming simple fruiting bodies composed of a stalk and a ball of spores. It contains numerous species, including '' P. aurantium'', which was initially classified in a different genus ''Planoprotostelium''. Phylogenetic analyses revealed that ''Planoprotostelium'' branches from within the genus ''Protostelium'', making them synonyms. The genus is placed in the family Protosteliidae within the monotypic order Protosteliida, which is part of a larger group of amoebozoans known as Variosea. Classification Many species from the genus ''Protostelium'' have been transferred over time to other protosteloid genera. The following species remain: * '' Protostelium apiculatum'' * ''Protostelium aurantium'' (=''Planoprotostelium aurantium'' ) * ''Protostelium mycophaga ''Protostelium'' is a genus of protosteloid amoebozoans, i.e., amoebae capable of forming simple fruiting bodies composed of a stalk and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protostelium Aurantium
''Protostelium'' is a genus of protosteloid amoebozoans, i.e., amoebae capable of forming simple fruiting bodies composed of a stalk and a ball of spores. It contains numerous species, including '' P. aurantium'', which was initially classified in a different genus ''Planoprotostelium''. Phylogenetic analyses revealed that ''Planoprotostelium'' branches from within the genus ''Protostelium'', making them synonyms. The genus is placed in the family Protosteliidae within the monotypic order Protosteliida, which is part of a larger group of amoebozoans known as Variosea Conosa is a grouping of Amoebozoa. It is subdivided into three groups: Archamoeba, Variosea and Mycetozoa. In some classifications, the mycetozoan Myxogastria and Dictyostelia are united in Macromycetozoa (= Eumycetozoa). Conosa includes t .... Classification Many species from the genus ''Protostelium'' have been transferred over time to other protosteloid genera. The following species remain: * '' Protost ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protostelium Nocturnum
''Protostelium'' is a genus of protosteloid amoebozoans, i.e., amoebae capable of forming simple fruiting bodies composed of a stalk and a ball of spores. It contains numerous species, including '' P. aurantium'', which was initially classified in a different genus ''Planoprotostelium''. Phylogenetic analyses revealed that ''Planoprotostelium'' branches from within the genus ''Protostelium'', making them synonyms. The genus is placed in the family Protosteliidae within the monotypic order Protosteliida, which is part of a larger group of amoebozoans known as Variosea. Classification Many species from the genus ''Protostelium'' have been transferred over time to other protosteloid genera. The following species remain: * ''Protostelium apiculatum'' * ''Protostelium aurantium'' (=''Planoprotostelium aurantium'' ) * ''Protostelium mycophaga ''Protostelium'' is a genus of protosteloid amoebozoans, i.e., amoebae capable of forming simple fruiting bodies composed of a stalk and a b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protostelium Okumukumu
''Protostelium okumukumu'' is a species of ''Protostelium'' found in Hawaii and New Zealand New Zealand () is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and List of islands of New Zealand, over 600 smaller islands. It is the List of isla .... See also * Protosteliales References Protosteloid amoebae Amoebozoa species Protists described in 2006 {{Amoebozoa-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |