|
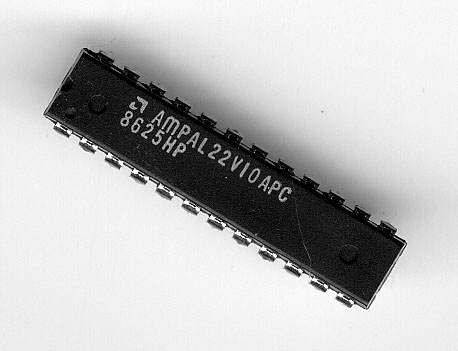
Programmable Array Logic
Programmable Array Logic (PAL) is a family of programmable logic device semiconductors used to implement logic functions in digital circuits introduced by Monolithic Memories, Inc. (MMI) in March 1978. Introductory advertisement on PAL (Programmable Array Logic). MMI obtained a registered trademark on the term PAL for use in "Programmable Semiconductor Logic Circuits". The trademark is currently held by Lattice Semiconductor.Monolithic Memories, Inc (MMI) filed for a work mark on the term "PAL" for use in "Programmable Semiconductor Logic Circuits" on April 13, 1978. A registered trademark was granted on April 29, 1980, registration number 1134025. MMI's first use of the term PAL in commerce was on February 21, 1978. The trademark is currently held by Lattice Semiconductor Corporation of Hillsboro, Oregon. Source: United States Patent and Trademark Office online database. PAL devices consisted of a small PROM (programmable read-only memory) core and additional output logic used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MMI PAL 16R6
MMI may refer to: Science and technology * Man-machine interface or user interface * Modified Mercalli intensity scale, an earthquake intensity measure * W3C MMI or Multimodal Interaction Activity * Monolithic Memories, Inc. (1969–1987), an American semiconductor manufacturer * Motorola Mobility (NYSE: MMI), a publicly traded electronics company, formerly part of Motorola * Multi Media Interface, an in-car interface system developed by Audi * Maximum mutual information criterion * Methimazole, a drug used to treat hyperthyroidism * Multi mode interferometer * Modified Mecalli Index Music * Miss May I, a metalcore band from Ohio * Madurai Mani Iyer, Indian singer Schools * Marion Military Institute, a military junior college in Marion, Alabama * Marymount International School of Rome, a private Catholic school in Rome, Italy * Miami Military Institute, a former military college that was located in Germantown, Ohio * Millersburg Military Institute, a defunct military ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NOR Gate
The NOR gate is a digital logic gate that implements logical NOR - it behaves according to the truth table to the right. A HIGH output (1) results if both the inputs to the gate are LOW (0); if one or both input is HIGH (1), a LOW output (0) results. NOR is the result of the negation of the OR operator. It can also in some senses be seen as the inverse of an AND gate. NOR is a functionally complete operation—NOR gates can be combined to generate any other logical function. It shares this property with the NAND gate. By contrast, the OR operator is ''monotonic'' as it can only change LOW to HIGH but not vice versa. In most, but not all, circuit implementations, the negation comes for free—including CMOS and TTL. In such logic families, OR is the more complicated operation; it may use a NOR followed by a NOT. A significant exception is some forms of the domino logic family. The original Apollo Guidance Computer used 4,100 integrated circuits (IC), each one containing o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Automation
Computer Automation Inc. was a computer manufacturer founded by David H. Methvin in 1968, based originally in Newport Beach, California, United States.Datamation, June 1968 p.167 It opened a sales, support and repair arm in the UK in 1972, based at Hertford House, Maple Cross, Rickmansworth, Hertfordshire. Later relocated to Suite 2 Milfield House, Croxley Centre, Croxley Green, Watford, Hertfordshire. In 1981 they moved the corporate offices to Boulder, Colorado, manufacturing and sales remained in California. In 1985 the offices moved to Irvine, California. Finally in 1990 they moved to Richardson, Texas. They had previously opened a manufacturing and engineering development facility there in 1978 as a way to escape high California tax and labor rates. The first products were the Computer Automation PDC 404 and PDC 808 "Programmed Digital Controllers". The PDC 808 announced circa July 1969 was designed for control, monitoring and/or data logging applications. It featured 4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Birkner
Programmable Array Logic (PAL) is a family of programmable logic device semiconductors used to implement logic functions in digital circuits introduced by Monolithic Memories, Inc. (MMI) in March 1978. Introductory advertisement on PAL (Programmable Array Logic). MMI obtained a registered trademark on the term PAL for use in "Programmable Semiconductor Logic Circuits". The trademark is currently held by Lattice Semiconductor.Monolithic Memories, Inc (MMI) filed for a work mark on the term "PAL" for use in "Programmable Semiconductor Logic Circuits" on April 13, 1978. A registered trademark was granted on April 29, 1980, registration number 1134025. MMI's first use of the term PAL in commerce was on February 21, 1978. The trademark is currently held by Lattice Semiconductor Corporation of Hillsboro, Oregon. Source: United States Patent and Trademark Office online database. PAL devices consisted of a small PROM (programmable read-only memory) core and additional output logic used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dual In-line Package
In microelectronics, a dual in-line package (DIP or DIL), is an electronic component package with a rectangular housing and two parallel rows of electrical connecting pins. The package may be through-hole mounted to a printed circuit board (PCB) or inserted in a socket. The dual-inline format was invented by Don Forbes, Rex Rice and Bryant Rogers at Fairchild R&D in 1964, when the restricted number of leads available on circular transistor-style packages became a limitation in the use of integrated circuits. Increasingly complex circuits required more signal and power supply leads (as observed in Rent's rule); eventually microprocessors and similar complex devices required more leads than could be put on a DIP package, leading to development of higher-density chip carriers. Furthermore, square and rectangular packages made it easier to route printed-circuit traces beneath the packages. A DIP is usually referred to as a DIP''n'', where ''n'' is the total number of pins. For e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thou (unit Of Length)
A thousandth of an inch is a derived unit of length in a system of units using inches. Equal to of an inch, a thousandth is commonly called a thou (used for both singular and plural) or particularly in North America a mil (plural mils). The words are shortened forms of the English and Latin words for "thousand" ( in Latin). In international engineering contexts, confusion can arise because ''mil'' is a formal unit name in North America but ''mil'' or ''mill'' is also a common colloquial clipped form of millimetre. The units are considerably different: a millimetre is approximately 39 mils. Contexts of use The thou, or mil, is most commonly used in engineering and manufacturing in non-metric countries. For example, in specifying: * The thickness of items such as paper, film, foil, wires, paint coatings, latex gloves, plastic sheeting, and fibers ** For example, most plastic ID cards are about in thickness. ** Card stock thickness in the United States, where mils are also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Field Programmable Logic Array
A field-programmable gate array (FPGA) is an integrated circuit designed to be configured by a customer or a designer after manufacturinghence the term '' field-programmable''. The FPGA configuration is generally specified using a hardware description language (HDL), similar to that used for an application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC). Circuit diagrams were previously used to specify the configuration, but this is increasingly rare due to the advent of electronic design automation tools. FPGAs contain an array of programmable logic blocks, and a hierarchy of reconfigurable interconnects allowing blocks to be wired together. Logic blocks can be configured to perform complex combinational functions, or act as simple logic gates like AND and XOR. In most FPGAs, logic blocks also include memory elements, which may be simple flip-flops or more complete blocks of memory. Many FPGAs can be reprogrammed to implement different logic functions, allowing flexible reconfigurable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signetics
Signetics Corporation was an American electronics manufacturer specifically established to make integrated circuits. Founded in 1961, they went on to develop a number of early microprocessors and support chips, as well as the widely used 555 timer chip. The company was bought by Philips in 1975 and incorporated in Philips Semiconductors (now NXP). History Signetics was started in 1961, by a group of engineers (David Allison, David James, Lionel Kattner, and Mark Weissenstern) who had left Fairchild Semiconductor. At the time, Fairchild was concentrating on its discrete component business (mostly transistors), and its management felt that by making integrated circuits (ICs) it would lose its customers. Signetics founders believed that ICs were the future of electronics (much like another contemporary Fairchild spinoff, Amelco) and wished to commercialize them. The name of the new company was coined from Signal Network Electronics. The venture was financed by a group organized t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Soul Of A New Machine
''The Soul of a New Machine'' is a non-fiction book written by Tracy Kidder and published in 1981. It chronicles the experiences of a computer engineering team racing to design a next-generation computer at a blistering pace under tremendous pressure. The machine was launched in 1980 as the Data General Eclipse MV/8000. The book, whose author was described by the ''New York Times'' as having "elevated it to a high level of narrative art" is "about real people working on a real computer for a real company," and it won the 1982 National Book Award for Nonfiction"National Book Awards – 1982" . Retrieved February 21, 2012. This ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tracy Kidder
John Tracy Kidder (born November 12, 1945) is an American writer of nonfiction books. He received the Pulitzer Prize for his ''The Soul of a New Machine'' (1981), about the creation of a new computer at Data General Corporation. He has received praise and awards for other works, including his biography of Paul Farmer, a physician and anthropologist, titled ''Mountains Beyond Mountains'' (2003). Kidder is considered a literary journalist because of the strong story line and personal voice in his writing. He has cited as his writing influences John McPhee, A. J. Liebling, and George Orwell. In a 1984 interview he said, "McPhee has been my model. He's the most elegant of all the journalists writing today, I think." Kidder wrote in a 1994 essay, "In fiction, believability may have nothing to do with reality or even plausibility. It has everything to do with those things in nonfiction. I think that the nonfiction writer's fundamental job is to make what is true believable." E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minicomputers
A minicomputer, or colloquially mini, is a class of smaller general purpose computers that developed in the mid-1960s and sold at a much lower price than mainframe and mid-size computers from IBM and its direct competitors. In a 1970 survey, ''The New York Times'' suggested a consensus definition of a minicomputer as a machine costing less than (), with an input-output device such as a teleprinter and at least four thousand words of memory, that is capable of running programs in a higher level language, such as Fortran or BASIC. The class formed a distinct group with its own software architectures and operating systems. Minis were designed for control, instrumentation, human interaction, and communication switching as distinct from calculation and record keeping. Many were sold indirectly to original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) for final end use application. During the two decade lifetime of the minicomputer class (1965–1985), almost 100 companies formed and only a half ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flip-flop (electronics)
In electronics, a flip-flop or latch is a circuit that has two stable states and can be used to store state information – a bistable multivibrator. The circuit can be made to change state by signals applied to one or more control inputs and will have one or two outputs. It is the basic storage element in sequential logic. Flip-flops and latches are fundamental building blocks of digital electronics systems used in computers, communications, and many other types of systems. Flip-flops and latches are used as data storage elements. A flip-flop is a device which stores a single ''bit'' (binary digit) of data; one of its two states represents a "one" and the other represents a "zero". Such data storage can be used for storage of ''state'', and such a circuit is described as sequential logic in electronics. When used in a finite-state machine, the output and next state depend not only on its current input, but also on its current state (and hence, previous inputs). It can also b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |