|
Pro-form
In linguistics, a pro-form is a type of function word or expression (linguistics) that stands in for (expresses the same content as) another word, phrase, clause or sentence where the meaning is recoverable from the context. They are used either to avoid repetitive expressions or in quantification (limiting the variables of a proposition). Pro-forms are divided into several categories, according to which part of speech they substitute: * A pronoun substitutes a noun or a noun phrase, with or without a determiner: ''it'', ''this''. * A prop-word: ''one'', as in "the blue one" * A pro-adjective substitutes an adjective or a phrase that functions as an adjective: ''so'' as in "It is less ''so'' than we had expected." * A pro-adverb substitutes an adverb or a phrase that functions as an adverb: ''how'' or ''this way''. * A pro-verb substitutes a verb or a verb phrase: ''do'', as in: "I will go to the party if you do". * A pro-sentence substitutes an entire sentence or subsentenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pronoun
In linguistics and grammar, a pronoun (Interlinear gloss, glossed ) is a word or a group of words that one may substitute for a noun or noun phrase. Pronouns have traditionally been regarded as one of the part of speech, parts of speech, but some modern theorists would not consider them to form a single class, in view of the variety of functions they perform cross-linguistically. An example of a pronoun is "you", which can be either singular or plural. Sub-types include personal pronoun, personal and possessive pronouns, reflexive pronoun, reflexive and reciprocal pronoun, reciprocal pronouns, demonstrative pronouns, relative pronoun, relative and interrogative pronouns, and indefinite pronouns. The use of pronouns often involves anaphora (linguistics), anaphora, where the meaning of the pronoun is dependent on an antecedent (grammar), antecedent. For example, in the sentence ''That poor man looks as if he needs a new coat'', the meaning of the pronoun ''he'' is dependent on its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
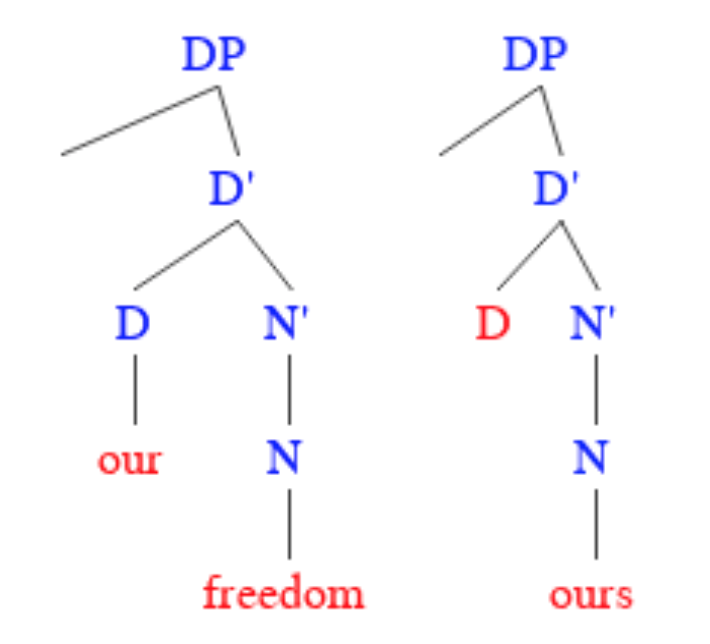
Prop-word
In linguistics and grammar, a pronoun ( glossed ) is a word or a group of words that one may substitute for a noun or noun phrase. Pronouns have traditionally been regarded as one of the parts of speech, but some modern theorists would not consider them to form a single class, in view of the variety of functions they perform cross-linguistically. An example of a pronoun is "you", which can be either singular or plural. Sub-types include personal and possessive pronouns, reflexive and reciprocal pronouns, demonstrative pronouns, relative and interrogative pronouns, and indefinite pronouns. The use of pronouns often involves anaphora, where the meaning of the pronoun is dependent on an antecedent. For example, in the sentence ''That poor man looks as if he needs a new coat'', the meaning of the pronoun ''he'' is dependent on its antecedent, ''that poor man''. The adjective form of the word "pronoun" is "pronominal". A pronominal is also a word or phrase that acts as a pron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Correlative
In grammar, a correlative is a word that is paired with another word with which it functions to perform a single function but from which it is separated in the sentence. In English, examples of correlative pairs are ''both–and, either–or, neither–nor, the–the'' ("the more the better"), ''so–that'' ("it ate so much food that it burst"), and ''if–then.'' In the Romance languages, the demonstrative pro-forms function as correlatives with the relative pro-forms, as ''autant–que'' in French; in English, demonstratives are not used in such constructions, which depend on the relative only: "I saw what you did", rather than *"I saw that, what you did". See also * Correlative conjunction *Pro-form In linguistics, a pro-form is a type of function word or expression (linguistics) that stands in for (expresses the same content as) another word, phrase, clause or sentence where the meaning is recoverable from the context. They are used eithe ... (namely section Table of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pro-sentence
A pro-sentence is a sentence where the subject pronoun has been dropped and therefore the sentence has a null subject. Overview Languages differ within this parameter, some languages such as Italian and Spanish have constant pro-drop, Finnish and Hebrew for example are partial pro-drop languages and Japanese and Tamil fall into the category of discourse or radical pro-drop languages. There are also languages such as English, German and Swedish that only allow pro-drop within very strict stylistic conditions. A pro-sentence is a kind of pro-form and is therefore anaphoric. In English, ''yes'', ''no'' and '' okay'' are common pro-sentences. In response to the question "Does Mars have two moons?", the sentence "Yes" can be understood to abbreviate "Mars does have two moons." Pro-sentences are sometimes seen as grammatical interjections, since they are capable of very limited syntactical relations. But they can also be classified as a distinct part of speech, given that (ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pro-verb
In linguistics, a pro-verb is a word or partial phrase that substitutes for a contextually recognizable verb phrase (via a process known as grammatical gapping), obviating the need to repeat an antecedent verb phrase. A pro-verb is a type of anaphora that falls within the general group of word classes called pro-forms (pro-verb is an analog of the pronoun that applies to verbs instead of nouns). Many languages use a replacement verb as a pro-verb to avoid repetition: English "do" (for example, "I like pie, and so does he"), , . The parallels between the roles of pronouns and pro-verbs on language are "striking": both are anaphoric and coreferential, able to replace very complex syntactic structures. The latter property makes it sometimes impossible to replace a pro-verb with a verb, thus its utility (like the one of a pronoun) goes beyond the stylistic variation of word substitution. When choosing between substituting a pro-verb and repeating a verb, in multiple languages, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demonstrative
Demonstratives (list of glossing abbreviations, abbreviated ) are words, such as ''this'' and ''that'', used to indicate which entities are being referred to and to distinguish those entities from others. They are typically deictic, their meaning depending on a particular Linguistic frame of reference, frame of reference, and cannot be understood without context. Demonstratives are often used in spatial deixis (where the speaker or sometimes the listener is to provide context), but also in intra-discourse reference (including Abstraction, abstract concepts) or anaphora (linguistics), anaphora, where the meaning is dependent on something other than the relative physical location of the speaker. An example is whether something is currently being said or was said earlier. Demonstrative constructions include demonstrative adjectives or demonstrative determiners, which specify nouns (as in ''Put that coat on''), and demonstrative pronouns, which stand independently (as in ''Put that on' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linguistics
Linguistics is the scientific study of language. The areas of linguistic analysis are syntax (rules governing the structure of sentences), semantics (meaning), Morphology (linguistics), morphology (structure of words), phonetics (speech sounds and equivalent gestures in sign languages), phonology (the abstract sound system of a particular language, and analogous systems of sign languages), and pragmatics (how the context of use contributes to meaning). Subdisciplines such as biolinguistics (the study of the biological variables and evolution of language) and psycholinguistics (the study of psychological factors in human language) bridge many of these divisions. Linguistics encompasses Outline of linguistics, many branches and subfields that span both theoretical and practical applications. Theoretical linguistics is concerned with understanding the universal grammar, universal and Philosophy of language#Nature of language, fundamental nature of language and developing a general ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Verb Phrase
In linguistics, a verb phrase (VP) is a syntax, syntactic unit composed of a verb and its argument (linguistics), arguments except the subject (grammar), subject of an independent clause or coordinate clause. Thus, in the sentence ''A fat man quickly put the money into the box'', the words ''quickly put the money into the box'' constitute a verb phrase; it consists of the verb ''put'' and its arguments, but not the subject ''a fat man''. A verb phrase is similar to what is considered a ''predicate (grammar), predicate'' in traditional grammars. Verb phrases generally are divided among two types: finite, of which the Head (linguistics), head of the phrase is a finite verb; and nonfinite, where the head is a nonfinite verb, such as an infinitive, participle or gerund. Phrase structure grammars acknowledge both types, but dependency grammars treat the subject as just another verbal dependent, and they do not recognize the finite verbal phrase constituent (linguistics), constituent. Un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interrogative Word
An interrogative word or question word is a function word used to ask a question, such as ''what, which'', ''when'', ''where'', '' who, whom, whose'', ''why'', ''whether'' and ''how''. They are sometimes called wh-words, because in English most of them start with '' wh-'' (compare Five Ws). Most may be used in both direct (''Where is he going?'') and in indirect questions (''I wonder where he is going''). In English and various other languages the same forms are also used as relative pronouns in certain relative clauses (''The country where he was born'') and certain adverb clauses (''I go where he goes''). It can also be used as a modal, since question words are more likely to appear in modal sentences, like (''Why was he walking?'') A particular type of interrogative word is the interrogative particle, which serves to convert a statement into a yes–no question, without having any other meaning. Examples include ''est-ce que'' in French, ли ''li'' in Russian, ''czy'' i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binding (linguistics)
In linguistics, binding is the phenomenon in which anaphoric elements such as pronouns are grammatically associated with their antecedents. For instance in the English sentence "Mary saw herself", the anaphor "herself" is bound by its antecedent "Mary". Binding can be licensed or blocked in certain contexts or syntactic configurations, e.g. the pronoun "her" cannot be bound by "Mary" in the English sentence "Mary saw her". While all languages have binding, restrictions on it vary even among closely related languages. Binding has been a major area of research in syntax and semantics since the 1970s and, as the name implies, is a core component of government and binding theory. Some basic examples and questions The following sentences illustrate some basic facts of binding. The words that bear the index i should be construed as referring to the same person or thing. ::a. Fredi is impressed with himselfi. – Indicated reading obligatory ::b. *Fredi is impressed with himi. – Ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relative Pronoun
A relative pronoun is a pronoun that marks a relative clause. An example is the word ''which'' in the sentence "This is the house which Jack built." Here the relative pronoun ''which'' introduces the relative clause. The relative clause modifies the noun ''house.'' The relative pronoun, "which," plays the role of an object within that clause, "which Jack built." In the English language, the following are the most common relative pronouns: ''which'', '' who'', ''whose'', ''whom'', ''whoever'', ''whomever'', and ''that'', though some linguists analyze ''that'' in relative clauses as a conjunction / complementizer. Antecedents The element in the main clause that the relative pronoun in the relative clause stands for (''house'' in the above example) is the ''antecedent'' of that pronoun. In most cases the antecedent is a nominal (noun or noun phrase), though the pronoun can also refer to a whole proposition, as in "The train was late, which annoyed me greatly", where the antecedent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morphological Derivation
Morphological derivation, in linguistics, is the process of forming a new word from an existing word, often by adding a prefix or suffix, such as For example, ''unhappy'' and ''happiness'' derive from the root word ''happy.'' It is differentiated from inflection, which is the modification of a word to form different grammatical categories without changing its core meaning: ''determines'', ''determining'', and ''determined'' are from the root ''determine''. Derivational patterns Derivational morphology often involves the addition of a derivational suffix or other affix. Such an affix usually applies to words of one lexical category (part of speech) and changes them into words of another such category. For example, one effect of the English derivational suffix ''-ly'' is to change an adjective into an adverb (''slow'' → ''slowly''). Here are examples of English derivational patterns and their suffixes: * adjective-to-noun: ''-ness'' (''slow'' → ''slowness'') * adjective ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |