|
Prince Of Wales's Own Civil Service Rifles
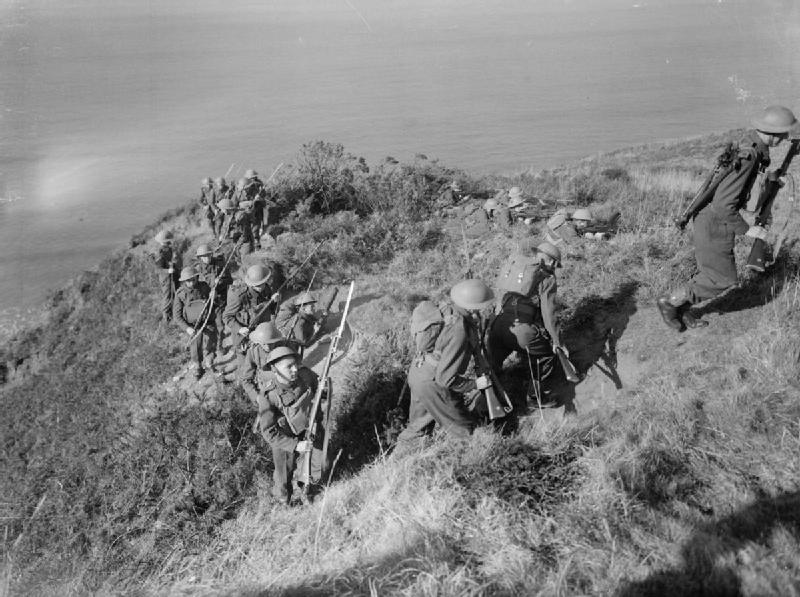
The Prince of Wales' Own Civil Service Rifles was an infantry regiment of the Volunteer Force and Territorial Force of the British Army from 1798 to 1921; it saw active service in the Boer War and World War I as part of the London Regiment. History Early history The regiment was originally formed as the Bank of England Volunteers in 1798 but was disbanded in 1814 at the end of the Napoleonic Wars. The regiment was re-raised by Viscount Bury on the formation of the Volunteer Force as the 21st Middlesex Middlesex Rifle Volunteers (Civil Service Rifles) in 1860. By 1880 and the re-numbering of London Rifle Volunteers the unit was titled 12th Middlesex (Civil Service) Rifle Volunteer Corps and were linked as a Volunteer Battalion of the King's Royal Rifle Corps. On formation of the Territorial Force in 1908 the Civil Service Rifles became part of the newly formed London Regiment and was titled 15th Battalion London Regiment (Civil Service Rifles). First World War At the start of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rifle Regiment
A rifle regiment is a military unit consisting of a regiment of infantry troops armed with rifles and known as riflemen. While all infantry units in modern armies are typically armed with rifled weapons the term is still used to denote regiments that follow the distinct traditions that differentiated them from other infantry units. Rifles had existed for decades before the formations of the first rifle regiments, but were initially too slow to load and too unreliable for use as practical weapons for mass issue. With improvements in the designs of rifles, the first rifle regiment was raised very late in the 18th century as armies could now equip entire units of troops with these new weapons in preference to earlier firearms such as muskets. Though rifles still took about twice as long to load as a musket the increase in accuracy and change in tactics more than compensated for this delay. History United Kingdom European armies in the 18th century largely consisted of large numbers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
140th (4th London) Brigade
The 140th (4th London) Brigade was an infantry brigade formation of the British Army's Territorial Army (TA) that had its origins in a South London Brigade (known as the 'Grey Brigade') of the former Volunteer Force. It served on the Western Front in the First World War and was recreated during the Second World War where it served only in the United Kingdom as a training formation. Origin: 'The Grey Brigade' An invasion scare in 1859 led to the creation of the Volunteer Force and huge enthusiasm for joining local Rifle Volunteer Corps (RVCs).Beckett. There were a large number of these units in and around London, and the opportunity was taken to group them together for Easter training under the temporary command of officers of the Brigade of Guards stationed in the capital. Initially they were brigaded by the colour of their uniforms – scarlet, Rifle green or grey, the latter being a popular colour for RVCs in the 1860s.Bailey & Hollier, pp. 4 & 382.Anon, ''Civil Service Rifles' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
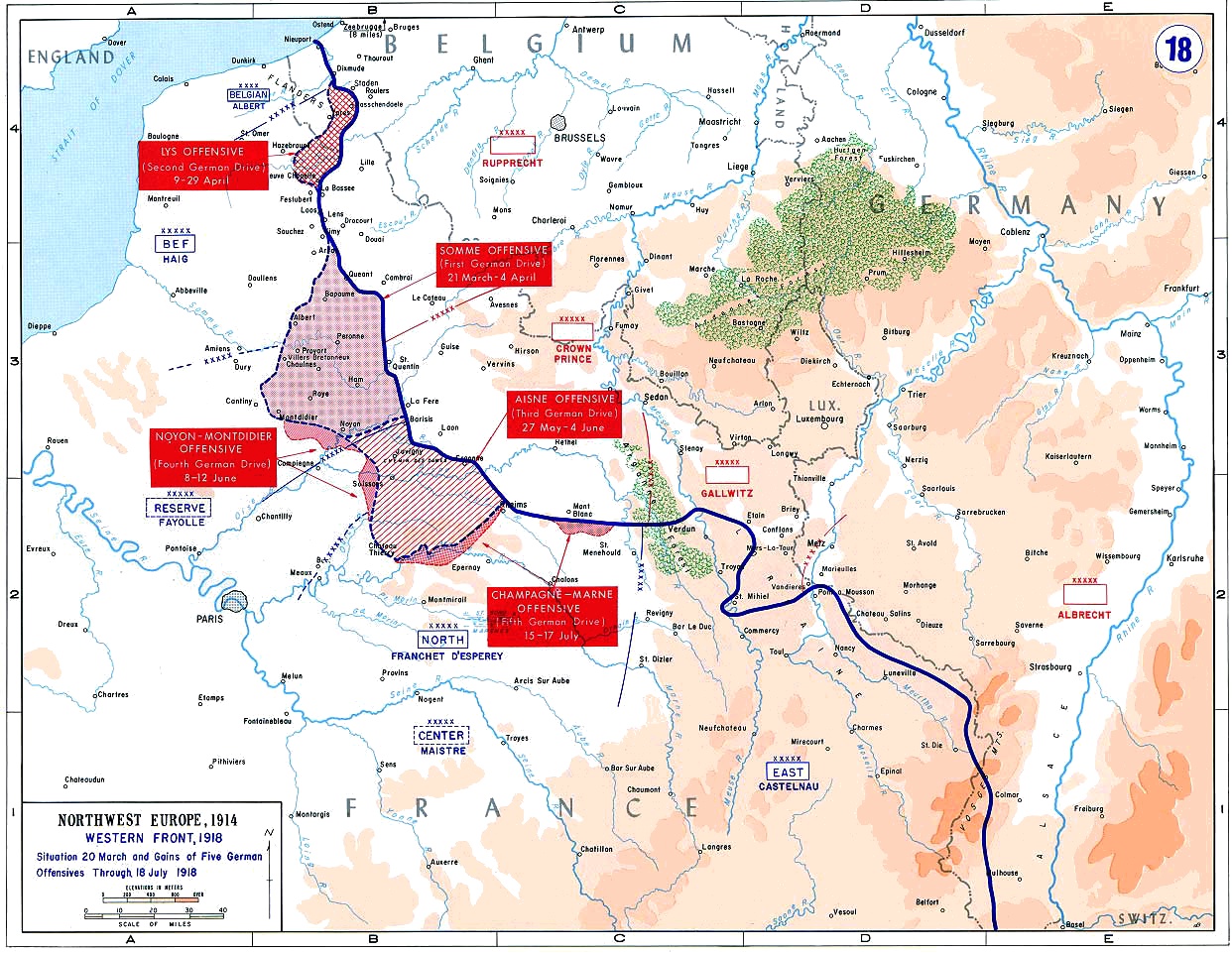
Operation Michael
Operation Michael was a major German military offensive during the First World War that began the German Spring Offensive on 21 March 1918. It was launched from the Hindenburg Line, in the vicinity of Saint-Quentin, France. Its goal was to break through the Allied (Entente) lines and advance in a north-westerly direction to seize the Channel Ports, which supplied the British Expeditionary Force (BEF) and to drive the BEF into the sea. Two days later General Erich Ludendorff, the chief of the German General Staff, adjusted his plan and pushed for an offensive due west, along the whole of the British front north of the River Somme. This was designed to first separate the French and British Armies before continuing with the original concept of pushing the BEF into the sea. The offensive ended at Villers-Bretonneux, to the east of the Allied communications centre at Amiens, where the Allies managed to halt the German advance; the German Army had suffered many casualties and was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint-Quentin, Aisne
Saint-Quentin (; pcd, Saint-Kintin; nl, label=older Dutch, Sint-Kwintens ) is a city in the Aisne department, Hauts-de-France, northern France. It has been identified as the ''Augusta Veromanduorum'' of antiquity. It is named after Saint Quentin of Amiens, who is said to have been martyred there in the 3rd century. Administration Saint-Quentin is a sub-prefecture of Aisne. Although Saint-Quentin is by far the largest city in Aisne, the capital is the third-largest city, Laon. Mayors The mayor of Saint-Quentin is Frédérique Macarez, a member of the centre-right LR Party. History The city was founded by the Romans, in the Augustean period, to replace the ''oppidum'' of Vermand (11 km away) as the capital of ''Viromandui'' (Celtic Belgian people who occupied the region). It received the name "''Augusta Viromanduorum''", ''Augusta'' of the ''Viromandui'', in honor of the emperor Augustus. The site is that of a ford across the River Somme. During the late Roman pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
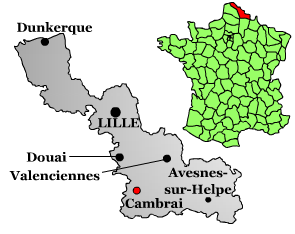
Cambrai 1917
Cambrai (, ; pcd, Kimbré; nl, Kamerijk), formerly Cambray and historically in English Camerick or Camericke, is a city in the Nord department and in the Hauts-de-France region of France on the Scheldt river, which is known locally as the Escaut river. A sub-prefecture of the department, Cambrai is a town which had 32,501 inhabitants in 2018. It is in the heart of the urban unit of Cambrai with 46,772 inhabitants. Its functional area, a more extensive range, included 94,576 inhabitants in 2018.Comparateur de territoire: Aire d'attraction des villes 2020 de Cambrai (108), Unité urbaine 2020 de Cambrai (59403), Commune de Cambrai (59122) INSEE With |
Battle Of Passchendaele
The Third Battle of Ypres (german: link=no, Dritte Flandernschlacht; french: link=no, Troisième Bataille des Flandres; nl, Derde Slag om Ieper), also known as the Battle of Passchendaele (), was a campaign of the First World War, fought by the Allies against the German Empire. The battle took place on the Western Front, from July to November 1917, for control of the ridges south and east of the Belgian city of Ypres in West Flanders, as part of a strategy decided by the Allies at conferences in November 1916 and May 1917. Passchendaele lies on the last ridge east of Ypres, from Roulers (now Roeselare), a junction of the Bruges-(Brugge)-to-Kortrijk railway. The station at Roulers was on the main supply route of the German 4th Army. Once Passchendaele Ridge had been captured, the Allied advance was to continue to a line from Thourout (now Torhout) to Couckelaere (Koekelare). Further operations and a British supporting attack along the Belgian coast from Nieuport ( Nieuwpoo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
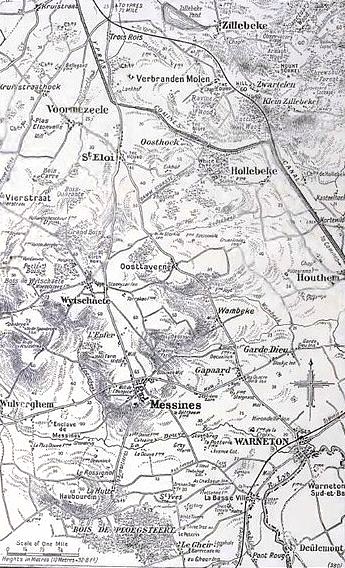
Battle Of Messines (1917)
The Battle of Messines (7–14 June 1917) was an attack by the British Second Army (General Sir Herbert Plumer), on the Western Front, near the village of Messines (now Mesen) in West Flanders, Belgium, during the First World War. The Nivelle Offensive in April and May had failed to achieve its more grandiose aims, had led to the 1917 French Army mutinies, demoralisation of French troops and confounded the Anglo-French strategy for 1917. The attack forced the Germans to move reserves to Flanders from the Arras and Aisne fronts, relieving pressure on the French. The British tactical objective was to capture the German defences on the ridge, which ran from Ploegsteert Wood (Plugstreet to the British) in the south, through Messines and Wytschaete to Mt Sorrel, depriving the German 4th Army (German Empire), 4th Army of the high ground. The ridge gave commanding views of the British defences and back areas of Ypres to the north, from which the British intended to conduct the North ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Le Transloy
The Battle of Le Transloy was the last big attack by the Fourth Army of the British Expeditionary Force (BEF) in the 1916 Battle of the Somme in France, during the First World War. The battle was fought in conjunction with attacks by the French Tenth and Sixth armies on the southern flank and the Reserve/5th Army on the northern flank, against Army Group Rupprecht of Bavaria () created on 28 August. General Ferdinand Foch, commander of (Northern Army Group) and co-ordinator of the armies on the Somme, was unable to continue the sequential attacks of September because persistent rain, mist and fog grounded aircraft, turned the battlefield into a swamp and greatly increased the difficulty of transporting supplies to the front over the roads land devastated since 1 July. The German armies on the Somme managed a recovery after the string of defeats in September, with fresh divisions to replace exhausted troops and more aircraft, artillery and ammunition diverted from Verdun and st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Flers–Courcelette
The Battle of Flers–Courcelette (, 15 to 22 September 1916) was fought during the Battle of the Somme in France, by the French Sixth Army and the British Fourth Army and Reserve Army, against the German 1st Army, during the First World War. The Anglo-French attack of 15 September began the third period of the Battle of the Somme but by its conclusion on 22 September, the strategic objective of a decisive victory had not been achieved. The infliction of many casualties on the German front divisions and the capture of the villages of Courcelette, Martinpuich and Flers had been a considerable tactical victory. The German defensive success on the British right flank made exploitation and the use of cavalry impossible. Tanks were used in battle for the first time; the Canadian Corps and the New Zealand Division fought their first engagements on the Somme. On 16 September, , a specialist fighter squadron, began operations with five new Albatros D.I fighters, which had a performa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Battle Of The Somme (1918)
The Second Battle of the Somme of 1918 was fought during the First World War on the Western Front from late August to early September, in the basin of the River Somme. It was part of a series of successful counter-offensives in response to the German Spring Offensive, after a pause for redeployment and supply. The most significant feature of the two 1918 Somme battles was that with the failure of the first 1918 Somme Battle (not to be confused with the 1916 Battle of the Somme) having halted what had begun as a large German offensive, the second formed the central part of the Allies' advance to the Armistice of 11 November. Battle On August 15, British Field Marshal Douglas Haig refused demands from Supreme Allied Commander Marshal Ferdinand Foch to continue the Amiens offensive, as that attack was faltering as the troops outran their supplies and artillery, and German reserves were being moved to the sector. Instead, Haig began to plan for an offensive at Albert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of The Somme
The Battle of the Somme ( French: Bataille de la Somme), also known as the Somme offensive, was a battle of the First World War fought by the armies of the British Empire and French Third Republic against the German Empire. It took place between 1 July and 18 November 1916 on both sides of the upper reaches of the Somme, a river in France. The battle was intended to hasten a victory for the Allies. More than three million men fought in the battle of whom one million were wounded or killed, making it one of the deadliest battles in human history. The French and British had committed themselves to an offensive on the Somme during the Chantilly Conference in December 1915. The Allies agreed upon a strategy of combined offensives against the Central Powers in 1916 by the French, Russian, British and Italian armies, with the Somme offensive as the Franco-British contribution. Initial plans called for the French army to undertake the main part of the Somme offensive, supported on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Loos
The Battle of Loos took place from 1915 in France on the Western Front, during the First World War. It was the biggest British attack of 1915, the first time that the British used poison gas and the first mass engagement of New Army units. The French and British tried to break through the German defences in Artois and Champagne and restore a war of movement. Despite improved methods, more ammunition and better equipment, the Franco-British attacks were largely contained by the Germans, except for local losses of ground. The British gas attack failed to neutralize the defenders and the artillery bombardment was too short to destroy the barbed wire or machine gun nests. German tactical defensive proficiency was still dramatically superior to the British offensive planning and doctrine, resulting in a British defeat. Background Strategic developments The battle was the British part of the Third Battle of Artois, an Anglo-French offensive (known to the Germans as the (Autumn Batt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |