|
Pretty Good Privacy
Pretty Good Privacy (PGP) is an encryption software, encryption program that provides cryptographic privacy and authentication for data communication. PGP is used for digital signature, signing, encrypting, and decrypting texts, Email, e-mails, files, directories, and whole disk partitions and to increase the security of e-mail communications. Phil Zimmermann developed PGP in 1991. PGP and similar software follow the OpenPGP standard (RFC 4880), an open standard for encryption, encrypting and decrypting data. Modern versions of PGP are interoperability, interoperable with GnuPG and other OpenPGP-compliant systems. The OpenPGP standard has received criticism for its long-lived keys and the difficulty in learning it, as well as the EFAIL, Efail security vulnerability that previously arose when select e-mail programs used OpenPGP with S/MIME. The new OpenPGP standard (RFC 9580) has also been criticised by the maintainer of GnuPG Werner Koch, who in response created his own speci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Phil Zimmermann
Philip R. Zimmermann (born 1954) is an American computer scientist and cryptographer. He is the creator of Pretty Good Privacy (PGP), the most widely used email encryption software in the world. He is also known for his work in VoIP encryption protocols, notably ZRTP and Zfone. Zimmermann is co-founder and Chief Scientist of the global encrypted communications firm Silent Circle. Background Zimmermann was born in Camden, New Jersey. He received a B.S. degree in computer science from Florida Atlantic University in Boca Raton, Florida, in 1978. In the 1980s, he worked in Boulder, Colorado, as a software engineer on the Nuclear Weapons Freeze Campaign as a military policy analyst. From 2016 to 2021, he worked at Delft University of Technology as an Associate Professor in the Cybersecurity section at the Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Mathematics, and Computer Science. PGP In 1991, he wrote the popular Pretty Good Privacy (PGP) program, and made it available (together wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Open Standard
An open standard is a standard that is openly accessible and usable by anyone. It is also a common prerequisite that open standards use an open license that provides for extensibility. Typically, anybody can participate in their development due to their inherently open nature. There is no single definition, and interpretations vary with usage. Examples of open standards include the GSM, 4G, and 5G standards that allow most modern mobile phones to work world-wide. Definitions The terms ''open'' and ''standard'' have a wide range of meanings associated with their usage. There are a number of definitions of open standards which emphasize different aspects of openness, including the openness of the resulting specification, the openness of the drafting process, and the ownership of rights in the standard. The term "standard" is sometimes restricted to technologies approved by formalized committees that are open to participation by all interested parties and operate on a consensus basis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Web Of Trust
In cryptography, a web of trust is a concept used in PGP, GnuPG, and other OpenPGP-compatible systems to establish the authenticity of the binding between a public key and its owner. Its decentralized trust model is an alternative to the centralized trust model of a public key infrastructure (PKI), which relies exclusively on a certificate authority (or a hierarchy of such). As with computer networks, there are many independent webs of trust, and any user (through their public key certificate) can be a part of, and a link between, multiple webs. The web of trust concept was first put forth by PGP creator Phil Zimmermann in 1992 in the manual for PGP version 2.0: Note the use of the word emergence in this context. The web of trust makes use of the concept of emergence. Operation of a web of trust All OpenPGP-compliant implementations include a certificate vetting scheme to assist with this; its operation has been termed a web of trust. OpenPGP certificates (which incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm () is a finite sequence of Rigour#Mathematics, mathematically rigorous instructions, typically used to solve a class of specific Computational problem, problems or to perform a computation. Algorithms are used as specifications for performing calculations and data processing. More advanced algorithms can use Conditional (computer programming), conditionals to divert the code execution through various routes (referred to as automated decision-making) and deduce valid inferences (referred to as automated reasoning). In contrast, a Heuristic (computer science), heuristic is an approach to solving problems without well-defined correct or optimal results.David A. Grossman, Ophir Frieder, ''Information Retrieval: Algorithms and Heuristics'', 2nd edition, 2004, For example, although social media recommender systems are commonly called "algorithms", they actually rely on heuristics as there is no truly "correct" recommendation. As an e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Public-key Cryptography
Public-key cryptography, or asymmetric cryptography, is the field of cryptographic systems that use pairs of related keys. Each key pair consists of a public key and a corresponding private key. Key pairs are generated with cryptographic algorithms based on mathematical problems termed one-way functions. Security of public-key cryptography depends on keeping the private key secret; the public key can be openly distributed without compromising security. There are many kinds of public-key cryptosystems, with different security goals, including digital signature, Diffie–Hellman key exchange, Key encapsulation mechanism, public-key key encapsulation, and public-key encryption. Public key algorithms are fundamental security primitives in modern cryptosystems, including applications and protocols that offer assurance of the confidentiality and authenticity of electronic communications and data storage. They underpin numerous Internet standards, such as Transport Layer Security, T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Symmetric-key Cryptography
Symmetric-key algorithms are algorithms for cryptography that use the same Key (cryptography), cryptographic keys for both the encryption of plaintext and the decryption of ciphertext. The keys may be identical, or there may be a simple transformation to go between the two keys. The keys, in practice, represent a shared secret between two or more parties that can be used to maintain a private information link. The requirement that both parties have access to the secret key is one of the main drawbacks of symmetric-key encryption, in comparison to Public key encryption, public-key encryption (also known as asymmetric-key encryption). However, symmetric-key encryption algorithms are usually better for bulk encryption. With exception of the one-time pad they have a smaller key size, which means less storage space and faster transmission. Due to this, asymmetric-key encryption is often used to exchange the secret key for symmetric-key encryption. Types Symmetric-key encryption can us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Data Compression
In information theory, data compression, source coding, or bit-rate reduction is the process of encoding information using fewer bits than the original representation. Any particular compression is either lossy or lossless. Lossless compression reduces bits by identifying and eliminating statistical redundancy. No information is lost in lossless compression. Lossy compression reduces bits by removing unnecessary or less important information. Typically, a device that performs data compression is referred to as an encoder, and one that performs the reversal of the process (decompression) as a decoder. The process of reducing the size of a data file is often referred to as data compression. In the context of data transmission, it is called source coding: encoding is done at the source of the data before it is stored or transmitted. Source coding should not be confused with channel coding, for error detection and correction or line coding, the means for mapping data onto a sig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cryptographic Hash Function
A cryptographic hash function (CHF) is a hash algorithm (a map (mathematics), map of an arbitrary binary string to a binary string with a fixed size of n bits) that has special properties desirable for a cryptography, cryptographic application: * the probability of a particular n-bit output result (hash value) for a random input string ("message") is 2^ (as for any good hash), so the hash value can be used as a representative of the message; * finding an input string that matches a given hash value (a ''pre-image'') is infeasible, ''assuming all input strings are equally likely.'' The ''resistance'' to such search is quantified as security strength: a cryptographic hash with n bits of hash value is expected to have a ''preimage resistance'' strength of n bits, unless the space of possible input values is significantly smaller than 2^ (a practical example can be found in ); * a ''second preimage'' resistance strength, with the same expectations, refers to a similar problem of f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
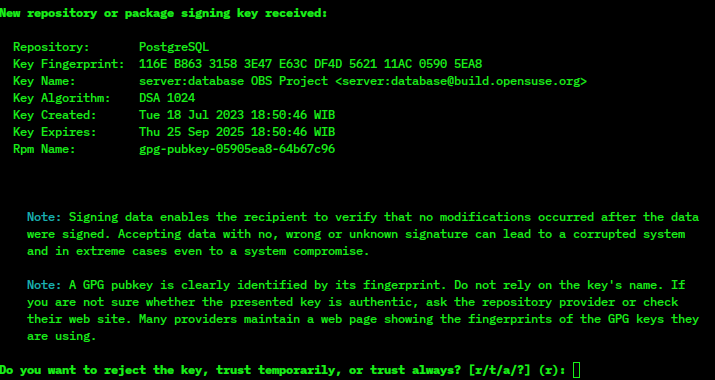
PGP Diagram
PGP or Pgp may refer to: Science and technology * P-glycoprotein, a type of protein * Pelvic girdle pain, a pregnancy discomfort * Personal Genome Project, to sequence genomes and medical records * Pretty Good Privacy Pretty Good Privacy (PGP) is an encryption software, encryption program that provides cryptographic privacy and authentication for data communication. PGP is used for digital signature, signing, encrypting, and decrypting texts, Email, e-mail ..., a computer program for the encryption and decryption of data * Penultimate Glacial Period, the ice age from c. 194,000 to c. 135,000 years ago Organizations * PGP Corporation, a software company, part of Symantec, which bought the rights to Pretty Good Privacy * Procter & Gamble Productions, former name of Procter & Gamble Entertainment * PGP-RTB, a Yugoslav record label and chain record store (1958-1993) * PGP-RTS, successor to PGP-RTB in Serbia Politics * Gabonese Party of Progress (''Parti gabonais du pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Werner Koch
Werner Koch (born July 11, 1961) is a German free software developer. He is best known as the principal author of the GNU Privacy Guard (GnuPG or GPG). He was also Head of Office and German Vice-Chancellor of the Free Software Foundation Europe. He is the winner of Award for the Advancement of Free Software in 2015 for founding GnuPG.Library Freedom Project and Werner Koch are 2015 Free Software Awards winners FSF Journalists and security professionals rely on GnuPG, and used it to evade monitoring whilst he [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
EFAIL
Efail, also written EFAIL, is a security hole in email systems with which content can be transmitted in encrypted form. This gap allows attackers to access the decrypted content of an email if it contains active content like HTML email, HTML or JavaScript, or if loading of external content has been enabled in the client. Affected email clients include Gmail, Mail (Apple), Apple Mail, and Microsoft Outlook. Two related Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures IDs, , have been issued. The security gap was made public on 13 May 2018 by Damian Poddebniak, Christian Dresen, Jens Müller, Fabian Ising, Sebastian Schinzel, Simon Friedberger, Juraj Somorovsky and Jörg Schwenk as part of a contribution to the 27th USENIX Security Symposium, Baltimore, August 2018. As a result of the vulnerability, the content of an attacked encrypted email can be transmitted to the attacker in plain text by a vulnerable email client. The used encryption keys are not disclosed. Description The security g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
GnuPG
GNU Privacy Guard (GnuPG or GPG) is a free-software replacement for Symantec's cryptographic software suite PGP. The software is compliant with the now obsoleted , the IETF standards-track specification of OpenPGP. Modern versions of PGP are interoperable with GnuPG and other OpenPGP v4-compliant systems. November 2023 saw two drafts aiming to update the 2007 OpenPGP v4 specification (RFC4880), ultimately resulting in thRFC 9580standard in July 2024. The proposal from the GnuPG developers, which is called LibrePGP, was not taken up by the OpenPGP Working Group and future versions of GnuPG will not support the current version of OpenPGP. GnuPG is part of the GNU Project and received major funding from the German government in 1999. Overview GnuPG is a hybrid-encryption software program because it uses a combination of conventional symmetric-key cryptography for speed, and public-key cryptography for ease of secure key exchange, typically by using the recipient's publi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |