|
Presentational Acting
Presentational acting and the related representational acting are opposing ways of sustaining the actor–audience relationship. With presentational acting, the actor acknowledges the audience. With representational acting, the audience is studiously ignored and treated as voyeurs. In the sense of actor-character relationship, the type of theatre that uses 'presentational acting' in the actor-audience relationship, is often associated with a performer using 'representational acting' in their actor-character methodology. Conversely, the type of theatre that uses 'representational acting' in the first sense is often associated with a performer using 'presentational acting' methodology. The actor–audience relationship In every theatrical performance the manner in which each individual actor treats the audience establishes, sustains or varies a particular kind of actor-audience relationship between them. In some plays all of the actors may adopt the same attitude towards the audien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
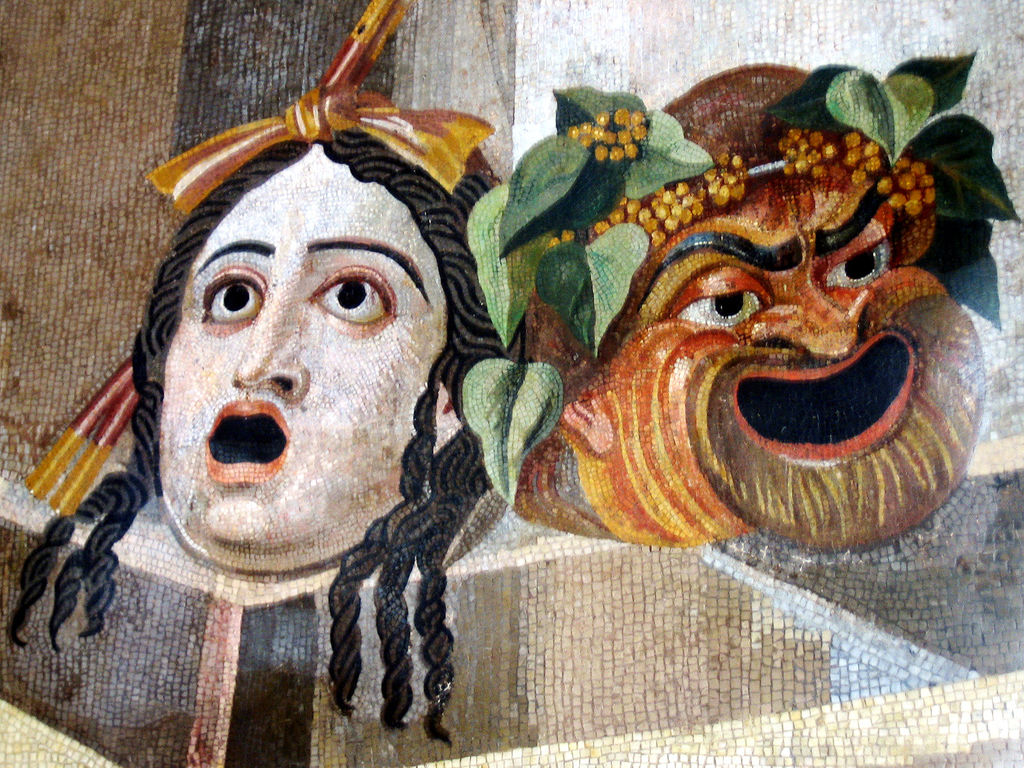
Tragic Comic Masks - Roman Mosaic
Tragedy (from the grc-gre, τραγῳδία, ''tragōidia'', ''tragōidia'') is a genre of drama based on human suffering and, mainly, the terrible or sorrowful events that befall a main character. Traditionally, the intention of tragedy is to invoke an accompanying catharsis, or a "pain hatawakens pleasure", for the audience. While many cultures have developed forms that provoke this paradoxical response, the term ''tragedy'' often refers to a specific tradition of drama that has played a unique and important role historically in the self-definition of Western civilization. That tradition has been multiple and discontinuous, yet the term has often been used to invoke a powerful effect of cultural identity and historical continuity—"the Greeks and the Elizabethans, in one cultural form; Hellenes and Christians, in a common activity," as Raymond Williams puts it. From its origins in the theatre of ancient Greece 2500 years ago, from which there survives only a fract ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fourth Wall
The fourth wall is a performance convention in which an invisible, imaginary wall separates actors from the audience. While the audience can see through this ''wall'', the convention assumes the actors act as if they cannot. From the 16th century onward, the rise of illusionism in staging practices, which culminated in the realism and naturalism of the theatre of the 19th century, led to the development of the fourth wall concept. The metaphor suggests a relationship to the mise-en-scène behind a proscenium arch. When a scene is set indoors and three of the walls of its room are presented onstage, in what is known as a box set, the fourth of them would run along the line (technically called the proscenium) dividing the room from the auditorium. The ''fourth wall'', though, is a theatrical convention, rather than of set design. The actors ignore the audience, focus their attention exclusively on the dramatic world, and remain absorbed in its fiction, in a state that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contradiction
In traditional logic, a contradiction occurs when a proposition conflicts either with itself or established fact. It is often used as a tool to detect disingenuous beliefs and bias. Illustrating a general tendency in applied logic, Aristotle's law of noncontradiction states that "It is impossible that the same thing can at the same time both belong and not belong to the same object and in the same respect." In modern formal logic and type theory, the term is mainly used instead for a ''single'' proposition, often denoted by the falsum symbol \bot; a proposition is a contradiction if false can be derived from it, using the rules of the logic. It is a proposition that is unconditionally false (i.e., a self-contradictory proposition). This can be generalized to a collection of propositions, which is then said to "contain" a contradiction. History By creation of a paradox, Plato's '' Euthydemus'' dialogue demonstrates the need for the notion of ''contradiction''. In the ensuing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Denis Diderot
Denis Diderot (; ; 5 October 171331 July 1784) was a French philosopher, art critic, and writer, best known for serving as co-founder, chief editor, and contributor to the '' Encyclopédie'' along with Jean le Rond d'Alembert. He was a prominent figure during the Age of Enlightenment. Diderot initially studied philosophy at a Jesuit college, then considered working in the church clergy before briefly studying law. When he decided to become a writer in 1734, his father disowned him. He lived a bohemian existence for the next decade. In the 1740s he wrote many of his best-known works in both fiction and non-fiction, including the 1748 novel '' The Indiscreet Jewels''. In 1751, Diderot co-created the ''Encyclopédie'' with Jean le Rond d'Alembert. It was the first encyclopedia to include contributions from many named contributors and the first to describe the mechanical arts. Its secular tone, which included articles skeptical about Biblical miracles, angered both religiou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benoît-Constant Coquelin
Benoît-Constant Coquelin (; 23 January 184127 January 1909), known as Coquelin aîné ("Coquelin the Elder"), was a French actor, "one of the greatest theatrical figures of the age." Biography Coquelin was born in Boulogne-sur-Mer, Pas-de-Calais. He was originally intended to follow his father's trade of baker (he was once called "un boulanger manqué" – "a failed baker" – by a hostile critic), but his love of acting led him to the Conservatoire, where he entered Régnier's class in 1859. He won the first prize for comedy within a year, and made his début on 7 December 1860 at the Comédie-Française as the comic valet, Gros-René, in Molière's ''Le Dépit amoureux'', but his first great success was as Figaro in ''The Barber of Seville'', in the following year. It was an honour for Coquelin to be a part of the Comédie-Française at such a young age. This company had already been in existence for around 150 years. He was made ''sociétaire'' in 1864. There were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Art Of Representation
The "art of representation" (russian: представление, predstavlenie) is a critical term used by the seminal Russian theatre practitioner Konstantin Stanislavski to describe a method of acting. It comes from his acting manual ''An Actor Prepares'' (1936). Stanislavski defines his own approach to acting as "experiencing the role" and contrasts it with the "art of representation". It is on the basis of this formulation that the American Method acting teacher Uta Hagen defines her recommended Stanislavskian approach as ' presentational' acting, as opposed to ' representational' acting. This use, however, directly contradicts mainstream critical use of these terms. Despite the distinction, Stanislavskian theatre, in which actors 'experience' their roles, remains ' representational' in the broader critical sense. 'Experiencing' and 'representing' In "When Acting is an Art", having watched his students' first attempts at a performance, Stanislavski's fictional persona Tort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
An Actor Prepares
''An Actor Prepares'' () is the first of Konstantin Stanislavski's books on acting, followed by ''Building a Character'' and ''Creating a Role''. Stanislavski intended to publish the contents of ''An Actor Prepares'' and ''Building a Character'' as a single volume, and in the Russian language. However, ''An Actor Prepares'' was first published as a single volume in English, and World War II delayed the publication of ''Building a Character'' for more than ten years. Summary ''An Actor Prepares'' is the diary of a fictional student named Kostya during his first year of training in Stanislavski's system. Kostya and his fellow students have little to no experience in acting. As they go through the class, Tortsov, their teacher and theatre director, addresses the many assumptions they have formed that do not coincide with the 'system'. Stanislavski relates his message with examples. He argues that his system is not a particular method, but a systematic analysis of the 'natural' order ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Konstantin Stanislavski
Konstantin Sergeyevich Stanislavski ( Alekseyev; russian: Константин Сергеевич Станиславский, p=kənstɐnʲˈtʲin sʲɪrˈgʲejɪvʲɪtɕ stənʲɪˈslafskʲɪj; 7 August 1938) was a seminal Soviet Russian theatre practitioner. He was widely recognized as an outstanding character actor and the many productions that he directed garnered him a reputation as one of the leading theatre directors of his generation. His principal fame and influence, however, rests on his "system" of actor training, preparation, and rehearsal technique. Stanislavski (his stage name) performed and directed as an amateur until the age of 33, when he co-founded the world-famous Moscow Art Theatre (MAT) company with Vladimir Nemirovich-Danchenko, following a legendary 18-hour discussion. Its influential tours of Europe (1906) and the US (1923–24), and its landmark productions of ''The Seagull'' (1898) and ''Hamlet'' (1911–12), established his reputation and o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theatre Practitioner
A theatre practitioner is someone who creates theatrical performances and/or produces a theoretical discourse that informs his or her practical work. A theatre practitioner may be a director, dramatist, actor, designer or a combination of these traditionally separate roles. ''Theatre practice'' describes the collective work that various theatre practitioners do. The term was not ordinarily applied to theatre-makers prior to the rise of modernism in the theatre. Instead, theatre praxis from Konstantin Stanislavski's development of his system is described through Vsevolod Meyerhold's biomechanics, Antonin Artaud's Theatre of cruelty, Bertolt Brecht's epic, and Jerzy Grotowski's poor theatre. Contemporary theatre practitioners include Augusto Boal with his Theatre of the Oppressed, Dario Fo's popular theatre, Eugenio Barba's theatre anthropology, and Anne Bogart's viewpoints Viewpoints is a technique of dance composition that acts as a medium for thinking about and acting upo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ambiguity
Ambiguity is the type of meaning in which a phrase, statement or resolution is not explicitly defined, making several interpretations plausible. A common aspect of ambiguity is uncertainty. It is thus an attribute of any idea or statement whose intended meaning cannot be definitively resolved according to a rule or process with a finite number of steps. (The '' ambi-'' part of the term reflects an idea of " two", as in "two meanings".) The concept of ambiguity is generally contrasted with vagueness. In ambiguity, specific and distinct interpretations are permitted (although some may not be immediately obvious), whereas with information that is vague, it is difficult to form any interpretation at the desired level of specificity. Linguistic forms Lexical ambiguity is contrasted with semantic ambiguity. The former represents a choice between a finite number of known and meaningful context-dependent interpretations. The latter represents a choice between any number of p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uta Hagen
Uta Thyra Hagen (12 June 1919 – 14 January 2004) was a German-American actress and theatre practitioner. She originated the role of Martha in the 1962 Broadway premiere of ''Who's Afraid of Virginia Woolf?'' by Edward Albee, who called her "a profoundly truthful actress." Because Hagen was on the Hollywood blacklist, in part because of her association with Paul Robeson, her film opportunities dwindled and she focused her career on New York theatre. She later became a highly influential acting teacher at New York's Herbert Berghof Studio and authored best-selling acting texts, '' Respect for Acting'', with Haskel Frankel, and '' A Challenge for the Actor''. Her most substantial contributions to theatre pedagogy were a series of "object exercises" that built on the work of Konstantin Stanislavski and Yevgeny Vakhtangov. She was elected to the American Theater Hall of Fame in 1981. She twice won the Tony Award for Best Actress in a Play and received a Special Tony Award for Li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |