|
Predator Avoidance
Anti-predator adaptations are mechanisms developed through evolution that assist prey organisms in their constant struggle against predators. Throughout the animal kingdom, adaptations have evolved for every stage of this struggle, namely by avoiding detection, warding off attack, fighting back, or escaping when caught. The first line of defence consists in avoiding detection, through mechanisms such as camouflage, masquerade, apostatic selection, living underground, or nocturnality. Alternatively, prey animals may ward off attack, whether by advertising the presence of strong defences in aposematism, by mimicking animals which do possess such defences, by startling the attacker, by signalling to the predator that pursuit is not worthwhile, by distraction, by using defensive structures such as spines, and by living in a group. Members of groups are at reduced risk of predation, despite the increased conspicuousness of a group, through improved vigilance, predator confusi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
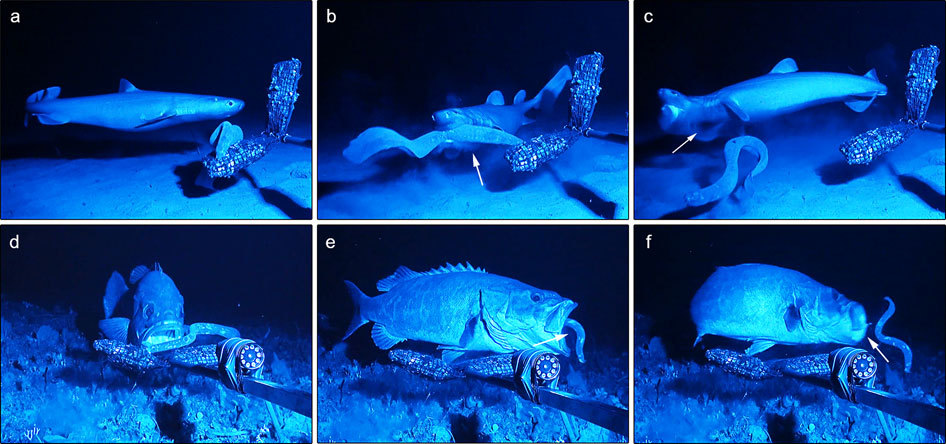
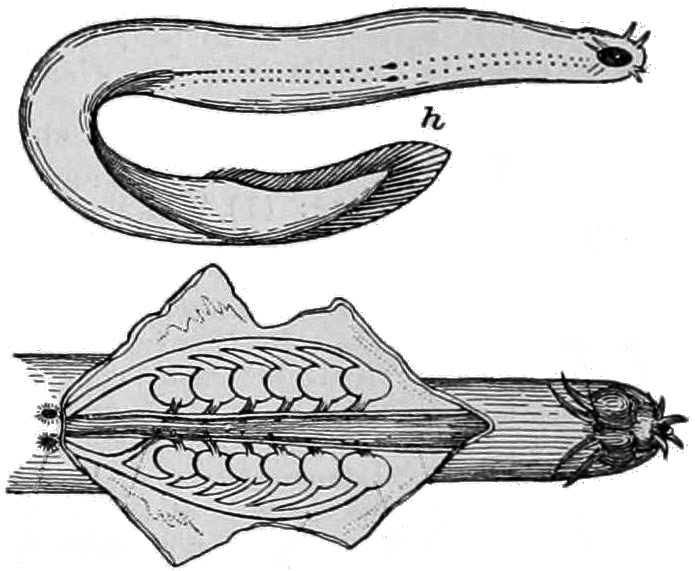
Hagfish Slime Predator Deterrence
Hagfish, of the class Myxini (also known as Hyperotreti) and order Myxiniformes , are eel-shaped, slime-producing marine fish (occasionally called slime eels). They are the only known living animals that have a skull but no vertebral column, although hagfish do have rudimentary vertebrae. Along with lampreys, hagfish are jawless; the two form the sister group to jawed vertebrates, and living hagfish remain similar to hagfish from around 300 million years ago. The classification of hagfish had been controversial. The issue was whether the hagfish was a degenerate type of vertebrate-fish that through evolution had lost its vertebrae (the original scheme) and was most closely related to lampreys, or whether hagfish represent a stage that precedes the evolution of the vertebral column (the alternative scheme) as is the case with lancelets. Recent DNA evidence has supported the original scheme. The original scheme groups hagfish and lampreys together as cyclostomata, cyclostomes ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autotomy
Autotomy (from the Greek ''auto-'', "self-" and ''tome'', "severing", αὐτοτομία) or self-amputation, is the behaviour whereby an animal sheds or discards one or more of its own appendages, usually as a self-defense mechanism to elude a predator's grasp or to distract the predator and thereby allow escape. Some animals have the ability to regenerate the lost body part later. Autotomy has multiple evolutionary origins and is thought to have evolved at least nine times independently in animalia. The term was coined in 1883 by Leon Fredericq. Vertebrates Reptiles and amphibians Some lizards, salamanders and tuatara when caught by the tail will shed part of it in attempting to escape. In many species the detached tail will continue to wriggle, creating a deceptive sense of continued struggle, and distracting the predator's attention from the fleeing prey animal. In addition, many species of lizards such as '' Plestiodon fasciatus'', '' Cordylosaurus subtessellatus'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Countershading
Countershading, or Thayer's law, is a method of camouflage in which an animal's coloration is darker on the top or upper side and lighter on the underside of the body. This pattern is found in many species of mammals, reptiles, birds, fish, and insects, both in predators and in prey. When light falls from above on a uniformly coloured three-dimensional object such as a sphere, it makes the upper side appear lighter and the underside darker, grading from one to the other. This pattern of light and shade makes the object appear solid, and therefore easier to detect. The classical form of countershading, discovered in 1909 by the artist Abbott Handerson Thayer, works by counterbalancing the effects of self-shadowing, again typically with grading from dark to light. In theory this could be useful for military camouflage, but in practice it has rarely been applied, despite the best efforts of Thayer and, later, in the Second World War, of the zoologist Hugh Cott. The precise fun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disruptive Coloration
Disruptive coloration (also known as disruptive camouflage or disruptive patterning) is a form of camouflage that works by breaking up the outlines of an animal, soldier or military vehicle with a strongly contrasting pattern. It is often combined with other methods of crypsis including background colour matching and countershading; special cases are coincident disruptive coloration and the disruptive eye mask seen in some fishes, amphibians, and reptiles. It appears paradoxical as a way of not being seen, since disruption of outlines depends on high contrast, so the patches of colour are themselves conspicuous. The importance of high-contrast patterns for successful disruption was predicted in general terms by the artist Abbott Thayer in 1909 and explicitly by the zoologist Hugh Cott in 1940. Later experimental research has started to confirm these predictions. Disruptive patterns work best when all their components match the background. While background matching works b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camouflage
Camouflage is the use of any combination of materials, coloration, or illumination for concealment, either by making animals or objects hard to see, or by disguising them as something else. Examples include the leopard's spotted coat, the battledress of a modern soldier, and the leaf-mimic katydid's wings. A third approach, motion dazzle, confuses the observer with a conspicuous pattern, making the object visible but momentarily harder to locate, as well as making general aiming easier. The majority of camouflage methods aim for crypsis, often through a general resemblance to the background, high contrast disruptive coloration, eliminating shadow, and countershading. In the open ocean, where there is no background, the principal methods of camouflage are transparency, silvering, and countershading, while the bioluminescence, ability to produce light is among other things used for counter-illumination on the undersides of cephalopods such as squid. Some animals, such as chamel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phrynosoma Mcallii
The flat-tail horned lizard (''Phrynosoma mcallii'' ) is a species of lizard in the family Phrynosomatidae. A species of reptile, it is endemic to the Sonoran desert of the southwestern United States and northwestern Mexico. Its multiple adaptations for camouflage help to minimize its shadow. The species is threatened, with a restricted range under pressure from human activities such as agriculture and development, and is specially protected in the United States. Description and geographic range The flat-tail horned lizard is named for United States Army Colonel George A. M'Call,Beolens, Bo; Watkins, Michael; Grayson, Michael (2011). ''The Eponym Dictionary of Reptiles''. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press. xiii + 296 pp. . (''Phrynosoma mcallii'', p. 172). who collected the first specimen in California in the 19th century. The species occupies a small range in the Sonoran Desert of southeastern California, southwestern Arizona, and extreme northern Mexico in the Baja Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kangaroo Rat
Kangaroo rats, small mostly nocturnal rodents of genus ''Dipodomys'', are native to arid areas of western North America. The common name derives from their bipedal form. They hop in a manner similar to the much larger kangaroo, but developed this mode of locomotion independently, like several other clades of rodents (e.g. dipodids and hopping mice). Description Kangaroo rats are four or five-toed heteromyid rodents with big hind legs, small front legs, and relatively large heads. Adults typically weigh between Nader, I.A. 1978"Kangaroo rats: Intraspecific Variation in ''Dipodomus spectabilis'' Merriami and ''Dipodomys deserti'' Stephens" ''Illinois biological monographs''; 49: 1-116. Chicago, University of Illinois Press. The tails of kangaroo rats are longer than both their bodies and their heads. Another notable feature of kangaroo rats is their fur-lined cheek pouches, which are used for storing food. The coloration of kangaroo rats varies from cinnamon buff to dark gray, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bat Falcon
The bat falcon (''Falco rufigularis'') is a falcon that is a resident breeder in tropical Mexico, Central and South America, Trinidad. It was long known as ''Falco albigularis''; the names ''Falco fusco-coerulescens'' or ''Falco fuscocaerulescens'', long used for the aplomado falcon, are now believed to refer to the present species. It is probably closely related to and looks like a small version of the orange-breasted falcon with which it has been misidentified. These two, in turn, are probably closest to the aplomado falcon and constitute a rather old American lineage of ''Falco'' species. The female bat falcon, at 30.5 cm length, is much larger than the 23-cm-long male. Adults have a black back, head, and tail. The throat, upper breast, and neck sides are creamy white, the lower breast and belly are black, finely barred white, and the thighs and lower belly are orange. Young birds are similar, but with a buffy throat. The call of this species is a high pitched ''ke-ke- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bat Hawk
The bat hawk (''Macheiramphus alcinus'') is a raptor found in sub-Saharan Africa and south Asia to New Guinea. It is named for its diet, which consists mainly of bats. It requires open space in which to hunt, but will live anywhere from dense rainforest to semi-arid veld. Description The bat hawk is a slender, medium-sized bird of prey, usually about 45 cm long. It has long wings and a falcon-like silhouette while in flight. Adults are dark brown or black, with a white patch on the throat and chest, and have a white streak above and below each eye. Juveniles are mottled brown and have more white plumage than adults. Behaviour Hunting Bats are the usual prey of the bat hawk, although they may eat small birds, such as swallows, swifts, and nightjars, or even insects. They hunt by chasing their prey at high speeds in flight. 49.3% of their hunts are successful. Bats are captured by the use of small talons, and swallowed whole immediately in flight. Hunting methods may be si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bats
Bats are mammals of the order Chiroptera.''cheir'', "hand" and πτερόν''pteron'', "wing". With their forelimbs adapted as wings, they are the only mammals capable of true and sustained flight. Bats are more agile in flight than most birds, flying with their very long spread-out digits covered with a thin membrane or patagium. The smallest bat, and arguably the smallest extant mammal, is Kitti's hog-nosed bat, which is in length, across the wings and in mass. The largest bats are the flying foxes, with the giant golden-crowned flying fox, ''Acerodon jubatus'', reaching a weight of and having a wingspan of . The second largest order of mammals after rodents, bats comprise about 20% of all classified mammal species worldwide, with over 1,400 species. These were traditionally divided into two suborders: the largely fruit-eating megabats, and the echolocating microbats. But more recent evidence has supported dividing the order into Yinpterochiroptera and Yangochiropt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crypsis
In ecology, crypsis is the ability of an animal or a plant to avoid observation or detection by other animals. It may be a predation strategy or an antipredator adaptation. Methods include camouflage, nocturnality, subterranean lifestyle and mimicry. Crypsis can involve visual, olfactory (with pheromones) or auditory concealment. When it is visual, the term cryptic coloration, effectively a synonym for animal camouflage, is sometimes used, but many different methods of camouflage are employed by animals or plants. Overview There is a strong evolutionary pressure for animals to blend into their environment or conceal their shape, for prey animals to avoid predators and for predators to be able to avoid detection by prey. Exceptions include large herbivores without natural enemies, brilliantly colored birds that rely on flight to escape predators, and venomous or otherwise powerfully armed animals with warning coloration. Cryptic animals include the tawny frogmouth (feat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nocturnality
Nocturnality is an animal behavior characterized by being active during the night and sleeping during the day. The common adjective is "nocturnal", versus diurnal meaning the opposite. Nocturnal creatures generally have highly developed senses of hearing, smell, and specially adapted eyesight. Some animals, such as cats and ferrets, have eyes that can adapt to both low-level and bright day levels of illumination (see metaturnal). Others, such as bushbabies and (some) bats, can function only at night. Many nocturnal creatures including tarsiers and some owls have large eyes in comparison with their body size to compensate for the lower light levels at night. More specifically, they have been found to have a larger cornea relative to their eye size than diurnal creatures to increase their : in the low-light conditions. Nocturnality helps wasps, such as '' Apoica flavissima'', avoid hunting in intense sunlight. Diurnal animals, including squirrels and songbirds, are ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |