|
Potapovka Culture
Potapovka culture (russian: Потаповская культура, Potapovskaya kul'tura) was a Bronze Age culture which flourished on the middle Volga in 2100—1800 BC. The Potapovka culture emerged out of the Poltavka culture with influences from the Abashevo culture. It had close relations with the Sintashta culture in the east, with whom it shares many similarities. Like the Sintashta culture, its people are believed to have spoken a form of Proto-Indo-Iranian. It was directly ancestral to the Srubnaya culture, and probably influenced the emergence of the Andronovo culture. Chronology The Potapovka culture emerged on the middle Volga around 2100 BC. It came to flourish around the middle Volga, the southwest Urals and western Kazakhstan. Potapovka sites are eventually found also on the Don and the Dnieper. The Potapovka culture has been considered a western variant of the Sintashta culture, with which it is closely related. The Potapovka culture is thought to have e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volga
The Volga (; russian: Во́лга, a=Ru-Волга.ogg, p=ˈvoɫɡə) is the List of rivers of Europe#Rivers of Europe by length, longest river in Europe. Situated in Russia, it flows through Central Russia to Southern Russia and into the Caspian Sea. The Volga has a length of , and a catchment area of «Река Волга» , Russian State Water Registry which is more than twice the size of Ukraine. It is also Europe's largest river in terms of average discharge (hydrology), discharge at delta – between and – and of drainage basin. It is widely regarded as the Rivers in Russia, national river of Russia. The hypothetical old Russian state, the Rus' Khaganate, arose along the Volga . Historically, the river served as an important meeting place of various Eurasian civilizations. The river flows in Russia through forests, Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horse Burial
Horse burial is the practice of burying a horse as part of the ritual of human burial, and is found among many Indo-European speaking peoples and others, including Chinese and Turkic peoples. The act indicates the high value placed on horses in the particular cultures and provides evidence of the migration of peoples with a horse culture. Human burials that contain other livestock are rare; in Britain, for example, 31 horse burials have been discovered but only one cow burial, unique in Europe. This process of horse burial is part of a wider tradition of horse sacrifice. An associated ritual is that of chariot burial, in which an entire chariot, with or without a horse, is buried with a dead person. Background and detail The horse carries great symbolic meaning in human cultures (see horse worship). In Celtic and Germanic cultures, for instance, the horse "could be associated with the journeying sun", and horses were deified and used in divination, but Celtic horse sacrifice i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nature (journal)
''Nature'' is a British weekly scientific journal founded and based in London, England. As a multidisciplinary publication, ''Nature'' features peer-reviewed research from a variety of academic disciplines, mainly in science and technology. It has core editorial offices across the United States, continental Europe, and Asia under the international scientific publishing company Springer Nature. ''Nature'' was one of the world's most cited scientific journals by the Science Edition of the 2019 ''Journal Citation Reports'' (with an ascribed impact factor of 42.778), making it one of the world's most-read and most prestigious academic journals. , it claimed an online readership of about three million unique readers per month. Founded in autumn 1869, ''Nature'' was first circulated by Norman Lockyer and Alexander Macmillan as a public forum for scientific innovations. The mid-20th century facilitated an editorial expansion for the journal; ''Nature'' redoubled its efforts in exp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
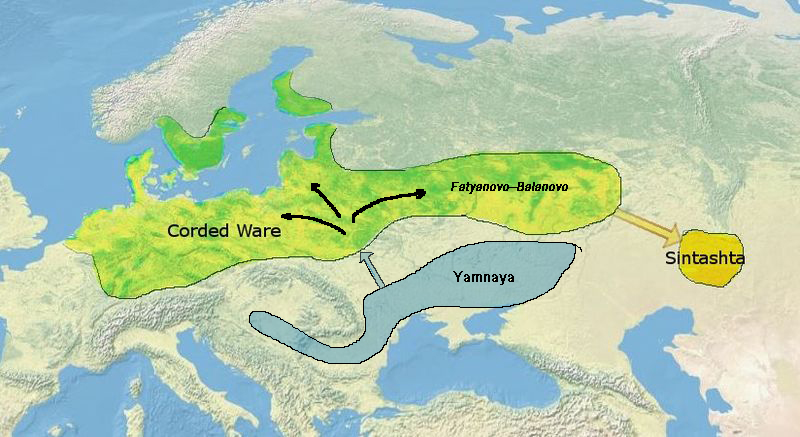
Yamnaya Culture
The Yamnaya culture or the Yamna culture (russian: Ямная культура, ua, Ямна культура literal translation, lit. 'culture of pits'), also known as the Pit Grave culture or Ochre Grave culture, was a late Copper Age to early Bronze Age archaeological culture of the region between the Southern Bug, Dniester, and Ural (river), Ural rivers (the Pontic steppe), dating to 3300–2600 BCE. It was discovered by Vasily Gorodtsov following his archaelogical excavations near Siversky Donets in 1901—1903. Its name derives from its characteristic burial tradition: (romanized, romanization: ) is a Russian adjective that means 'related to pits ()', as these people used to bury their dead in tumuli (kurgans) containing simple pit chambers. The people of the Yamnaya culture were likely the result of a genetic admixture between the descendants of Eastern European Hunter-Gatherers (EHG)The Eastern European hunter-gatherers were themselves mostly descended from ancie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatyanovo–Balanovo Culture
The Fatyanovo–Balanovo culture (russian: Фатьяновская культура, Fatyanovskaya kul'tura) was a Chalcolithic and early Bronze Age culture within the wider Corded Ware complex which flourished in the forests of Russia from c. 2900 to 2050 BC. The Fatyanovo culture developed on the northeastern edge of the Middle Dnieper culture around 2900 BC, probably as a result of a mass migration of Corded Ware peoples from Central Europe. Expanding eastwards at the expense of the Volosovo culture, the Fatyanovo people developed copper mines in the western Urals. From 2300 BC they established settlements engaged in Bronze metallurgy, giving rise to the Balanovo culture. Although belonging to the southeastern part of the Fatyanovo horizon, the Balanovo culture is quite distinct from the rest. The Balanovo culture contributed to the formation of the Abashevo culture, which in turn contributed to the formation of the Sintashta culture. The Fatyanovo-Balanovo culture ended ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dolichocephaly
Dolichocephaly (derived from the Ancient Greek δολιχός 'long' and κεφαλή 'head') is a condition where the head is longer than would be expected, relative to its width. In humans, scaphocephaly is a form of dolichocephaly. Dolichocephalic dogs (such as German Shepherds) have elongated noses. This makes them vulnerable to fungal diseases of the nose such as aspergillosis. In humans the anterior–posterior diameter (length) of dolichocephaly head is more than the transverse diameter (width). It can be present in cases of Sensenbrenner syndrome, Crouzon syndrome, Sotos syndrome, CMFTD as well as Marfan syndrome. See also * Brachycephaly * Cephalic index * Plagiocephaly Plagiocephaly, also known as flat head syndrome, is a condition characterized by an asymmetrical distortion (flattening of one side) of the skull. A mild and widespread form is characterized by a flat spot on the back or one side of the head cause ... References External links Congenital di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Europoids
The Caucasian race (also Caucasoid or Europid, Europoid) is an obsolete racial classification of human beings based on a now-disproven theory of biological race. The ''Caucasian race'' was historically regarded as a biological taxon which, depending on which of the historical race classifications was being used, usually included ancient and modern populations from all or parts of Europe, Western Asia, Central Asia, South Asia, North Africa, and the Horn of Africa. First introduced in the 1780s by members of the Göttingen school of history, the term denoted one of three purported major races of humankind (those three being Caucasoid, Mongoloid, and Negroid). In biological anthropology, ''Caucasoid'' has been used as an umbrella term for phenotypically similar groups from these different regions, with a focus on skeletal anatomy, and especially cranial morphology, without regard to skin tone. Ancient and modern "Caucasoid" populations were thus not exclusively "white", but ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avesta
The Avesta () is the primary collection of religious texts of Zoroastrianism, composed in the Avestan language. The Avesta texts fall into several different categories, arranged either by dialect, or by usage. The principal text in the liturgical group is the ''Yasna'', which takes its name from the Yasna ceremony, Zoroastrianism's primary act of worship, and at which the ''Yasna'' text is recited. The most important portion of the ''Yasna'' texts are the five Gathas, consisting of seventeen hymns attributed to Zoroaster himself. These hymns, together with five other short Old Avestan texts that are also part of the ''Yasna'', are in the Old (or 'Gathic') Avestan language. The remainder of the ''Yasna'''s texts are in Younger Avestan, which is not only from a later stage of the language, but also from a different geographic region. Extensions to the Yasna ceremony include the texts of the ''Vendidad'' and the ''Visperad''. The ''Visperad'' extensions consist mainly of addit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vedas
upright=1.2, The Vedas are ancient Sanskrit texts of Hinduism. Above: A page from the '' Atharvaveda''. The Vedas (, , ) are a large body of religious texts originating in ancient India. Composed in Vedic Sanskrit, the texts constitute the oldest layer of Sanskrit literature and the oldest scriptures of Hinduism. There are four Vedas: the Rigveda, the Yajurveda, the Samaveda and the Atharvaveda. Each Veda has four subdivisions – the Samhitas (mantras and benedictions), the Aranyakas (text on rituals, ceremonies, sacrifices and symbolic-sacrifices), the Brahmanas (commentaries on rituals, ceremonies and sacrifices), and the Upanishads (texts discussing meditation, philosophy and spiritual knowledge).Gavin Flood (1996), ''An Introduction to Hinduism'', Cambridge University Press, , pp. 35–39A Bhattacharya (2006), ''Hindu Dharma: Introduction to Scriptures and Theology'', , pp. 8–14; George M. Williams (2003), Handbook of Hindu Mythology, Oxford University Press, , p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spoked Wheel
A spoke is one of some number of rods radiating from the center of a wheel (the Bicycle hub, hub where the axle connects), connecting the hub with the round traction surface. The term originally referred to portions of a log that had been riving, riven (split lengthwise) into four or six sections. The radial members of a wagon wheel were made by carving a spoke (from a log) into their finished shape. A spokeshave is a tool originally developed for this purpose. Eventually, the term spoke was more commonly applied to the finished product of the wheelwright's work, than to the materials they used. History The spoked wheel was invented to allow the construction of lighter and swifter vehicles. Earliest physical evidence for spoked wheels were found in Sintashta culture, dating to 2000 BC. Soon after this, horse cultures of the Caucasus region used horse-drawn spoked-wheel war chariots for the greater part of three centuries. They moved deep into the Greek peninsula where they j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atharvan
Atharvan ( '; an ''n''-stem with nominative singular ') is a legendary Vedic sage (rishi) of Hinduism, who along with Angiras, is supposed to have authored (" heard") the Atharvaveda. He is also said to have first instituted the fire-sacrifice or yagna. Sometimes he is also reckoned among the seven seers, the Saptarishi. His clan is known as the Atharvanas. Atharvan married Shanti, daughter of Sage Kardama, and had a great sage Dadhichi as a son. He is referred to as a member of the Bhrigu clan. According to the Mundaka Upanishad and other texts, he was the eldest son and ( Manasaputra) born from mind of the creator deity, Brahma. Etymology Vedic ''atharvan'' is cognate with Avestan ''āθrauuan'' / ''aθaurun'', "priest", but the etymology of the term is not yet conclusively established. It was once thought to be etymologically related to the Avestan '' ātar'', but that is now considered unlikely (Boyce, 2002:16). It has been suggested by scholars that the Vedic and Aves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dadhichi
Dadhichi (), also rendered Dadhyanga and Dadhyancha, is a sage in Hinduism. He is best known for his sacrifice in the Puranas, where he gives up his life so that his bones could be used to manufacture the Vajra, the diamond-like celestial thunderbolt of the deity Indra, in order to slay Vritra. Literature In the Bhagavata Purana, Dadhichi is described as the son of the sage Atharvan and his wife, Chitti. Atharvan is said to be the author of Atharvaveda, which is one of the four Vedas. Chitti was the daughter of the sage Kardama. The names of Dadhichi's wife and son were Suvarcas and Pippalada, respectively. After the death of Dadhichi, when Suvarcas was about to ascend the funeral pyre, she heard an ''aśarīriṇī vāṇī'' (a celestial voice) that informed her that she was pregnant. Suvarcas removed the foetus from her womb with a stone, and placed it near a banyan tree, proceeding to end her life. Her child, Pippalada, became a famous rishi, associated with the Pippal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |