|
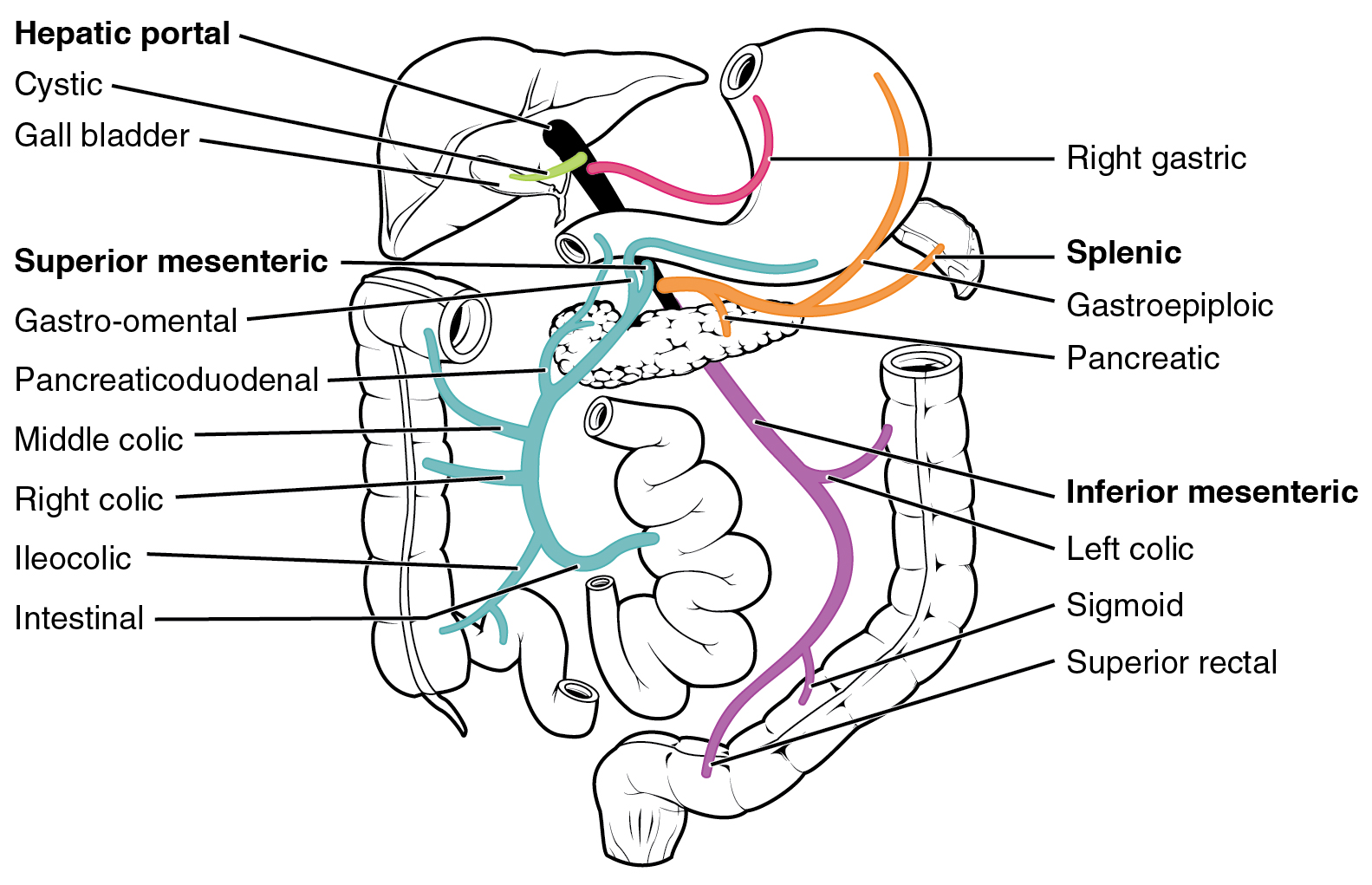
Portosystemic Shunt
A portosystemic shunt or portasystemic shunt (medical subject heading term; PSS), also known as a liver shunt, is a bypass of the liver by the body's circulatory system. It can be either a congenital (present at birth) or acquired condition and occurs in humans as well as in other species of animals. Congenital PSS are extremely rare in humans but are relatively common in dogs. Thus a large part of medical and scientific literature on the subject is grounded in veterinary medicine. Background Blood leaving the digestive tract is rich in nutrients, as well as in toxins, which under normal conditions undergo processing and detoxification in the liver. The liver's position downstream to the intestines in the body's circulatory system - the hepatic portal vein conveys blood from the intestines to the liver - allows it to filter this nutrient rich blood before it passes to the rest of the body. The presence of a shunt, a bypass of the liver, causes blood to flow directly to the hear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liver
The liver is a major Organ (anatomy), organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it is located in the quadrant (anatomy), right upper quadrant of the abdomen, below the thoracic diaphragm, diaphragm. Its other roles in metabolism include the regulation of Glycogen, glycogen storage, decomposition of red blood cells, and the production of hormones. The liver is an accessory digestive organ that produces bile, an alkaline fluid containing cholesterol and bile acids, which helps the fatty acid degradation, breakdown of fat. The gallbladder, a small pouch that sits just under the liver, stores bile produced by the liver which is later moved to the small intestine to complete digestion. The liver's highly specialized biological tissue, tissue, consisting mostly of hepatocytes, regulates a w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatic Veins
In human anatomy, the hepatic veins are the veins that drain venous blood from the liver into the inferior vena cava (as opposed to the hepatic portal vein which conveys blood from the gastrointestinal organs to the liver). There are usually three large upper hepatic veins draining from the left, middle, and right parts of the liver, as well as a number (6-20) of lower hepatic veins. All hepatic veins are valveless. Structure All the hepatic veins drain into the inferior vena cava. The hepatic veins are divided into an upper and a lower group. Upper group The upper group consists of three hepatic veins - the right, middle, and left hepatic veins - draining the central veins from the right, middle, and left regions of the liver and are larger than the lower group of veins. The veins of the upper group drain into the suprahepatic part of the inferior vena cava (i.e. part superior to the liver). Right hepatic vein The right hepatic vein is the longest and largest of all the h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatic Encephalopathy
Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) is an altered level of consciousness as a result of liver failure. Its onset may be gradual or sudden. Other symptoms may include movement problems, changes in mood, or changes in personality. In the advanced stages it can result in a coma. Hepatic encephalopathy can occur in those with acute or chronic liver disease. Episodes can be triggered by infections, GI bleeding, constipation, electrolyte problems, or certain medications. The underlying mechanism is believed to involve the buildup of ammonia in the blood, a substance that is normally removed by the liver. The diagnosis is typically based on symptoms after ruling out other potential causes. It may be supported by blood ammonia levels, an electroencephalogram, or a CT scan of the brain. Hepatic encephalopathy is possibly reversible with treatment. This typically involves supportive care and addressing the triggers of the event. Lactulose is frequently used to decrease ammonia levels. Cert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encephalopathy
Encephalopathy (; from grc, ἐνκέφαλος "brain" + πάθος "suffering") means any disorder or disease of the brain, especially chronic degenerative conditions. In modern usage, encephalopathy does not refer to a single disease, but rather to a syndrome of overall brain dysfunction; this syndrome has many possible organic and inorganic causes. Signs and symptoms The hallmark of encephalopathy is an altered mental state or delirium. Characteristic of the altered mental state is impairment of the cognition, attention, orientation, sleep–wake cycle and consciousness. An altered state of consciousness may range from failure of selective attention to drowsiness. Hypervigilance may be present; with or without: cognitive deficits, headache, epileptic seizures, myoclonus (involuntary twitching of a muscle or group of muscles) or asterixis ("flapping tremor" of the hand when wrist is extended). Depending on the type and severity of encephalopathy, common neurological sym ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatopulmonary Syndrome
In medicine, hepatopulmonary syndrome is a syndrome of shortness of breath and hypoxemia (low oxygen levels in the blood of the arteries) caused by vasodilation (broadening of the blood vessels) in the lungs of patients with liver disease. Dyspnea and hypoxemia are worse in the upright position (which is called platypnea and orthodeoxia, respectively). Pathophysiology The hepatopulmonary syndrome results from the formation of microscopic intrapulmonary arteriovenous dilatations in patients with both chronic and far less common, acute liver failure. The mechanism is unknown but is thought to be due to increased liver production or decreased liver clearance of vasodilators, possibly involving nitric oxide. The dilation of these blood vessels causes overperfusion relative to ventilation, leading to ventilation-perfusion mismatch and hypoxemia. There is an increased gradient between the partial pressure of oxygen in the alveoli of the lung and adjacent arteries (alveolar-arterial -a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cholestasis
Cholestasis is a condition where bile cannot flow from the liver to the duodenum. The two basic distinctions are an obstructive type of cholestasis where there is a mechanical blockage in the duct system that can occur from a gallstone or malignancy, and metabolic types of cholestasis which are disturbances in bile formation that can occur because of genetic defects or acquired as a side effect of many medications. Classification is further divided into acute or chronic and extrahepatic or intrahepatic. Signs and symptoms The signs and symptoms of cholestasis vary according to the cause. In case of sudden onset, the disease is likely to be acute, while the gradual appearance of symptoms suggests chronic pathology. In many cases, patients may experience pain in the abdominal area. Localization of pain to the upper right quadrant can be indicative of cholecystitis or choledocholithiasis, which can progress to cholestasis. Pruritus or itching is often present in many patients with c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Pass Effect
The first pass effect (also known as first-pass metabolism or presystemic metabolism) is a phenomenon of drug metabolism whereby the concentration of a drug, specifically when administered orally, is greatly reduced before it reaches the systemic circulation. It is the fraction of drug lost during the process of absorption which is generally related to the liver and gut wall. Notable drugs that experience a significant first-pass effect are buprenorphine, chlorpromazine, cimetidine, diazepam, ethanol (drinking alcohol), imipramine, insulin, lidocaine, midazolam, morphine, pethidine, propranolol, and tetrahydrocannabinol (THC). First pass metabolism may occur in the liver (for propranolol, lidocaine, clomethiazole, and NTG) or in the gut (for benzylpenicillin and insulin). After a drug is swallowed, it is absorbed by the digestive system and enters the hepatic portal system. It is carried through the portal vein into the liver before it reaches the rest of the body. The liver met ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heart
The heart is a muscular organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide to the lungs. In humans, the heart is approximately the size of a closed fist and is located between the lungs, in the middle compartment of the chest. In humans, other mammals, and birds, the heart is divided into four chambers: upper left and right atria and lower left and right ventricles. Commonly the right atrium and ventricle are referred together as the right heart and their left counterparts as the left heart. Fish, in contrast, have two chambers, an atrium and a ventricle, while most reptiles have three chambers. In a healthy heart blood flows one way through the heart due to heart valves, which prevent backflow. The heart is enclosed in a protective sac, the pericardium, which also contains a small amount of fluid. The wall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venae Cavae
In anatomy, the venae cavae (; singular: vena cava ; ) are two large veins (great vessels) that return deoxygenated blood from the body into the heart. In humans they are the superior vena cava and the inferior vena cava, and both empty into the right atrium. They are located slightly off-center, toward the right side of the body. The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood through coronary sinus and two large veins called venae cavae. The inferior vena cava (or caudal vena cava in some animals) travels up alongside the abdominal aorta with blood from the lower part of the body. It is the largest vein in the human body. MadSci Network: Anatomy. Retrieved 19 September 2013. The superior vena cava (or cranial vena cava in animals) is above the heart, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capillary
A capillary is a small blood vessel from 5 to 10 micrometres (μm) in diameter. Capillaries are composed of only the tunica intima, consisting of a thin wall of simple squamous endothelial cells. They are the smallest blood vessels in the body: they convey blood between the arterioles and venules. These microvessels are the site of exchange of many substances with the interstitial fluid surrounding them. Substances which cross capillaries include water, oxygen, carbon dioxide, urea, glucose, uric acid, lactic acid and creatinine. Lymph capillaries connect with larger lymph vessels to drain lymphatic fluid collected in the microcirculation. During early embryonic development, new capillaries are formed through vasculogenesis, the process of blood vessel formation that occurs through a '' de novo'' production of endothelial cells that then form vascular tubes. The term '' angiogenesis'' denotes the formation of new capillaries from pre-existing blood vessels and already present ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intestines
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans and other animals, including the esophagus, stomach, and intestines. Food taken in through the mouth is digested to extract nutrients and absorb energy, and the waste expelled at the anus as feces. ''Gastrointestinal'' is an adjective meaning of or pertaining to the stomach and intestines. Most animals have a "through-gut" or complete digestive tract. Exceptions are more primitive ones: sponges have small pores ( ostia) throughout their body for digestion and a larger dorsal pore (osculum) for excretion, comb jellies have both a ventral mouth and dorsal anal pores, while cnidarians and acoels have a single pore for both digestion and excretion. The human gastrointestinal tract consists of the esophagus, stomach, and intestines, and is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |