|
Porfimer Sodium
Porfimer sodium, sold as Photofrin, is a photosensitizer used in photodynamic therapy and radiation therapy and for palliative treatment of obstructing endobronchial non-small cell lung carcinoma and obstructing esophageal cancer. Porfimer is a mixture of oligomers formed by ether and ester linkages of up to eight porphyrin units. In practice, a red light source emitting at 630 nm is used to excite the Porfimer oligomers. Porfimer is Haematoporphyrin Derivative (HpD) (See PDT). Approvals and indications It was approved in Canada in 1993 for the treatment of bladder cancer. It was approved in Japan in 1994 (for early stage lung cancer?). It was approved by the U.S. FDA in December 1995 for esophageal cancer, and in 1998, it was approved for the treatment of early non-small cell lung cancer. In August 2003 the FDA approved its use for Barrett's esophagus Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which there is an abnormal (metaplastic) change in the mucosal cells lining the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intravenous Therapy
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutrients for those who cannot, or will not—due to reduced mental states or otherwise—consume food or water by mouth. It may also be used to administer medications or other medical therapy such as blood products or electrolytes to correct electrolyte imbalances. Attempts at providing intravenous therapy have been recorded as early as the 1400s, but the practice did not become widespread until the 1900s after the development of techniques for safe, effective use. The intravenous route is the fastest way to deliver medications and fluid replacement throughout the body as they are introduced directly into the circulatory system and thus quickly distributed. For this reason, the intravenous route of administration is also used for the consump ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photosensitizer
Photosensitizers produce a physicochemical change in a neighboring molecule by either donating an electron to the substrate or by abstracting a hydrogen atom from the substrate. At the end of this process, the photosensitizer eventually returns to its ground state, where it remains chemically intact until the photosensitizer absorbs more light. This means that the photosensitizer remains unchanged before and after the energetic exchange, much like heterogeneous photocatalysis. One branch of chemistry which frequently utilizes photosensitizers is polymer chemistry, using photosensitizers in reactions such as photopolymerization, photocrosslinking, and photodegradation. Photosensitizers are also used to generate prolonged excited electronic states in organic molecules with uses in photocatalysis, photon upconversion and photodynamic therapy. Generally, photosensitizers absorb electromagnetic radiation consisting of infrared radiation, visible light radiation, and ultraviolet radiati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photodynamic Therapy
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is a form of phototherapy involving light and a photosensitizing chemical substance, used in conjunction with molecular oxygen to elicit cell death (phototoxicity). PDT is popularly used in treating acne. It is used clinically to treat a wide range of medical conditions, including wet age-related macular degeneration, psoriasis, atherosclerosis and has shown some efficacy in anti-viral treatments, including herpes. It also treats malignant cancers including head and neck, lung, bladder and particular skin. The technology has also been tested for treatment of prostate cancer, both in a dog model and in human prostate cancer patients. It is recognised as a treatment strategy that is both minimally invasive and minimally toxic. Other light-based and laser therapies such as laser wound healing and rejuvenation, or intense pulsed light hair removal do not require a photosensitizer. Photosensitisers have been employed to sterilise blood plasma and wate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy, often abbreviated RT, RTx, or XRT, is a therapy using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of cancer treatment to control or kill malignant cells and normally delivered by a linear accelerator. Radiation therapy may be curative in a number of types of cancer if they are localized to one area of the body. It may also be used as part of adjuvant therapy, to prevent tumor recurrence after surgery to remove a primary malignant tumor (for example, early stages of breast cancer). Radiation therapy is synergistic with chemotherapy, and has been used before, during, and after chemotherapy in susceptible cancers. The subspecialty of oncology concerned with radiotherapy is called radiation oncology. A physician who practices in this subspecialty is a radiation oncologist. Radiation therapy is commonly applied to the cancerous tumor because of its ability to control cell growth. Ionizing radiation works by damaging the DNA of cancerous tissue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palliative Care
Palliative care (derived from the Latin root , or 'to cloak') is an interdisciplinary medical caregiving approach aimed at optimizing quality of life and mitigating suffering among people with serious, complex, and often terminal illnesses. Within the published literature, many definitions of palliative care exist. The World Health Organization (WHO) describes palliative care as "an approach that improves the quality of life of patients and their families facing the problems associated with life-threatening illness, through the prevention and relief of suffering by means of early identification and impeccable assessment and treatment of pain and other problems, physical, psychosocial, and spiritual." In the past, palliative care was a disease specific approach, but today the WHO takes a more broad approach, that the principles of palliative care should be applied as early as possible to any chronic and ultimately fatal illness. Palliative care is appropriate for individuals with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-small Cell Lung Carcinoma
Non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is any type of epithelial lung cancer other than small-cell lung carcinoma (SCLC). NSCLC accounts for about 85% of all lung cancers. As a class, NSCLCs are relatively insensitive to chemotherapy, compared to small-cell carcinoma. When possible, they are primarily treated by surgical resection with curative intent, although chemotherapy has been used increasingly both preoperatively (neoadjuvant chemotherapy) and postoperatively (adjuvant chemotherapy). Types The most common types of NSCLC are squamous-cell carcinoma, large-cell carcinoma, and adenocarcinoma, but several other types occur less frequently. A few of the less common types are pleomorphic, carcinoid tumor, salivary gland carcinoma, and unclassified carcinoma. All types can occur in unusual histologic variants and as mixed cell-type combinations. Nonsquamous-cell carcinoma almost occupies the half of NSCLC. In the tissue classification, the central type contains about one-ninth. Som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Esophageal Cancer
Esophageal cancer is cancer arising from the esophagus—the food pipe that runs between the throat and the stomach. Symptoms often include difficulty in swallowing and weight loss. Other symptoms may include pain when swallowing, a hoarse voice, enlarged lymph nodes ("glands") around the collarbone, a dry cough, and possibly coughing up or vomiting blood. The two main sub-types of the disease are esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma (often abbreviated to ESCC), which is more common in the developing world, and esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC), which is more common in the developed world. A number of less common types also occur. Squamous-cell carcinoma arises from the epithelial cells that line the esophagus. Adenocarcinoma arises from glandular cells present in the lower third of the esophagus, often where they have already transformed to intestinal cell type (a condition known as Barrett's esophagus). Causes of the squamous-cell type include tobacco, alcohol, very hot drinks, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oligomers
In chemistry and biochemistry, an oligomer () is a molecule that consists of a few repeating units which could be derived, actually or conceptually, from smaller molecules, monomers.Quote: ''Oligomer molecule: A molecule of intermediate relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises a small plurality of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of lower relative molecular mass.'' The name is composed of Greek elements '' oligo-'', "a few" and '' -mer'', "parts". An adjective form is ''oligomeric''. The oligomer concept is contrasted to that of a polymer, which is usually understood to have a large number of units, possibly thousands or millions. However, there is no sharp distinction between these two concepts. One proposed criterion is whether the molecule's properties vary significantly with the removal of one or a few of the units. An oligomer with a specific number of units is referred to by the Greek prefix denoting that number, wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porphyrin
Porphyrins ( ) are a group of heterocyclic macrocycle organic compounds, composed of four modified pyrrole subunits interconnected at their α carbon atoms via methine bridges (=CH−). The parent of porphyrin is porphine, a rare chemical compound of exclusively theoretical interest. Substituted porphines are called porphyrins. With a total of 26 π-electrons, of which 18 π-electrons form a planar, continuous cycle, the porphyrin ring structure is often described as aromatic. One result of the large conjugated system is that porphyrins typically absorb strongly in the visible region of the electromagnetic spectrum, i.e. they are deeply colored. The name "porphyrin" derives from the Greek word πορφύρα (''porphyra''), meaning ''purple''. Complexes of porphyrins Concomitant with the displacement of two N-''H'' protons, porphyrins bind metal ions in the N4 "pocket". The metal ion usually has a charge of 2+ or 3+. A schematic equation for these syntheses is shown: :H2porp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haematoporphyrin
Hematoporphyrin (Photodyn, Sensibion) is a porphyrin prepared from hemin. It is a derivative of protoporphyrin IX, where the two vinyl groups have been hydrated (converted to alcohols). It is a deeply colored solid that is usually encountered as a solution. Its chemical structure was determined in 1900. It is used as a photosensitizer in photodynamic therapy. Acetylation of hematoporphyrin followed by hydrolysis of the product of that reaction affords a mixture called ''hematoporphyrin derivative'' (HPD), which is also used in photodynamic therapy. Hematoporphyrin has also been used as an antidepressant and antipsychotic Antipsychotics, also known as neuroleptics, are a class of Psychiatric medication, psychotropic medication primarily used to manage psychosis (including delusions, hallucinations, paranoia or disordered thought), principally in schizophrenia but ... since the 1920s. References Antidepressants Antipsychotics Hematology Tetrapyrroles {{ner ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photodynamic Therapy
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is a form of phototherapy involving light and a photosensitizing chemical substance, used in conjunction with molecular oxygen to elicit cell death (phototoxicity). PDT is popularly used in treating acne. It is used clinically to treat a wide range of medical conditions, including wet age-related macular degeneration, psoriasis, atherosclerosis and has shown some efficacy in anti-viral treatments, including herpes. It also treats malignant cancers including head and neck, lung, bladder and particular skin. The technology has also been tested for treatment of prostate cancer, both in a dog model and in human prostate cancer patients. It is recognised as a treatment strategy that is both minimally invasive and minimally toxic. Other light-based and laser therapies such as laser wound healing and rejuvenation, or intense pulsed light hair removal do not require a photosensitizer. Photosensitisers have been employed to sterilise blood plasma and wate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
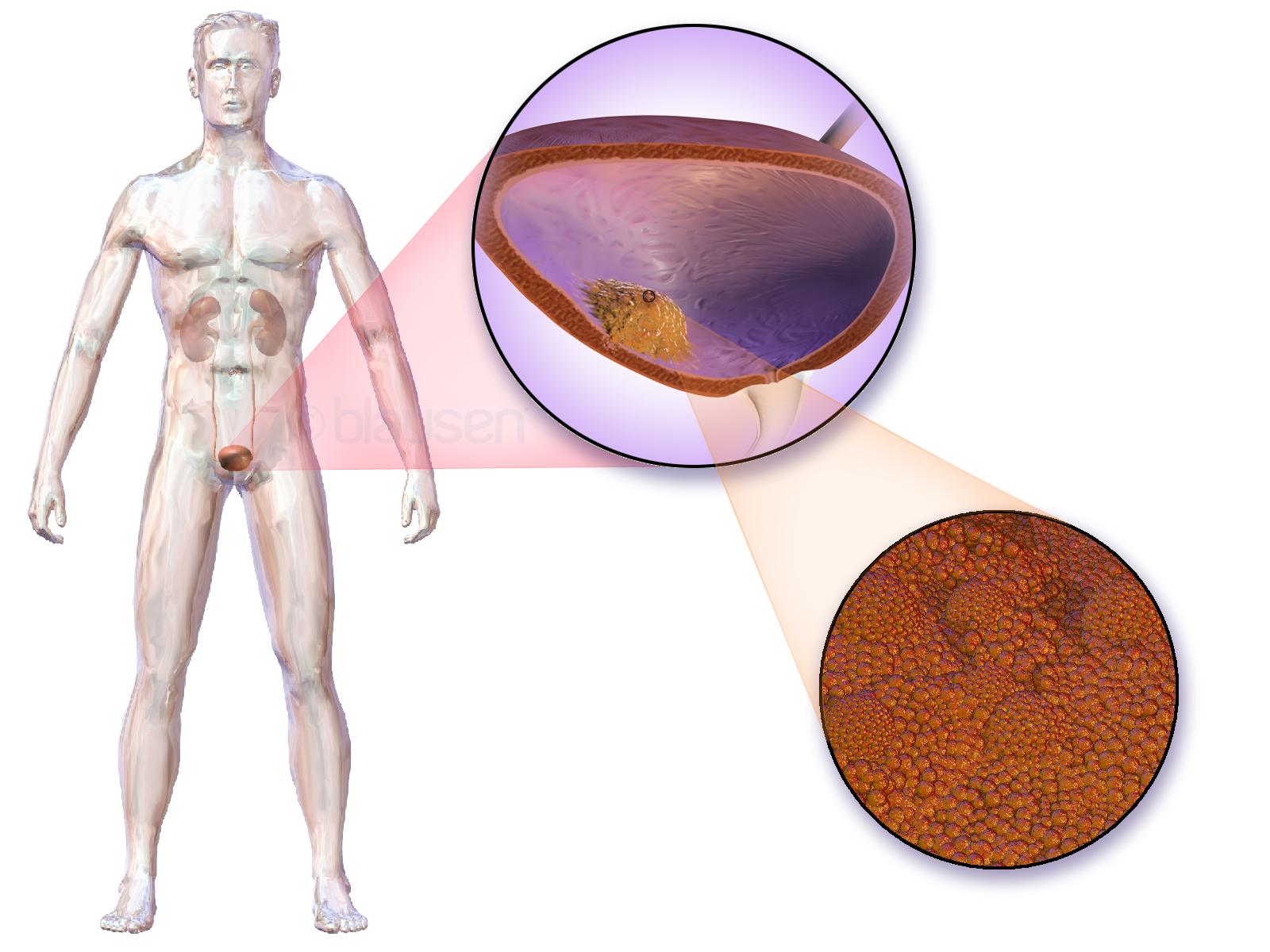
Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancer is any of several types of cancer arising from the tissues of the urinary bladder. Symptoms include blood in the urine, pain with urination, and low back pain. It is caused when epithelial cells that line the bladder become malignant. Risk factors for bladder cancer include smoking, family history, prior radiation therapy, frequent bladder infections, and exposure to certain chemicals. The most common type is transitional cell carcinoma. Other types include squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma. Diagnosis is typically by cystoscopy with tissue biopsies. Staging of the cancer is determined by transurethral resection and medical imaging. Treatment depends on the stage of the cancer. It may include some combination of surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or immunotherapy. Surgical options may include transurethral resection, partial or complete removal of the bladder, or urinary diversion. The typical five-year survival rates in the United States i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)