|
Pomeranians (Slavic Tribe)
The Pomeranians (german: Pomoranen; csb, Pòmòrzónie; pl, Pomorzanie), first mentioned as such in the 10th century, were a West Slavic tribe, which since the 5th to the 6th centuries had settled at the shore of the Baltic Sea between the mouths of the Oder and Vistula Rivers (the latter Farther Pomerania and Pomerelia). They spoke the Pomeranian language that belonged to the Lechitic languages, a branch of the West Slavic language family. The name ''Pomerania'' has its origin in the Old Polish ''po more'', which means "Land at the Sea". Prehistory Following the exit of the Hamburgian hunters, the area was inhabited successively by Celts and the Wielbark Culture (Germanic tribes similar to the Goths and the Rugians). Groups of Slavs populated the area as a result of the Slavic migration. The Pomeranian tribes formed around the 6th century. There was also a Pomeranian culture, which was replaced by the Jastorf culture. From around the 6th century, West Slavic tribes mig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Slavs 9th-10th C
West or Occident is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from east and is the direction in which the Sun sets on the Earth. Etymology The word "west" is a Germanic word passed into some Romance languages (''ouest'' in French, ''oest'' in Catalan, ''ovest'' in Italian, ''oeste'' in Spanish and Portuguese). As in other languages, the word formation stems from the fact that west is the direction of the setting sun in the evening: 'west' derives from the Indo-European root ''*wes'' reduced from ''*wes-pero'' 'evening, night', cognate with Ancient Greek ἕσπερος hesperos 'evening; evening star; western' and Latin vesper 'evening; west'. Examples of the same formation in other languages include Latin occidens 'west' from occidō 'to go down, to set' and Hebrew מַעֲרָב maarav 'west' from עֶרֶב erev 'evening'. Navigation To go west using a compass for navigation (in a place where magnetic north is the same dire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rugians
The Rugii, Rogi or Rugians ( grc, Ρογοί, Rogoi), were a Roman-era Germanic people. They were first clearly recorded by Tacitus, in his ''Germania'' who called them the ''Rugii'', and located them near the south shore of the Baltic Sea. Some centuries later, they were considered one of the "Gothic" or "Scythian" peoples who were located in the Middle Danube region. Like several other Gothic peoples there, they possibly arrived in the area as allies of Attila until his death in 453. They settled in what is now Lower Austria after the defeat of the Huns at Nedao in 454. The Baltic Rugii mentioned by Tacitus are possibly related to the people known as the ''Rutikleioi'', and the place known as Rougion, both mentioned in the second century by Ptolemy. Both these names are associated with the coastal island known today as Rügen. They have also been associated with the ''Ulmerugi'' mentioned in the sixth century by Jordanes, as people who had lived on the Baltic coast near the V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
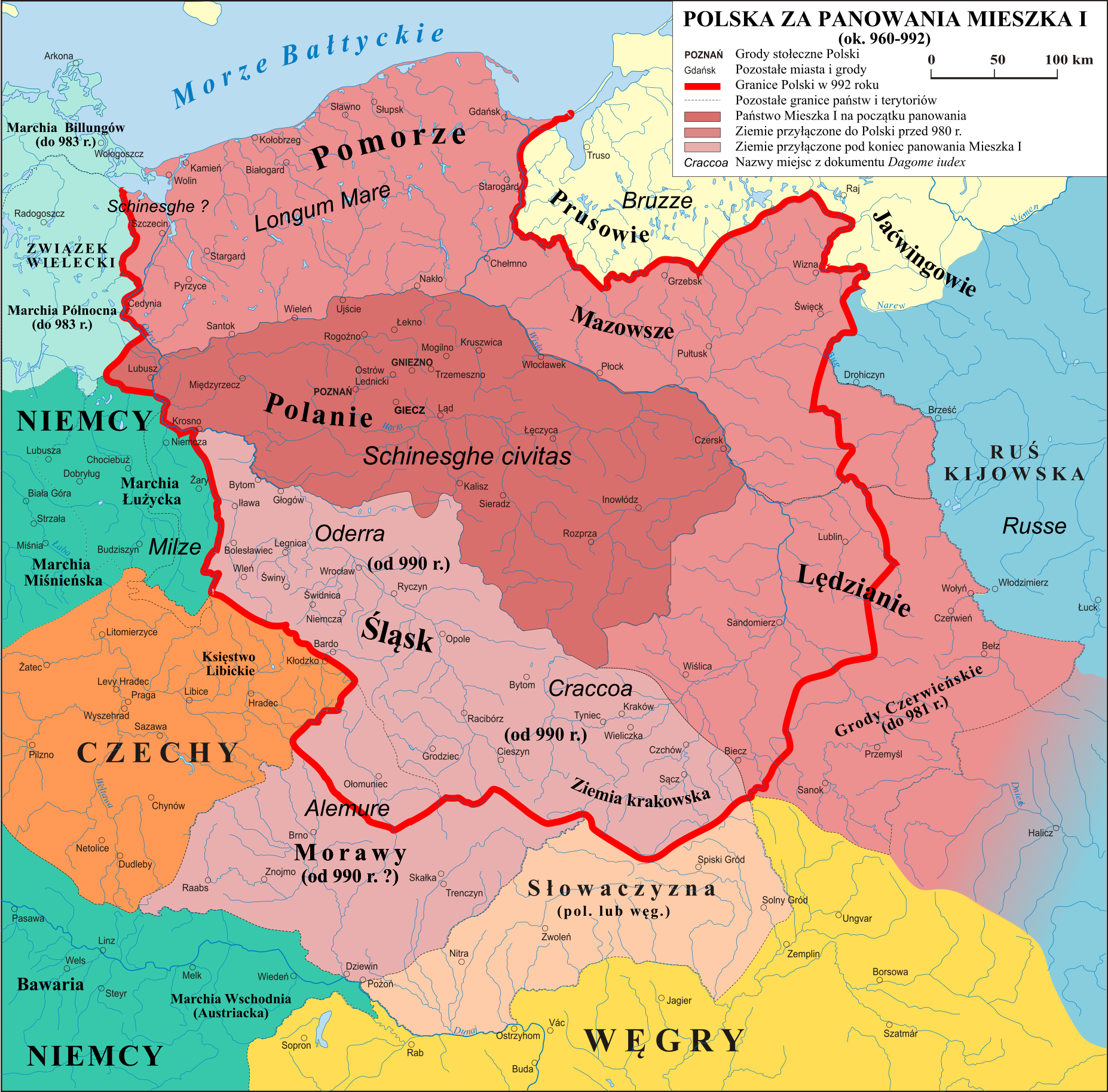
Poland During The Piast Dynasty
The period of rule by the Piast dynasty between the 10th and 14th centuries is the first major stage of the history of the Polish state. The dynasty was founded by a series of dukes listed by the chronicler Gall Anonymous in the early 12th century: Siemowit, Lestek and Siemomysł. It was Mieszko I, the son of Siemomysł, who is now considered the proper founder of the Polish state at about 960 AD. The ruling house then remained in power in the Polish lands until 1370. Mieszko converted to Christianity of the Western Latin Rite in an event known as the Baptism of Poland in 966, which established a major cultural boundary in Europe based on religion. He also completed a unification of the Lechitic tribal lands that was fundamental to the existence of the new country of Poland. Following the emergence of the Polish state, a series of rulers converted the population to Christianity, created a kingdom of Poland in 1025 and integrated Poland into the prevailing culture of Europe. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piast Dynasty
The House of Piast was the first historical ruling dynasty of Poland. The first documented Polish monarch was Duke Mieszko I (c. 930–992). The Piasts' royal rule in Poland ended in 1370 with the death of king Casimir III the Great. Branches of the Piast dynasty continued to rule in the Duchy of Masovia and in the Duchies of Silesia until the last male Silesian Piast died in 1675. The Piasts intermarried with several noble lines of Europe, and possessed numerous titles, some within the Holy Roman Empire. The Jagiellonian kings after John I Albert were also descended in the female line from Casimir III's daughter. Origin of the name The early dukes and kings of Poland are said to have regarded themselves as descendants of the semi-legendary Piast the Wheelwright (''Piast Kołodziej''), first mentioned in the '' Cronicae et gesta ducum sive principum Polonorum'' (Chronicles and deeds of the dukes or princes of the Poles), written c. 1113 by Gallus Anonymus. However, the ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Pomerania
The Duchy of Pomerania (german: Herzogtum Pommern; pl, Księstwo Pomorskie; Latin: ''Ducatus Pomeraniae'') was a duchy in Pomerania on the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, ruled by dukes of the House of Pomerania (''Griffins''). The country had existed in the Middle Ages, in years 1121–1160, 1264–1295, 1478–1531 and 1625–1637. The duchy originated from the realm of Wartislaw I, a Slavic Pomeranian duke, and was extended by the Lands of Schlawe and Stolp in 1317, the Principality of Rügen in 1325, and the Lauenburg and Bütow Land in 1455. During the High Middle Ages, it also comprised the northern Neumark and Uckermark areas as well as Circipania and Mecklenburg-Strelitz. The Duchy of Pomerania was established as a vassal state of Poland in 1121, which it remained until the fragmentation of Poland after the death of Polish ruler Bolesław III Wrymouth in 1138. Afterwards the Dukes of Pomerania were independent, and later were vassals of the Duchy of Saxony from 1164 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wichmann The Younger
Wichmann II the Younger (also spelled ''Wigmann'' or ''Wichman'') (about 930 – 22 September 967) was a member of the Saxon House of Billung. He was a son of Count Wichmann the Elder and his wife Frederuna, a niece of Queen Matilda. The cousin of Emperor Otto I became known as a fierce enemy of the ruling Ottonian dynasty. Wichmann was perhaps born at present-day ''Wichmannsburg'', part of Bienenbüttel, at the residence of his father. Wichmann I the Elder, though the first-born of three Billung brothers and by his marriage related to King Otto I, was ignored at the enfeoffment with the Saxon Billung March, which in 936 fell to his younger brother Hermann. Wichmann the Elder at first rebelled against the king, joining the uprising of Duke Eberhard of Franconia, but gave up soon afterwards. Upon his father's death in 944, Wichmann the Younger remained under the tutelage of his uncle Hermann. When he came of age, he was only able to succeed to the rank of a count in Angria, though ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wolinians
The Wolinians ( la, Velunzani, Uelunzani, pl, Wolinianie) were a Lechitic tribe in Early Middle Age Pomerania. They were first mentioned as "Velunzani" with 70 ''civitates'' by the Bavarian Geographer, ca. 845.Johannes Hoops, Herbert Jankuhn, Heinrich Beck, Reallexikon der germanischen Altertumskunde Band 23, Walter de Gruyter, 2003, p.261, Associated with both the Veleti (later Lutici) and the Pomeranians, they were based on the island of Wolin and the adjacent mainland.Jan M Piskorski, Pommern im Wandel der Zeiten, p.30, Compared to other tribes of these groups, the Wolinians' territory was relatively small but densely settled: in the 11th century, there was one settlement per four square kilometers.Jan M Piskorski, Pommern im Wandel der Zeiten, p.31, The Wolinians are described by Jan Maria Piskorski as the most powerful Pomeranian tribe. This position resulted from the multi-ethnic emporium at the site of the present-day town of Wolin (Wollin), then known as Jomsborg, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mieszko I
Mieszko I (; – 25 May 992) was the first ruler of Poland and the founder of the first independent Polish state, the Duchy of Poland. His reign stretched from 960 to his death and he was a member of the Piast dynasty, a son of Siemomysł and a grandson of Lestek. He was the father of Bolesław I the Brave (the first crowned king of Poland) and of Gunhild of Wenden. Most sources identify Mieszko I as the father of Sigrid the Haughty, a Scandinavian queen (though one source identifies her father as Skoglar Toste), the grandfather of Canute the Great (Gundhild's son) and the great-grandfather of Gunhilda of Denmark, Canute the Great's daughter and wife of Henry III, Holy Roman Emperor. He was the first Christian ruler of Poland, but he continued the policies of both his father and grandfather, who initiated the process of creation of the Polish state. Through both alliances and military force, Mieszko extended ongoing Polish conquests and early in his reign subjugated Kuyavia an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duke Of Poland
Poland was ruled at various times either by dukes and princes (10th to 14th centuries) or by kings (11th to 18th centuries). During the latter period, a tradition of free election of monarchs made it a uniquely electable position in Europe (16th to 18th centuries). The first known Polish ruler is Duke Mieszko I, who adopted Christianity under the authority of Rome in the year 966. He was succeeded by his son, Bolesław I the Brave, who greatly expanded the boundaries of the Polish state and ruled as the first king in 1025. The following centuries gave rise to the mighty Piast dynasty, consisting of both kings such as Mieszko II Lambert, Przemysł II or Władysław I the Elbow-high and dukes like Bolesław III Wrymouth. The dynasty ceased to exist with the death of Casimir III the Great in 1370. In the same year, the Capetian House of Anjou became the ruling house with Louis I as king of both Poland and Hungary. His daughter, Jadwiga, later married Jogaila, the pagan Grand Duke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lechites
Lechites (, german: Lechiten), also known as the Lechitic tribes (, german: Lechitische Stämme), is a name given to certain West Slavic tribes who inhabited modern-day Poland and eastern Germany, and were speakers of the Lechitic languages. Distinct from the Czech–Slovak subgroup, they are the closest ancestors of ethnic Poles and the Pomeranians, Lusatians and Polabians. History According to Polish legend, Mieszko I inherited the ducal throne from his father who probably ruled over two-thirds of the territory inhabited by eastern Lechite tribes. He united the Lechites east of the Oder (Polans, Masovians, Pomeranians, Vistulans, Silesians) into a single country of Poland. His son, Bolesław I the Brave, founded the bishoprics at Wrocław, Kołobrzeg, and Kraków, and an archbishopric at Gniezno. Bolesław carried out successful wars against Bohemia, Moravia, Kievan Rus' and Lusatia, and forced the western Pomeranians to pay Poland a tribute. Shortly before his death Bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primary Chronicle
The ''Tale of Bygone Years'' ( orv, Повѣсть времѧньныхъ лѣтъ, translit=Pověstĭ vremęnĭnyxŭ lětŭ; ; ; ; ), often known in English as the ''Rus' Primary Chronicle'', the ''Russian Primary Chronicle'', or simply the ''Primary Chronicle'', as well as also, after the author it has traditionally been ascribed to, '' Nestor's Chronicle'', is an Old East Slavic chronicle (letopis) of Kievan Rus' from about 850 to 1110, originally compiled in Kiev around 1113. The work’s name originates from the opening sentence of the text, which reads: “These are the narratives of bygone years regarding the origin of the land of Rus’ (Old East Slavic: Рѹсь), the first princes of Kyiv, and from what source the land of Rus’ had its beginning.” The work has long been considered to be a fundamental source in the interpretation of the history of the East Slavs. The ''Chronicle's'' content is known today from several surviving editions and codices that have been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parsęta
Parsęta (; german: Persante ) is a river in the West Pomeranian Voivodeship (''Zachodniopomorskie'') of north-western Poland, with a length of and a basin area of . , p. 85-86 It flows into the . [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |