|
Polymer Blend
In materials science, a polymer blend, or polymer mixture, is a member of a class of materials analogous to metal alloys, in which at least two polymers are blended together to create a new material with different physical properties. History During the 1940s, '50s and '60s, the commercial development of new monomers for production of new polymers seemed endless. In this period, it was discovered that the development of the new techniques for the modification of the already existing polymers, would be economically viable. The first technique of modification developed was the polymerization, in other words, the joint polymerization of more than one kind of polymer. A new polymers modification process, based on a simple mechanical mixture of two polymers first appeared when Thomas Hancock got one mixture of natural rubber with gutta-percha. This process generated a new polymer class called "polymer blends". Basic concepts Polymer blends can be broadly divided into three categori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyethylene Terephthalate
Polyethylene terephthalate (or poly(ethylene terephthalate), PET, PETE, or the obsolete PETP or PET-P), is the most common thermoplastic polymer resin of the polyester family and is used in fibres for clothing, containers for liquids and foods, and thermoforming for manufacturing, and in combination with glass fibre for engineering resins. In 2016, annual production of PET was 56 million tons. The biggest application is in fibres (in excess of 60%), with bottle production accounting for about 30% of global demand. In the context of textile applications, PET is referred to by its common name, polyester, whereas the acronym ''PET'' is generally used in relation to packaging. Polyester makes up about 18% of world polymer production and is the fourth-most-produced polymer after polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP) and polyvinyl chloride (PVC). PET consists of repeating (C10H8O4) units. PET is commonly recycled, and has the digit 1 (♳) as its resin identification code (R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
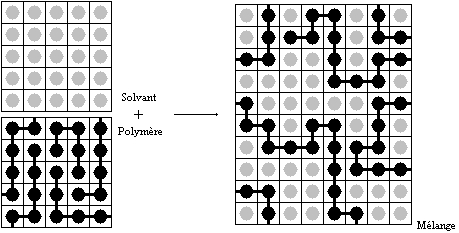
Flory–Huggins Solution Theory
Flory–Huggins solution theory is a lattice model of the thermodynamics of polymer solutions which takes account of the great dissimilarity in molecular sizes in adapting the usual expression for the entropy of mixing. The result is an equation for the Gibbs free energy change \Delta G_m for mixing a polymer with a solvent. Although it makes simplifying assumptions, it generates useful results for interpreting experiments. Theory The thermodynamic equation for the Gibbs energy change accompanying mixing at constant temperature and (external) pressure is :\Delta G_m = \Delta H_m - T\Delta S_m \, A change, denoted by \Delta, is the value of a variable for a solution or mixture minus the values for the pure components considered separately. The objective is to find explicit formulas for \Delta H_m and \Delta S_m, the enthalpy and entropy increments associated with the mixing process. The result obtained by Flory and Huggins is :\Delta G_m = RT ,n_1\ln\phi_1 + n_2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermoplastic Elastomer
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE), sometimes referred to as thermoplastic rubbers, are a class of copolymers or a physical mix of polymers (usually a plastic and a rubber) that consist of materials with both thermoplastic and elastomeric properties. While most elastomers are thermosets, thermoplastics are in contrast relatively easy to use in manufacturing, for example, by injection moulding. Thermoplastic elastomers show advantages typical of both rubbery materials and plastic materials. The benefit of using thermoplastic elastomers is the ability to stretch to moderate elongations and return to its near original shape creating a longer life and better physical range than other materials. The principal difference between thermoset elastomers and thermoplastic elastomers is the type of cross-linking bond in their structures. In fact, crosslinking is a critical structural factor which imparts high elastic properties. Types There are six generic classes of commercial TPEs (de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) (chemical formula (C8H8)''x''·(C4H6)''y''·(C3H3N)''z'' is a common thermoplastic polymer. Its glass transition temperature is approximately . ABS is amorphous and therefore has no true melting point. ABS is a terpolymer made by polymerizing styrene and acrylonitrile in the presence of polybutadiene. The proportions can vary from 15% to 35% acrylonitrile, 5% to 30% butadiene and 40% to 60% styrene. The result is a long chain of polybutadiene crisscrossed with shorter chains of poly(styrene-co-acrylonitrile). The nitrile groups from neighboring chains, being polar, attract each other and bind the chains together, making ABS stronger than pure polystyrene. The acrylonitrile also contributes chemical resistance, fatigue resistance, hardness, and rigidity, while increasing the heat deflection temperature. The styrene gives the plastic a shiny, impervious surface, as well as hardness, rigidity, and improved processing ease. The polybutadiene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polycarbonate
Polycarbonates (PC) are a group of thermoplastic polymers containing carbonate groups in their chemical structures. Polycarbonates used in engineering are strong, tough materials, and some grades are optically transparent. They are easily worked, molded, and thermoformed. Because of these properties, polycarbonates find many applications. Polycarbonates do not have a unique resin identification code (RIC) and are identified as "Other", 7 on the RIC list. Products made from polycarbonate can contain the precursor monomer bisphenol A (BPA). Structure Carbonate esters have planar OC(OC)2 cores, which confers rigidity. The unique O=C bond is short (1.173 Å in the depicted example), while the C-O bonds are more ether-like (the bond distances of 1.326 Å for the example depicted). Polycarbonates received their name because they are polymers containing carbonate groups (−O−(C=O)−O−). A balance of useful features, including temperature resistance, impact resistance and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polypropylene
Polypropylene (PP), also known as polypropene, is a thermoplastic polymer used in a wide variety of applications. It is produced via chain-growth polymerization from the monomer propylene. Polypropylene belongs to the group of polyolefins and is partially crystalline and non-polar. Its properties are similar to polyethylene, but it is slightly harder and more heat-resistant. It is a white, mechanically rugged material and has a high chemical resistance. Bio-PP is the bio-based counterpart of polypropylene (PP). Polypropylene is the second-most widely produced commodity plastic (after polyethylene). In 2019, the global market for polypropylene was worth $126.03 billion. Revenues are expected to exceed US$145 billion by 2019. The sales of this material are forecast to grow at a rate of 5.8% per year until 2021. History Phillips Petroleum chemists J. Paul Hogan and Robert Banks first demonstrated the polymerization of propylene in 1951. The stereoselective polymerization ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copolymer
In polymer chemistry, a copolymer is a polymer derived from more than one species of monomer. The polymerization of monomers into copolymers is called copolymerization. Copolymers obtained from the copolymerization of two monomer species are sometimes called ''bipolymers''. Those obtained from three and four monomers are called ''terpolymers'' and ''quaterpolymers'', respectively. Copolymers can be characterized by a variety of techniques such as NMR spectroscopy and size-exclusion chromatography to determine the molecular size, weight, properties, and composition of the material. Commercial copolymers include acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), styrene/butadiene co-polymer (SBR), nitrile rubber, styrene-acrylonitrile, styrene-isoprene-styrene (SIS) and ethylene-vinyl acetate, all of which are formed by chain-growth polymerization. Another production mechanism is step-growth polymerization, which is used to produce the nylon-12/6/66 copolymer of nylon 12, nylon 6 and n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyvinylidene Fluoride
Polyvinylidene fluoride or polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) is a highly non-reactive thermoplastic fluoropolymer produced by the polymerization of vinylidene difluoride. PVDF is a specialty plastic used in applications requiring the highest purity, as well as resistance to solvents, acids and hydrocarbons. PVDF has low density 1.78 g/cm3 in comparison to other fluoropolymers, like polytetrafluoroethylene. It is available in the form of piping products, sheet, tubing, films, plate and an insulator for premium wire. It can be injected, molded or welded and is commonly used in the chemical, semiconductor, medical and defense industries, as well as in lithium-ion batteries. It is also available as a cross-linked closed-cell foam, used increasingly in aviation and aerospace applications, and as an exotic 3D printer filament. It can also be used in repeated contact with food products, as it is FDA-compliant and non-toxic below its degradation temperature. As a fine powder grade, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poly(methyl Methacrylate)
Poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) belongs to a group of materials called engineering plastics. It is a transparent thermoplastic. PMMA is also known as acrylic, acrylic glass, as well as by the trade names and brands Crylux, Plexiglas, Acrylite, Astariglas, Lucite, Perclax, and Perspex, among several others ( see below). This plastic is often used in sheet form as a lightweight or shatter-resistant alternative to glass. It can also be used as a casting resin, in inks and coatings, and for many other purposes. Although not a type of familiar silica-based glass, the substance, like many thermoplastics, is often technically classified as a type of glass, in that it is a non-crystalline vitreous substance—hence its occasional historic designation as ''acrylic glass''. Chemically, it is the synthetic polymer of methyl methacrylate. It was developed in 1928 in several different laboratories by many chemists, such as William Chalmers, Otto Röhm, and Walter Bauer, and first brou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polybutylene Terephthalate
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) is a thermoplastic engineering polymer that is used as an insulator in the electrical and electronics industries. It is a thermoplastic (semi-)crystalline polymer, and a type of polyester. PBT resists solvents, shrinks very little during forming, is mechanically strong, is heat-resistant up to (or with glass-fibre reinforcement), and can be treated with flame retardants to make it noncombustible. It was developed by Britain's Imperial Chemical Industries (ICI). PBT is closely related to other thermoplastic polyesters. Compared to PET ( polyethylene terephthalate), PBT has slightly lower strength and rigidity, slightly better impact resistance, and a slightly lower glass transition temperature. PBT and PET are sensitive to hot water above (140 °F). PBT and PET need UV protection if used outdoors, and most grades of these polyesters are flammable, although additives can be used to improve both UV and flammability properties. Applicatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |