|
Policy Network Analysis
Policy network analysis is a field of research in political science focusing on the links and interdependence between government's sections and other societal actors, aiming to understand the policy-making process and public policy outcomes. Definition of policy networks Although the number of definitions is almost as large as the number of approaches of analysis, Rhodes aims to offer a minimally exclusive starting point: "Policy networks are sets of formal institutional and informal linkages between governmental and other actors structured around shared if endlessly negotiated beliefs and interests in public policy making and implementation." Possible typologies of policy networks As Thatcher notes, policy network approaches initially aimed to model specific forms of state-interest group relations, without giving exhaustive typologies. Policy communities vs. Issue networks The most widely used paradigm of the 1970s and 1980s only analyzed two specific types of policy ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Political Science
Political science is the scientific study of politics. It is a social science dealing with systems of governance and power, and the analysis of political activities, political thought, political behavior, and associated constitutions and laws. Modern political science can generally be divided into the three subdisciplines of comparative politics, international relations, and Political philosophy, political theory. Other notable subdisciplines are Public administration, public policy and administration, Domestic politics, domestic politics and government, political economy, and political methodology. Furthermore, political science is related to, and draws upon, the fields of economics, Legal education, law, sociology, history, philosophy, human geography, political anthropology, and psychology. Political science is methodologically diverse and appropriates many methods originating in psychology, social research, and political philosophy. Approaches include positivism, Vers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
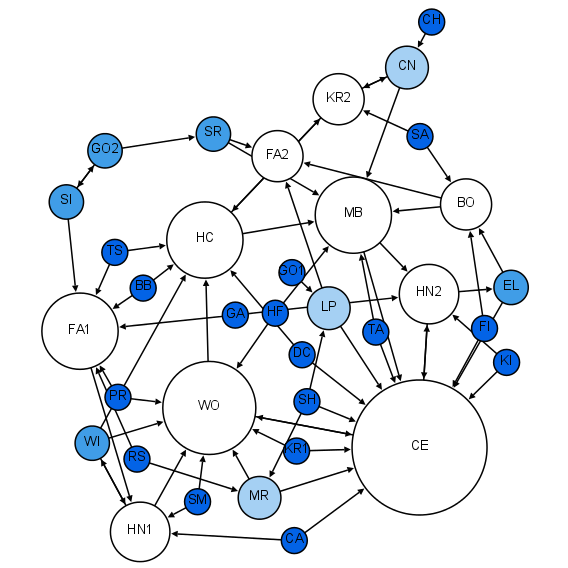
Node (networking)
In telecommunications networks, a node (, ‘knot’) is either a redistribution point or a communication endpoint. The definition of a node depends on the network and protocol layer referred to. A physical network node is an electronic device that is attached to a network, and is capable of creating, receiving, or transmitting information over a communication channel. A passive distribution point such as a distribution frame or patch panel is consequently not a node. Computer networks In data communication, a physical network node may either be data communication equipment (DCE) such as a modem, hub, bridge or switch; or data terminal equipment (DTE) such as a digital telephone handset, a printer or a host computer. If the network in question is a local area network (LAN) or wide area network (WAN), every LAN or WAN node that participates on the data link layer must have a network address, typically one for each network interface controller it possesses. Examples a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Network Science
Network science is an academic field which studies complex networks such as telecommunication networks, computer networks, biological networks, cognitive and semantic networks, and social networks, considering distinct elements or actors represented by ''nodes'' (or ''vertices'') and the connections between the elements or actors as ''links'' (or ''edges''). The field draws on theories and methods including graph theory from mathematics, statistical mechanics from physics, data mining and information visualization from computer science, inferential modeling from statistics, and social structure from sociology. The United States National Research Council defines network science as "the study of network representations of physical, biological, and social phenomena leading to predictive models of these phenomena." Background and history The study of networks has emerged in diverse disciplines as a means of analyzing complex relational data. The earliest known paper in this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Issue Networks
Issue networks are an alliance of various interest groups and individuals who unite in order to promote a common cause or agenda in a way that influences government policy. Issue networks can be either domestic or international in scope depending on their collective goal. With the rise of the internet, many interest groups have turned to online resources, such as blogs and social media, to promote and spread their cause because of its low cost and high efficiency in outreach. An issue network's tactics vary depending on their goals and purpose. In developed countries, issue networks often push for a change in policy within the government bureaucracy. An example includes the wide-ranging network of environmental groups and individuals who push for more environmental regulation in government policy. Other issue networks may revolve around such controversial issues as abortion, gun ownership rights, and drug laws. In the most extreme circumstances, issue networks may seek to achieve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rational Choice Theory
Rational choice theory refers to a set of guidelines that help understand economic and social behaviour. The theory originated in the eighteenth century and can be traced back to political economist and philosopher, Adam Smith. The theory postulates that an individual will perform a cost-benefit analysis to determine whether an option is right for them.Gary Browning, Abigail Halcli, Frank Webster (2000). ''Understanding Contemporary Society: Theories of the Present'', London: SAGE Publications. It also suggests that an individual's self-driven rational actions will help better the overall economy. Rational choice theory looks at three concepts: rational actors, self interest and the invisible hand. Rationality can be used as an assumption for the behaviour of individuals in a wide range of contexts outside of economics. It is also used in political science, sociology, and philosophy. Overview The basic premise of rational choice theory is that the decisions made by individua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advocacy Group
Advocacy groups, also known as interest groups, special interest groups, lobbying groups or pressure groups use various forms of advocacy in order to influence public opinion and ultimately policy. They play an important role in the development of political and social systems. Motives for action may be based on political, religious, moral, or commercial positions. Groups use varied methods to try to achieve their aims, including lobbying, media campaigns, awareness raising publicity stunts, polls, research, and policy briefings. Some groups are supported or backed by powerful business or political interests and exert considerable influence on the political process, while others have few or no such resources. Some have developed into important social, political institutions or social movements. Some powerful advocacy groups have been accused of manipulating the democratic system for narrow commercial gain and in some instances have been found guilty of corruption, fra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Political Economy
Political economy is the study of how economic systems (e.g. markets and national economies) and political systems (e.g. law, institutions, government) are linked. Widely studied phenomena within the discipline are systems such as labour markets and financial markets, as well as phenomena such as growth, distribution, inequality, and trade, and how these are shaped by institutions, laws, and government policy. Originating in the 16th century, it is the precursor to the modern discipline of economics. Political economy in its modern form is considered an interdisciplinary field, drawing on theory from both political science and modern economics. Political economy originated within 16th century western moral philosophy, with theoretical works exploring the administration of states' wealth; "political" signifying the Greek word '' polity'' and "economy" signifying the Greek word '; household management. The earliest works of political economy are usually attributed to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Political Science
Political science is the scientific study of politics. It is a social science dealing with systems of governance and power, and the analysis of political activities, political thought, political behavior, and associated constitutions and laws. Modern political science can generally be divided into the three subdisciplines of comparative politics, international relations, and Political philosophy, political theory. Other notable subdisciplines are Public administration, public policy and administration, Domestic politics, domestic politics and government, political economy, and political methodology. Furthermore, political science is related to, and draws upon, the fields of economics, Legal education, law, sociology, history, philosophy, human geography, political anthropology, and psychology. Political science is methodologically diverse and appropriates many methods originating in psychology, social research, and political philosophy. Approaches include positivism, Vers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Political Studies (journal)
''Political Studies'' is a peer-reviewed academic journal covering all areas of political science, established in 1953 and published quarterly by SAGE Publications on behalf of the Political Studies Association. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2016 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as ... of 1.200, ranking it 76th out of 165 journals in the category "Political Science". The journal's editorial approach is not constrained by any particular methodological or theoretical framework wishes to encourage a pluralistic approach and debate among the different approaches. Innovative submissions, which cross and challenge traditional discipline boundaries, reconsider the relationship between international and domestic politics or offer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Institutionalism
New institutionalism (also referred to as neo-institutionalist theory or institutionalism) is an approach to the study of institutions that focuses on the constraining and enabling effects of formal and informal rules on the behavior of individuals and groups. New institutionalism traditionally encompasses three strands: sociological institutionalism, rational choice institutionalism, and historical institutionalism. New institutionalism originated in work by sociologist John Meyer published in 1977. History The study of institutions and their interactions has been a focus of academic research for many years. In the late 19th and early 20th century, social theorists began to systematize this body of literature. One of the most prominent examples of this was the work of German economist and social theorist Max Weber; Weber focused on the organizational structure (i.e. bureaucracy) within society, and the institutionalization created by means of the iron cage which organizationa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Policy Making
Policy is a deliberate system of guidelines to guide decisions and achieve rational outcomes. A policy is a statement of intent and is implemented as a procedure or protocol. Policies are generally adopted by a governance body within an organization. Policies can assist in both ''subjective'' and ''objective'' decision making. Policies used in subjective decision-making usually assist senior management with decisions that must be based on the relative merits of a number of factors, and as a result, are often hard to test objectively, e.g. work–life balance policy... Moreover, Governments and other institutions have policies in the form of laws, regulations, procedures, administrative actions, incentives and voluntary practices. Frequently, resource allocations mirror policy decisions. Policy is a blueprint of the organizational activities which are repetitive/routine in nature. In contrast, policies to assist in objective decision-making are usually operational in nature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scandinavian Political Studies
''Scandinavian Political Studies'' is a quarterly peer-reviewed academic journal covering political science in the Nordic countries published by Wiley-Blackwell. The current joint editors-in-chief are Åse Gornitzka ( Oslo University) and Carl Henrik Knutsen ( Oslo University). Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2014 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as ... of 1.114, ranking it 50th out of 161 journals in the category "Political Science". See also * List of political science journals References External links * English-language journals Political science journals Publications established in 1966 Quarterly journals Wiley-Blackwell academic jo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |