|
Polarization Controller
A polarization controller is an optical device which allows one to modify the polarization state of light. Types and operation Polarization controllers can be operated without feedback, typically by manual adjustment or by electrical signals from a generator, or with automatic feedback. The latter allows for fast polarization tracking. A polarization controller can have the task of transforming a fixed, known polarization into an arbitrary one. Since polarization states are defined by two degrees of freedom, for example azimuth angle and ellipticity angle of the polarization state, such a polarization controller needs two degrees of freedom. The same holds for the task of transforming an arbitrary polarization into a fixed, known one. More difficult is the transformation of an arbitrary polarization into another arbitrary polarization. Yet this requires just two degrees of freedom. Such a polarization controller can for example be obtained by placing on the optical path thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Space Optics
Free-space optical communication (FSO) is an optical communication technology that uses light propagating in free space to wirelessly transmit data for telecommunications or computer networking. "Free space" means air, outer space, vacuum, or something similar. This contrasts with using solids such as optical fiber cable. The technology is useful where the physical connections are impractical due to high costs or other considerations. History Optical communications, in various forms, have been used for thousands of years. The ancient Greeks used a coded alphabetic system of signalling with torches developed by Cleoxenus, Democleitus and Polybius. In the modern era, semaphores and wireless solar telegraphs called heliographs were developed, using coded signals to communicate with their recipients. In 1880, Alexander Graham Bell and his assistant Charles Sumner Tainter created the photophone, at Bell's newly established Volta Laboratory in Washington, DC. Bell considered it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polarization Scrambling
Polarization scrambling is the process of rapidly varying the polarization of light within a system using a polarization controller so that the average polarization over time is effectively randomized. Polarization scrambling can be used in scientific experiments to cancel out errors caused by polarization effects. Polarization scrambling is also used on long-distance fibre optic transmission systems with optical amplifiers, in order to avoid polarization hole-burning. Polarization scrambling, also for the variation of polarization mode dispersion, is a mandatory test procedure for fiber optic data transmission systems based on polarization-division multiplexing. Polarization scramblers usually vary the normalized Stokes vector of the polarization state over the entire Poincaré sphere. They are commercially available with speeds of 20 Mrad/s on the Poincaré sphere (see external link). Various speed distributions such as peaked and quasi-Rayleigh can be generated. Some exp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
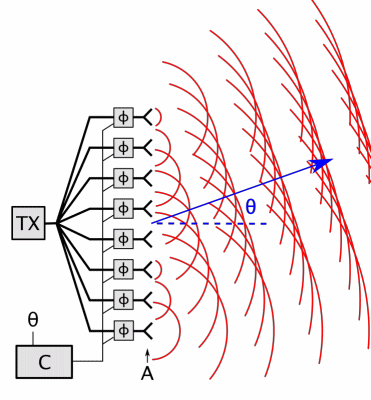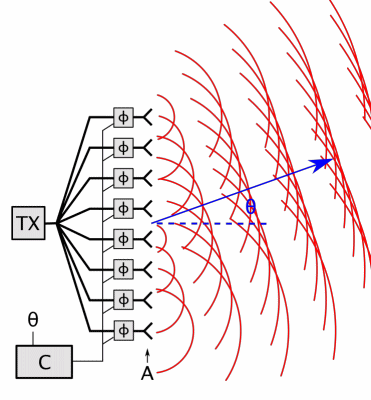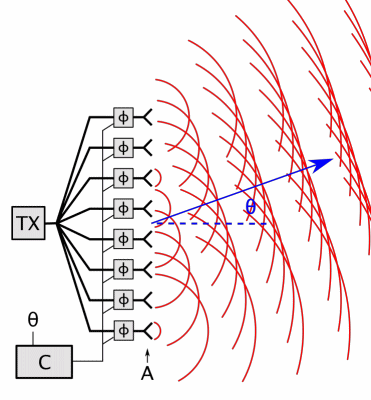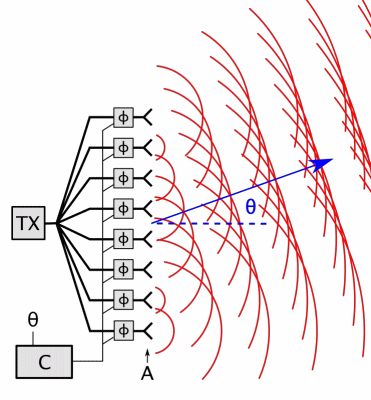
Phased Array
In antenna theory, a phased array usually means an electronically scanned array, a computer-controlled array of antennas which creates a beam of radio waves that can be electronically steered to point in different directions without moving the antennas. In a simple array antenna, the radio frequency current from the transmitter is fed to multiple individual antenna elements with the proper phase relationship so that the radio waves from the separate elements combine ( superpose) to form beams, to increase power radiated in desired directions and suppress radiation in undesired directions. In a phased array, the power from the transmitter is fed to the radiating elements through devices called '' phase shifters'', controlled by a computer system, which can alter the phase or signal delay electronically, thus steering the beam of radio waves to a different direction. Since the size of an antenna array must extend many wavelengths to achieve the high gain needed for narrow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BB84
BB84 is a quantum key distribution scheme developed by Charles Bennett and Gilles Brassard in 1984. It is the first quantum cryptography protocol. The protocol is provably secure, relying on two conditions: (1) the quantum property that information gain is only possible at the expense of disturbing the signal if the two states one is trying to distinguish are not orthogonal (see no-cloning theorem); and (2) the existence of an authenticated public classical channel. It is usually explained as a method of securely communicating a private key from one party to another for use in one-time pad encryption.''Quantum Computing and Quantum Information'', Michael Nielsen and Isaac Chuang, Cambridge University Press 2000 Description In the BB84 scheme, Alice wishes to send a private key to Bob. She begins with two strings of bits, a and b, each n bits long. She then encodes these two strings as a tensor product In mathematics, the tensor product V \otimes W of two vector spaces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poincaré Sphere (optics)
Polarization ( also polarisation) is a property applying to transverse waves that specifies the geometrical orientation of the oscillations. In a transverse wave, the direction of the oscillation is perpendicular to the direction of motion of the wave. A simple example of a polarized transverse wave is vibrations traveling along a taut string ''(see image)''; for example, in a musical instrument like a guitar string. Depending on how the string is plucked, the vibrations can be in a vertical direction, horizontal direction, or at any angle perpendicular to the string. In contrast, in longitudinal waves, such as sound waves in a liquid or gas, the displacement of the particles in the oscillation is always in the direction of propagation, so these waves do not exhibit polarization. Transverse waves that exhibit polarization include electromagnetic waves such as light and radio waves, gravitational waves, and transverse sound waves (shear waves) in solids. An electromagnetic w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithium Niobate
Lithium niobate () is a non-naturally-occurring salt consisting of niobium, lithium, and oxygen. Its single crystals are an important material for optical waveguides, mobile phones, piezoelectric sensors, optical modulators and various other linear and non-linear optical applications. Lithium niobate is sometimes referred to by the brand name linobate. Properties Lithium niobate is a colorless solid, and it is insoluble in water. It has a trigonal crystal system, which lacks inversion symmetry and displays ferroelectricity, the Pockels effect, the piezoelectric effect, photoelasticity and nonlinear optical polarizability. Lithium niobate has negative uniaxial birefringence which depends slightly on the stoichiometry of the crystal and on temperature. It is transparent for wavelengths between 350 and 5200 nanometers. Lithium niobate can be doped by magnesium oxide, which increases its resistance to optical damage (also known as photorefractive damage) when doped above the o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halfwave Plate
A waveplate or retarder is an optical device that alters the polarization state of a light wave travelling through it. Two common types of waveplates are the ''half-wave plate'', which shifts the polarization direction of linearly polarized light, and the ''quarter-wave plate'', which converts linearly polarized light into circularly polarized light and vice versa. A quarter-wave plate can be used to produce elliptical polarization as well. Waveplates are constructed out of a birefringent material (such as quartz or mica, or even plastic), for which the index of refraction is different for light linearly polarized along one or the other of two certain perpendicular crystal axes. The behavior of a waveplate (that is, whether it is a half-wave plate, a quarter-wave plate, etc.) depends on the thickness of the crystal, the wavelength of light, and the variation of the index of refraction. By appropriate choice of the relationship between these parameters, it is possible to introduce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Device
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behaviour of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light. Because light is an electromagnetic wave, other forms of electromagnetic radiation such as X-rays, microwaves, and radio waves exhibit similar properties. Most optical phenomena can be accounted for by using the classical electromagnetic description of light. Complete electromagnetic descriptions of light are, however, often difficult to apply in practice. Practical optics is usually done using simplified models. The most common of these, geometric optics, treats light as a collection of rays that travel in straight lines and bend when they pass through or reflect from surfaces. Physical optics is a more comprehensive model of light, which includes wave effects such as diffraction and interference that cannot b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quarterwave Plate
A waveplate or retarder is an optical device that alters the polarization state of a light wave travelling through it. Two common types of waveplates are the ''half-wave plate'', which shifts the polarization direction of linearly polarized light, and the ''quarter-wave plate'', which converts linearly polarized light into circularly polarized light and vice versa. A quarter-wave plate can be used to produce elliptical polarization as well. Waveplates are constructed out of a birefringent material (such as quartz or mica, or even plastic), for which the index of refraction is different for light linearly polarized along one or the other of two certain perpendicular crystal axes. The behavior of a waveplate (that is, whether it is a half-wave plate, a quarter-wave plate, etc.) depends on the thickness of the crystal, the wavelength of light, and the variation of the index of refraction. By appropriate choice of the relationship between these parameters, it is possible to introduce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |