|
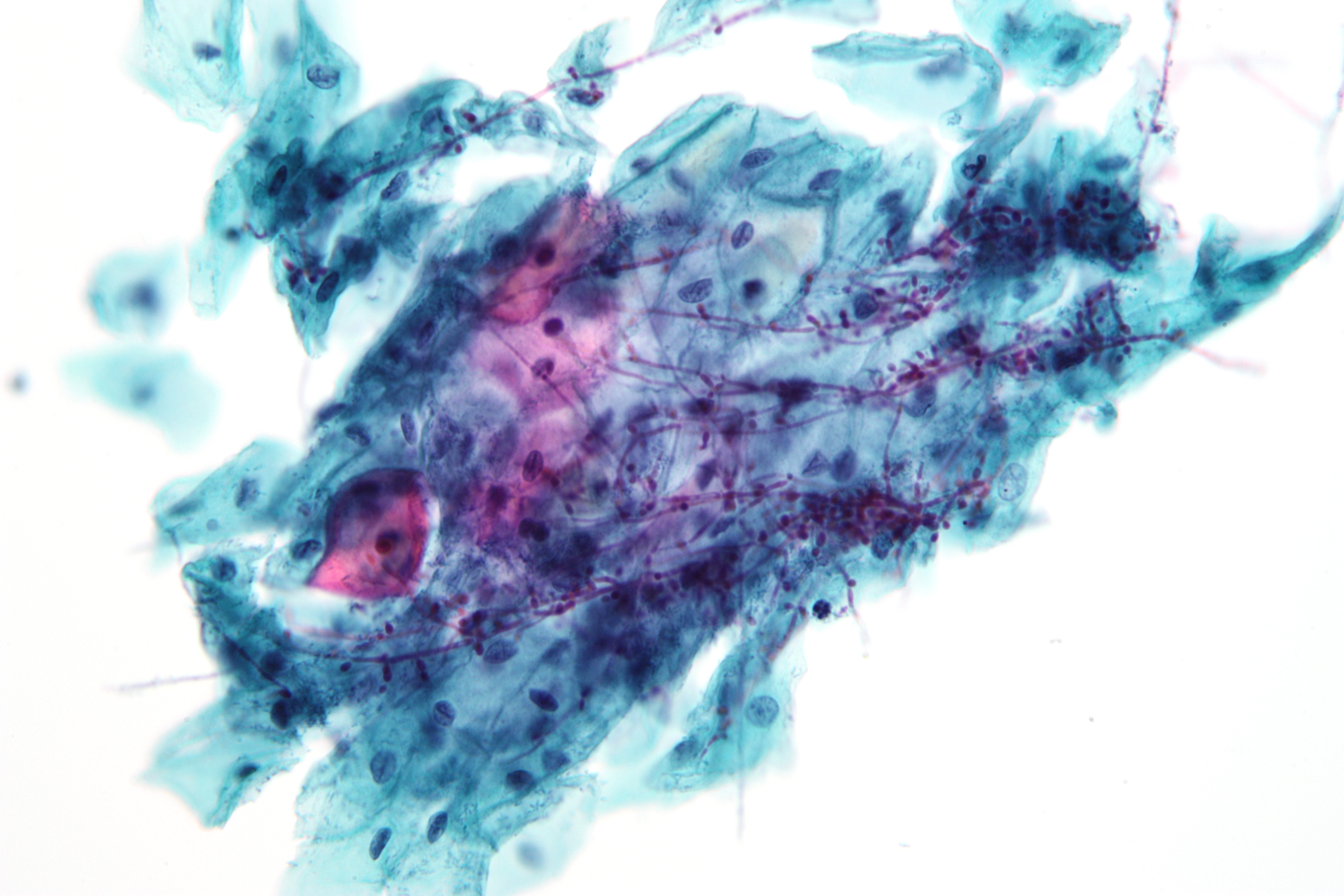
Pohlia Nutans
''Pohlia nutans'', the nodding thread-moss, is a species of moss in the family Mniaceae. It has a Cosmopolitan distribution, found on all seven continents; Europe, Iceland, Siberia, Japan, North America, Greenland, the Andes of South America, South Africa, Tasmania and nearby mainland Australia, New Zealand, and the Antarctic Peninsula and Mount Rittmann in Antarctica. An extremophile, it is resistant to cold, drought, salt, acid, heavy metals, and intense UV radiation. ''Pohlia nutans'' is subject to fungal infections which cause fairy rings to appear. Some causative agents have been identified, including species of ''Cladosporium ''Cladosporium'' is a genus of fungi including some of the most common indoor and outdoor molds. Species produce olive-green to brown or black colonies, and have dark-pigmented conidia that are formed in simple or branching chains. Many species ...'', '' Mortierella gamsii'' and '' Mortierella fimbricystis''. Subtaxa The following subtaxa are acce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Hedwig
Johann Hedwig (8 December 1730 – 18 February 1799), also styled as Johannes Hedwig, was a German botanist notable for his studies of mosses. He is sometimes called the "father of bryology". He is known for his particular observations of sexual reproduction in the cryptogams. Many of his writings were in Latin, and his name is rendered in Latin as Ioannis Hedwig or Ioanne Hedwig. Early life Hedwig was born in Brașov, Transylvania, on 8 December 1730. As the son of a shoemaker, he grew up in poverty. It was in his childhood he became fascinated with mosses.Isely, Duane. One Hundred and One Botanists. Purdue University Press, 2002. He went on to study medicine at the University of Leipzig, and received his medical degree in 1759. Career After receiving his degree, Hedwig worked as a physician for the next twenty years. When he was not granted a license to practice in Transylvania with his Leipzig degree, he worked as a general practitioner in Chemnitz. It was during this time ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sextus Otto Lindberg
Sextus Otto Lindberg (29 March 1835 – 20 February 1889) was a Swedish physician and botanist, known as a bryologist. Life He was born in Stockholm, and educated in Uppsala. He worked in the Grand Duchy of Finland, then part of the Russian Empire. He became professor of botany, and dean of the physics-mathematics faculty, at the University of Helsingfors. He was honored with the genus name ''Lindbergia'' in the family Leskeaceae, published by Swedish bryologist Nils Conrad Kindberg in 1897. His son Harald was honored with the genus name '' Lindbergella'' in the family Poaceae, published by Irish botanist Norman Loftus Bor in 1969. Lindberg died at Helsingfors Helsinki ( or ; ; sv, Helsingfors, ) is the capital, primate, and most populous city of Finland. Located on the shore of the Gulf of Finland, it is the seat of the region of Uusimaa in southern Finland, and has a population of . The cit .... He was the father of the botanist Harald Lindberg (1871–1963). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moss
Mosses are small, non-vascular flowerless plants in the taxonomic division Bryophyta (, ) '' sensu stricto''. Bryophyta (''sensu lato'', Schimp. 1879) may also refer to the parent group bryophytes, which comprise liverworts, mosses, and hornworts. Mosses typically form dense green clumps or mats, often in damp or shady locations. The individual plants are usually composed of simple leaves that are generally only one cell thick, attached to a stem that may be branched or unbranched and has only a limited role in conducting water and nutrients. Although some species have conducting tissues, these are generally poorly developed and structurally different from similar tissue found in vascular plants. Mosses do not have seeds and after fertilisation develop sporophytes with unbranched stalks topped with single capsules containing spores. They are typically tall, though some species are much larger. ''Dawsonia'', the tallest moss in the world, can grow to in height. There are a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mniaceae
Mniaceae is a moss family in the order Bryales. Taxonomy The family Mniaceae includes the following genera: * '' Cinclidium'' * '' Cyrtomnium'' * '' Epipterygium'' * ''Leucolepis'' * '' Mielichhoferia'' * ''Mnium'' * '' Orthomnion'' * ''Plagiomnium'' * ''Pohlia'' * ''Pseudobryum'' * '' Pseudopohlia'' * ''Rhizomnium ''Rhizomnium'' is a genus of mosses in the family Mniaceae commonly referred to as leafy mosses. They grow nearly worldwide, mostly in the northern hemisphere. Species * ''Rhizomnium andrewsianum'' * ''Rhizomnium appalachianum'' * ''Rhizomnium g ...'' * '' Schizymenium'' * '' Synthetodontium'' * '' Trachycystis'' References Moss families {{Bryophyte-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmopolitan Distribution
In biogeography, cosmopolitan distribution is the term for the range of a taxon that extends across all or most of the world in appropriate habitats. Such a taxon, usually a species, is said to exhibit cosmopolitanism or cosmopolitism. The extreme opposite of a cosmopolitan species is an endemic one, being found only in a single geographical location. Qualification The caveat “in appropriate habitat” is used to qualify the term "cosmopolitan distribution", excluding in most instances polar regions, extreme altitudes, oceans, deserts, or small, isolated islands. For example, the housefly is highly cosmopolitan, yet is neither oceanic nor polar in its distribution. Related terms and concepts The term pandemism also is in use, but not all authors are consistent in the sense in which they use the term; some speak of pandemism mainly in referring to diseases and pandemics, and some as a term intermediate between endemism and cosmopolitanism, in effect regarding pandemism as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctic Peninsula
The Antarctic Peninsula, known as O'Higgins Land in Chile and Tierra de San Martín in Argentina, and originally as Graham Land in the United Kingdom and the Palmer Peninsula in the United States, is the northernmost part of mainland Antarctica. The Antarctic Peninsula is part of the larger peninsula of West Antarctica, protruding from a line between Cape Adams (Weddell Sea) and a point on the mainland south of the Eklund Islands. Beneath the ice sheet that covers it, the Antarctic Peninsula consists of a string of bedrock islands; these are separated by deep channels whose bottoms lie at depths considerably below current sea level. They are joined by a grounded ice sheet. Tierra del Fuego, the southernmost tip of South America, is about away across the Drake Passage. The Antarctic Peninsula is in area and 80% ice-covered. The marine ecosystem around the western continental shelf of the Antarctic Peninsula (WAP) has been subjected to rapid climate change. Over the past 50 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Rittmann
Mount Rittmann is a volcano in Antarctica. Discovered in 1988–1989 by an Italian expedition, it was named after the volcanologist Alfred Rittmann (1893–1980). It features a or wide caldera which crops out from underneath the Aviator Glacier. The volcano was active during the Pliocene and into the Holocene, including large explosive eruptions; a major eruption occurred in 1254 CE and deposited tephra over much of Antarctica. Currently, the volcano is classified as dormant. The volcano is fumarolically active. The geothermal activity keeps part of the caldera ice-free; mosses and various microorganisms grow on this ice-free terrain. Such an occurrence of mosses on fumarolically active volcanoes of Antarctica is limited to Mount Rittmann, Mount Melbourne and Mount Erebus and has led to efforts to establish a protected area on the volcano. Geography and geomorphology It lies in Victoria Land on the Ross Sea, from Terranova Bay and from the Italian Mario Zucchelli Sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extremophile
An extremophile (from Latin ' meaning "extreme" and Greek ' () meaning "love") is an organism that is able to live (or in some cases thrive) in extreme environments, i.e. environments that make survival challenging such as due to extreme temperature, radiation, salinity, or pH level. These organisms are ecologically dominant in the evolutionary history of the planet. Some spores and cocooned bacteria samples have been dormant for more than 40 million years, extremophiles have continued to thrive in the most extreme conditions, making them one of the most abundant lifeforms. Characteristics In the 1980s and 1990s, biologists found that microbial life has great flexibility for surviving in extreme environments—niches that are acidic, extraordinarily hot or within irregular air pressure for example—that would be completely inhospitable to complex organisms. Some scientists even concluded that life may have begun on Earth in hydrothermal vents far under the ocean's surfa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pathogenic Fungi
Pathogenic fungi are fungi that cause disease in humans or other organisms. Approximately 300 fungi are known to be pathogenic to humans. Markedly more fungi are known to be pathogenic to plant life than those of the animal kingdom. The study of fungi pathogenic to humans is called "medical mycology". Although fungi are eukaryotic, many pathogenic fungi are microorganisms. The study of fungi and other organisms pathogenic to plants is called plant pathology. ''Candida'' ''Candida'' species cause infections in individuals with deficient immune systems. Th1-type cell-mediated immunity (CMI) is required for clearance of a fungal infection. ''Candida albicans'' is a kind of diploid yeast that commonly occurs among the human gut microflora. ''C. albicans'' is an opportunistic pathogen in humans. Abnormal over-growth of this fungus can occur, particularly in immunocompromised individuals. ''C. albicans'' has a parasexual cycle that appears to be stimulated by environmental stress. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
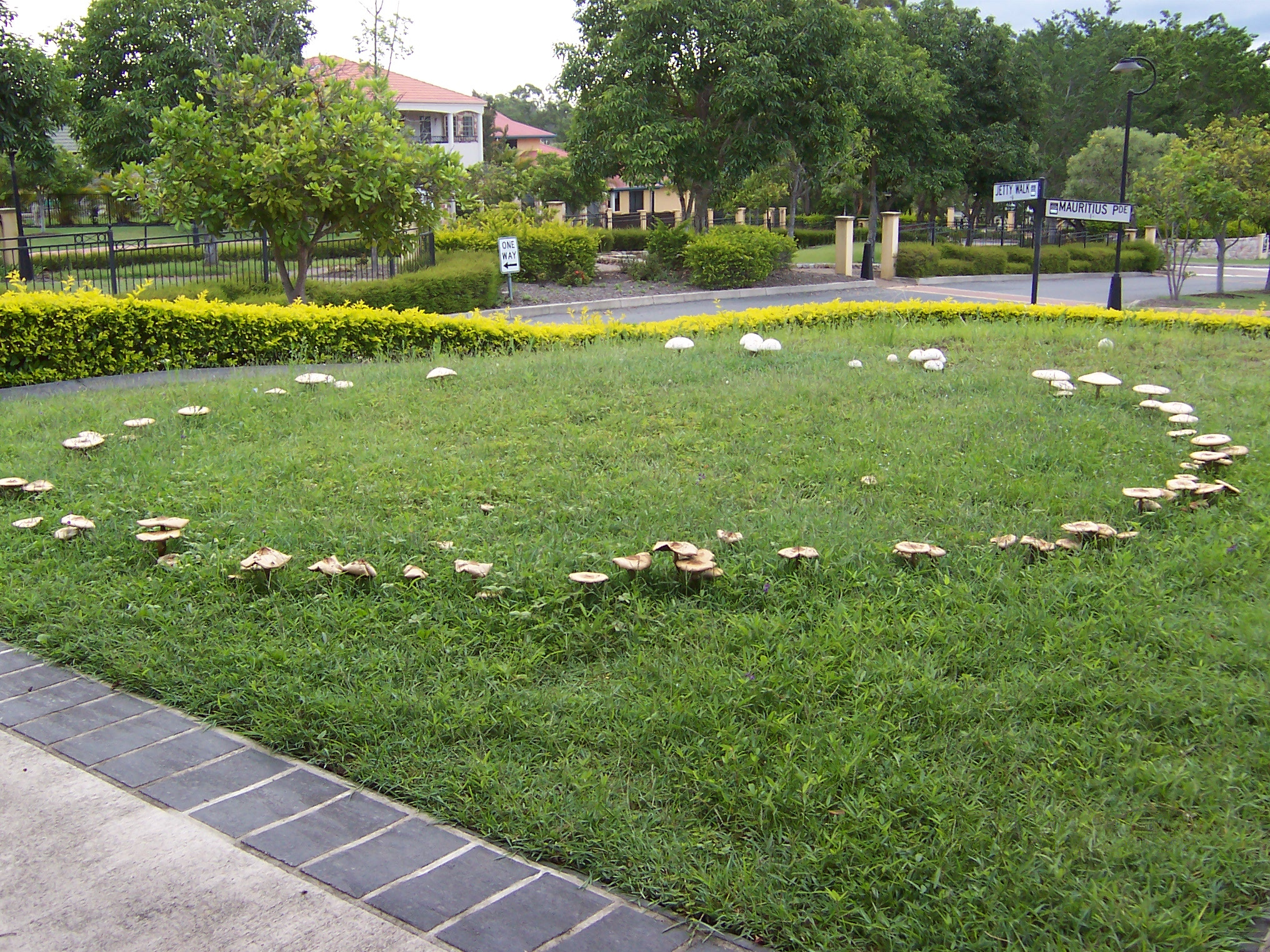
Fairy Rings
A fairy ring, also known as fairy circle, elf circle, elf ring or pixie ring, is a naturally occurring ring or arc of mushrooms. They are found mainly in forested areas, but also appear in grasslands or rangelands. Fairy rings are detectable by sporocarps (fungal spore pods) in rings or arcs, as well as by a necrotic zone (dead grass), or a ring of dark green grass. Fungus mycelium is present in the ring or arc underneath. The rings may grow to over in diameter, and they become stable over time as the fungus grows and seeks food underground. Fairy rings are the subject of much folklore and myth worldwide—particularly in Western Europe. They are often seen as hazardous or dangerous places, and linked with witches or the Devil in folklore. Conversely, they can sometimes be linked with good fortune. Genesis The mycelium of a fungus growing in the ground absorbs nutrients by secretion of enzymes from the tips of the hyphae (threads making up the mycelium). This breaks down lar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cladosporium
''Cladosporium'' is a genus of fungi including some of the most common indoor and outdoor molds. Species produce olive-green to brown or black colonies, and have dark-pigmented conidia that are formed in simple or branching chains. Many species of ''Cladosporium'' are commonly found on living and dead plant material. Some species are endophytes or plant pathogens, while others parasitize fungi. ''Cladosporium'' spores are wind-dispersed and they are often extremely abundant in outdoor air. Indoors ''Cladosporium'' species may grow on surfaces when moisture is present. '' Cladosporium fulvum'', cause of tomato leaf mould, has been an important genetic model, in that the genetics of host resistance are understood. In the 1960s, it was estimated that the genus ''Cladosporium'' contained around 500 plant-pathogenic and saprotrophic species, but this number has since been increased to over 772 species. The genus ''Cladosporium'' is very closely related to black yeasts in the order Do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mortierella Gamsii
''Mortierella'' species are soil fungi belonging to the order Mortierellales within the subphylum Mortierellomycotina (phylum: Mucoromycota). The widespread genus contains about 85 species. Taxonomy The genus name of ''Mortierella'' is in honour of Barthélemy Dumortier (1797–1878), who was a Belgian who conducted a parallel career of botanist and Member of Parliament. The genus was circumscribed by Henri Eugène Lucien Gaëtan Coemans in Bull. Acad. Roy. Sci. Belgique series 2, Vol.15 on pages 536-539 in 1863. Ecology Species of ''Mortierella'' live as saprotrophs in soil, on decaying leaves and other organic material. Other species live on fecal pellets or on exoskeletons of arthropods ''Penicillium'', ''Trichoderma'', ''Mucor'' and ''Mortierella'' species belong to an ecology group which are the first organisms growing on roots. Salt described that the frequency of ''Mortierella'' species growing on the surface of roots from spruce is higher in comparison to other species ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)