|
Plummer–Vinson Syndrome
Plummer–Vinson syndrome is a rare disease characterized by difficulty swallowing, iron-deficiency anemia, glossitis, cheilosis and esophageal webs. Treatment with iron supplementation and mechanical widening of the esophagus generally provides an excellent outcome. While exact data about the epidemiology is unknown, this syndrome has become extremely rare. The reduction in the prevalence of Plummer–Vinson syndrome has been hypothesized to be the result of improvements in nutritional status and availability in countries where the syndrome was previously described. It generally occurs in perimenopausal women. Its identification and follow-up is considered relevant due to increased risk of squamous cell carcinomas of the esophagus and pharynx. Presentation Patients with Plummer–Vinson syndrome often have a burning sensation with the tongue and oral mucosa, and atrophy of lingual papillae produces a smooth, shiny, red, dorsum of the tongue. Symptoms include: * Dysphagia (dif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
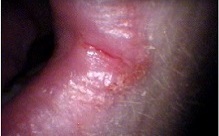
Angular Stomatitis
Angular cheilitis (AC) is inflammation of one or both corners of the mouth. Often the corners are red with skin breakdown and crusting. It can also be itchy or painful. The condition can last for days to years. Angular cheilitis is a type of cheilitis (inflammation of the lips). Angular cheilitis can be caused by infection, irritation, or allergies. Infections include by fungi such as ''Candida albicans'' and bacteria such as '' Staph. aureus''. Irritants include poorly fitting dentures, licking the lips or drooling, mouth breathing resulting in a dry mouth, sun exposure, overclosure of the mouth, smoking, and minor trauma. Allergies may include substances like toothpaste, makeup, and food. Often a number of factors are involved. Other factors may include poor nutrition or poor immune function. Diagnosis may be helped by testing for infections and patch testing for allergies. Treatment for angular cheilitis is typically based on the underlying causes along with the use of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Splenomegaly
Splenomegaly is an enlargement of the spleen. The spleen usually lies in the left upper quadrant (LUQ) of the human abdomen. Splenomegaly is one of the four cardinal signs of ''hypersplenism'' which include: some reduction in number of circulating blood cells affecting granulocytes, erythrocytes or platelets in any combination; a compensatory proliferative response in the bone marrow; and the potential for correction of these abnormalities by splenectomy. Splenomegaly is usually associated with increased workload (such as in hemolytic anemias), which suggests that it is a response to hyperfunction. It is therefore not surprising that splenomegaly is associated with any disease process that involves abnormal red blood cells being destroyed in the spleen. Other common causes include congestion due to portal hypertension and infiltration by leukemias and lymphomas. Thus, the finding of an enlarged spleen, along with caput medusae, is an important sign of portal hypertension. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cervical Esophageal Web
In anatomy, cervical is an adjective that has two meanings: # of or pertaining to any neck. # of or pertaining to the female cervix: i.e., the ''neck'' of the uterus. *Commonly used medical phrases involving the neck are ** cervical collar **cervical disc (intervertebral disc) ** cervical lymph nodes ** cervical nerves **cervical vertebrae **cervical rib *Phrases that involve the uterine cervix include **cervical cancer Cervical cancer is a cancer arising from the cervix. It is due to the abnormal growth of cells that have the ability to invade or spread to other parts of the body. Early on, typically no symptoms are seen. Later symptoms may include abnormal ... **cervical smear or Pap smear {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhagades
Rhagades are fissures, cracks, or linear scars in the skin, especially at the angles of the mouth and nose. They tend to form at areas of motion. They can be a result from bacterial infection of skin lesions. They are associated with late stages of congenital syphilis. This is one of the late stage manifestations of congenital syphilis, others are saber shins, Hutchinson teeth, saddle nose, and Clutton's joints (usually knee synovitis). See also *Angular cheilitis *Anal fissure An anal fissure is a break or tear in the skin of the anal canal. Anal fissures may be noticed by bright red anal bleeding on toilet paper and undergarments, or sometimes in the toilet. If acute they are painful after defecation, but with chroni ... References Cutaneous congenital anomalies {{Cutaneous-condition-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nutrition
Nutrition is the biochemical and physiological process by which an organism uses food to support its life. It provides organisms with nutrients, which can be metabolized to create energy and chemical structures. Failure to obtain sufficient nutrients causes malnutrition. Nutritional science is the study of nutrition, though it typically emphasizes human nutrition. The type of organism determines what nutrients it needs and how it obtains them. Organisms obtain nutrients by consuming organic matter, consuming inorganic matter, absorbing light, or some combination of these. Some can produce nutrients internally by consuming basic elements, while some must consume other organisms to obtain preexisting nutrients. All forms of life require carbon, energy, and water as well as various other molecules. Animals require complex nutrients such as carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins, obtaining them by consuming other organisms. Humans have developed agriculture and cooking to rep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetics
Genetics is the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms.Hartl D, Jones E (2005) It is an important branch in biology because heredity is vital to organisms' evolution. Gregor Mendel, a Moravian Augustinian friar working in the 19th century in Brno, was the first to study genetics scientifically. Mendel studied "trait inheritance", patterns in the way traits are handed down from parents to offspring over time. He observed that organisms (pea plants) inherit traits by way of discrete "units of inheritance". This term, still used today, is a somewhat ambiguous definition of what is referred to as a gene. Trait inheritance and molecular inheritance mechanisms of genes are still primary principles of genetics in the 21st century, but modern genetics has expanded to study the function and behavior of genes. Gene structure and function, variation, and distribution are studied within the context of the cell, the organism (e.g. dominance), and within the con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dysplasia
Dysplasia is any of various types of abnormal growth or development of cells ( microscopic scale) or organs (macroscopic scale), and the abnormal histology or anatomical structure(s) resulting from such growth. Dysplasias on a mainly microscopic scale include epithelial dysplasia and fibrous dysplasia of bone. Dysplasias on a mainly macroscopic scale include hip dysplasia, myelodysplastic syndrome, and multicystic dysplastic kidney. In one of the modern histopathological senses of the term, dysplasia is sometimes differentiated from other categories of tissue change including hyperplasia, metaplasia, and neoplasia, and dysplasias are thus generally not cancerous. An exception is that the myelodysplasias include a range of benign, precancerous, and cancerous forms. Various other dysplasias tend to be precancerous. The word's meanings thus cover a spectrum of histopathological variations. Microscopic scale Epithelial dysplasia Epithelial dysplasia consists of an exp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microcytic Anemia
Microcytic anaemia is any of several types of anemia characterized by smaller than normal red blood cells (called microcytes). The normal mean corpuscular volume (abbreviated to MCV on full blood count results, and also known as mean cell volume) is approximately 80–100 fL. When the MCV is 100 fL, macrocytic (the latter occurs in macrocytic anemia). The MCV is the average red blood cell size. In microcytic anemia, the red blood cells (erythrocytes) contain less hemoglobin and are usually also hypochromic, meaning that the red blood cells appear paler than usual. This can be reflected by a low mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC), a measure representing the amount of hemoglobin per unit volume of fluid inside the cell; normally about 320–360 g/L or 32–36 g/dL. Typically, therefore, anemia of this category is described as "microcytic, hypochromic anemia". Causes Typical causes of microcytic anemia include: * Childhood ** Iron deficiency anemia by far the most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Tests
A blood test is a laboratory analysis performed on a blood sample that is usually extracted from a vein in the arm using a hypodermic needle, or via fingerprick. Multiple tests for specific blood components, such as a glucose test or a cholesterol test, are often grouped together into one test panel called a blood panel or blood work. Blood tests are often used in health care to determine physiological and biochemical states, such as disease, mineral content, pharmaceutical drug effectiveness, and organ function. Typical clinical blood panels include a basic metabolic panel or a complete blood count. Blood tests are also used in drug tests to detect drug abuse. Extraction A venipuncture is useful as it is a minimally invasive way to obtain cells and extracellular fluid ( plasma) from the body for analysis. Blood flows throughout the body, acting as a medium that provides oxygen and nutrients to tissues and carries waste products back to the excretory systems for disposal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endoscopy
An endoscopy is a procedure used in medicine to look inside the body. The endoscopy procedure uses an endoscope to examine the interior of a hollow organ or cavity of the body. Unlike many other medical imaging techniques, endoscopes are inserted directly into the organ. There are many types of endoscopies. Depending on the site in the body and type of procedure, an endoscopy may be performed by either a doctor or a surgeon. A patient may be fully conscious or anaesthetised during the procedure. Most often, the term ''endoscopy'' is used to refer to an examination of the upper part of the gastrointestinal tract, known as an esophagogastroduodenoscopy. For nonmedical use, similar instruments are called borescopes. History Adolf Kussmaul was fascinated by sword swallowers who would insert a sword down their throat without gagging. This drew inspiration to insert a camera, the next problem to solve was how to insert a source of light, as they were still relying on candles a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |