|
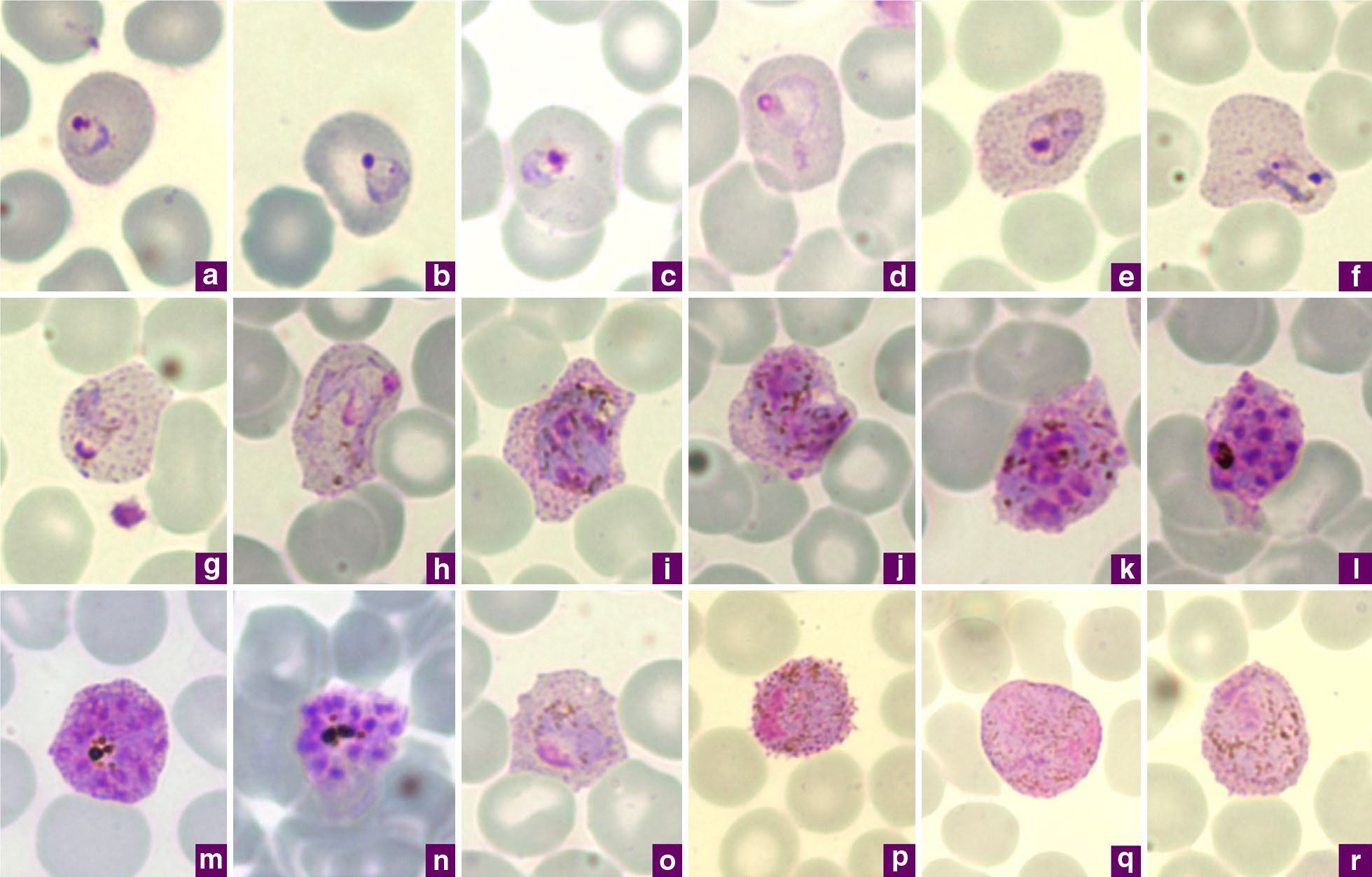
Plasmodium Vivax
''Plasmodium vivax'' is a protozoal parasite and a human pathogen. This parasite is the most frequent and widely distributed cause of recurring malaria. Although it is less virulent than '' Plasmodium falciparum'', the deadliest of the five human malaria parasites, ''P. vivax'' malaria infections can lead to severe disease and death, often due to splenomegaly (a pathologically enlarged spleen). ''P. vivax'' is carried by the female '' Anopheles'' mosquito; the males do not bite. Health Epidemiology ''Plasmodium vivax'' is found mainly in Asia, Latin America, and in some parts of Africa. ''P. vivax'' is believed to have originated in Asia, but recent studies have shown that wild chimpanzees and gorillas throughout central Africa are endemically infected with parasites that are closely related to human ''P. vivax.'' These findings indicate that human P. vivax is of African origin. ''Plasmodium vivax'' accounts for 65% of malaria cases in Asia and South America. Unlike ''Pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trophozoite
A trophozoite (G. ''trope'', nourishment + ''zoon'', animal) is the activated, feeding stage in the life cycle of certain protozoa such as malaria-causing ''Plasmodium falciparum'' and those of the ''Giardia'' group. (The complement of the trophozoite state is the thick-walled cyst form). Life cycle stages Trophozoite and cyst stages are shown in the life cycle of '' Balantidium coli'' the causative agent of balantidiasis. In the apicomplexan life cycle the trophozoite undergoes schizogony (asexual reproduction) and develops into a schizont which contains merozoites. The trophozoite life stage of ''Giardia ''Giardia'' ( or ) is a genus of anaerobic flagellated protozoan parasites of the phylum Metamonada that colonise and reproduce in the small intestines of several vertebrates, causing the disease giardiasis. Their life cycle alternates betwee ...'' colonizes and proliferates in the small intestine. Trophozoites develop during the course of the infection into cysts which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horn Of Africa
The Horn of Africa (HoA), also known as the Somali Peninsula, is a large peninsula and geopolitical region in East Africa.Robert Stock, ''Africa South of the Sahara, Second Edition: A Geographical Interpretation'', (The Guilford Press; 2004), p. 26 Located on the easternmost part of the African mainland, it is the fourth largest peninsula in the world. It is composed of Ethiopia, Eritrea, Somalia and Djibouti; broader definitions also include parts or all of Kenya, Sudan, South Sudan, and Uganda. The term Greater Horn Region (GHR) can additionally include Burundi, Rwanda, and Tanzania. It lies along the southern boundary of the Red Sea and extends hundreds of kilometres into the Guardafui Channel, Gulf of Aden, and Indian Ocean and shares a maritime border with the Arabian Peninsula of Western Asia. Names This peninsula has been known by various names. Ancient Greeks and Romans referred to it as Regio Aromatica or Regio Cinnamonifora due to the aromatic plants or as Regio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Odynophagia
Odynophagia is pain when swallowing. The pain may be felt in the mouth or throat and can occur with or without difficulty swallowing. The pain may be described as an ache, burning sensation, or occasionally a stabbing pain that radiates to the back. Odynophagia often results in inadvertent weight loss. The term is from ''-'' 'pain' and ' 'to eat'. Causes Odynophagia may have environmental or behavioral causes, such as: * Very hot or cold food and drinks (termed cryodynophagia when associated with cold drinks, classically in the setting of cryoglobulinaemia). * Taking certain medications * Using drugs, tobacco, or alcohol * Trauma or injury to the mouth, throat, or tongue It can also be caused by certain medical conditions, such as: * Ulcers * Abscesses * Upper respiratory tract infections * Inflammation or infection of the mouth, tongue, or throat ( esophagitis, pharyngitis, tonsillitis Tonsillitis is inflammation of the tonsils in the upper part of the throat. It can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apyrexy
In pathology, apyrexy, or apyrexia (Greek grc, απυρεξια, from α-, privative, grc, πυρεσσειν, to be in a fever, grc, πυρ, fire, fever) is the normal interval or period of intermission in a fever Fever, also referred to as pyrexia, is defined as having a temperature above the normal range due to an increase in the body's temperature set point. There is not a single agreed-upon upper limit for normal temperature with sources using val .... Also, the absence of a fever.apyrexia. (n.d.) ''Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary''. (2012). Retrieved November 11 2022 from https://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/apyrexia References Fever {{symptom-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ageusia
Ageusia (from negative prefix ''a-'' and Ancient Greek ''γεῦσις'' geûsis 'taste') is the loss of taste functions of the tongue, particularly the inability to detect sweetness, sourness, bitterness, saltiness, and umami (meaning 'pleasant/savory taste'). It is sometimes confused with anosmia – a loss of the sense of smell. Because the tongue can only indicate texture and differentiate between sweet, sour, bitter, salty, and umami, most of what is perceived as the sense of taste is actually derived from smell. True ageusia is relatively rare compared to hypogeusia – a partial loss of taste – and dysgeusia – a distortion or alteration of taste. Causes The main causes of taste disorders are head trauma, infections of upper respiratory tract, exposure to toxic substances, iatrogenic causes, medicines, glossodynia ("burning mouth syndrome (BMS)") and COVID-19. Head trauma can cause lesions in regions of the central nervous system which are involved in processing taste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hiccup
A hiccup (scientific name ''singultus'', from a Latin word meaning "to catch one's breath while sobbing"; also spelled hiccough) is an involuntary contraction ( myoclonic jerk) of the diaphragm that may repeat several times per minute. The hiccup is an involuntary action involving a reflex arc. Once triggered, the reflex causes a strong contraction of the diaphragm followed about a quarter of a second later by closure of the vocal cords, which results in the "hic" sound. Hiccups may occur individually, or they may occur in bouts. The rhythm of the hiccup, or the time between hiccups, tends to be relatively constant. A bout of hiccups generally resolves itself without intervention, although many home remedies are often used to attempt to shorten the duration. Medical treatment is occasionally necessary in cases of chronic hiccups. Incidence Hiccups affect people of all ages, even being observed '' in utero''. They become less frequent with advancing age. Intractable hiccups ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symptom
Signs and symptoms are the observed or detectable signs, and experienced symptoms of an illness, injury, or condition. A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature than normal, raised or lowered blood pressure or an abnormality showing on a medical scan. A symptom is something out of the ordinary that is experienced by an individual such as feeling feverish, a headache or other pain or pains in the body. Signs and symptoms Signs A medical sign is an objective observable indication of a disease, injury, or abnormal physiological state that may be detected during a physical examination, examining the patient history, or diagnostic procedure. These signs are visible or otherwise detectable such as a rash or bruise. Medical signs, along with symptoms, assist in formulating diagnostic hypothesis. Examples of signs include elevated blood pressure, nail clubbing of the fingernails or toenails, staggering gait, and arcus senilis and arcus juvenilis of the eyes. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bloodstream
The blood circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the entire body of a human or other vertebrate. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, that consists of the heart and blood vessels (from Greek ''kardia'' meaning ''heart'', and from Latin ''vascula'' meaning ''vessels''). The circulatory system has two divisions, a systemic circulation or circuit, and a pulmonary circulation or circuit. Some sources use the terms ''cardiovascular system'' and ''vascular system'' interchangeably with the ''circulatory system''. The network of blood vessels are the great vessels of the heart including large elastic arteries, and large veins; other arteries, smaller arterioles, capillaries that join with venules (small veins), and other veins. The circulatory system is closed in vertebrates, which means that the blood never leaves the network of blood vessels. Some invertebrates such as arth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bed Nets
A mosquito net is a type of meshed curtain that is circumferentially draped over a bed or a sleeping area, to offer the sleeper barrier protection against bites and stings from mosquitos, flies, and other pest insects, and thus against the diseases they may carry. Examples of such preventable insect-borne diseases include malaria, dengue fever, yellow fever, zika virus, Chagas disease and various forms of encephalitis, including the West Nile virus. To be effective the mesh of a mosquito net must be fine enough to exclude such insects without obscuring visibility or ventilation to unacceptable levels. It is possible to increase the effectiveness of a mosquito net greatly by pretreating it with an appropriate insecticide or insect repellent. Research has shown mosquito nets to be an extremely effective method of malaria prevention, averting approximately 663 million cases of malaria over the period 2000–2015. History Mosquito netting is mainly used for the protection ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insecticide
Insecticides are substances used to kill insects. They include ovicides and larvicides used against insect eggs and larvae, respectively. Insecticides are used in agriculture, medicine, industry and by consumers. Insecticides are claimed to be a major factor behind the increase in the 20th-century's agricultural productivity. Nearly all insecticides have the potential to significantly alter ecosystems; many are toxic to humans and/or animals; some become concentrated as they spread along the food chain. Insecticides can be classified into two major groups: systemic insecticides, which have residual or long term activity; and contact insecticides, which have no residual activity. The mode of action describes how the pesticide kills or inactivates a pest. It provides another way of classifying insecticides. Mode of action can be important in understanding whether an insecticide will be toxic to unrelated species, such as fish, birds and mammals. Insecticides may be repe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temperate Climate
In geography, the temperate climates of Earth occur in the middle latitudes (23.5° to 66.5° N/S of Equator), which span between the tropics and the polar regions of Earth. These zones generally have wider temperature ranges throughout the year and more distinct seasonal changes compared to tropical climates, where such variations are often small and usually only have precipitation changes. In temperate climates, not only do latitudinal positions influence temperature changes, but sea currents, prevailing wind direction, continentality (how large a landmass is) and altitude also shape temperate climates. The Köppen climate classification defines a climate as "temperate" C, when the mean temperature is above but below in the coldest month to account for the persistency of frost. However, other climate classifications set the minimum at . Zones and climates The north temperate zone extends from the Tropic of Cancer (approximately 23.5° north latitude) to the A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea (abbreviated PNG; , ; tpi, Papua Niugini; ho, Papua Niu Gini), officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea ( tpi, Independen Stet bilong Papua Niugini; ho, Independen Stet bilong Papua Niu Gini), is a country in Oceania that comprises the eastern half of the island of New Guinea and its offshore islands in Melanesia (a region of the southwestern Pacific Ocean north of Australia). Its capital, located along its southeastern coast, is Port Moresby. The country is the world's third largest island country, with an area of . At the national level, after being ruled by three external powers since 1884, including nearly 60 years of Australian administration starting during World War I, Papua New Guinea established its sovereignty in 1975. It became an independent Commonwealth realm in 1975 with Elizabeth II as its queen. It also became a member of the Commonwealth of Nations in its own right. There are 839 known languages of Papua New Guinea, on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |