|
Pitch Drive
The Breakthrough Propulsion Physics Project (BPP) was a research project funded by NASA from 1996-2002 to study various proposals for revolutionary methods of spacecraft propulsion that would require breakthroughs in physics before they could be realized. The project ended in 2002, when the Advanced Space Transportation Program was reorganized and all speculative research (less than Technology readiness level 3) was cancelled. During its six years of operational funding, this program received a total investment of $1.2 million. The Breakthrough Propulsion Physics project addressed a selection of “incremental and affordable” research questions towards the overall goal of propellantless propulsion, hyperfast travel, and breakthrough propulsion methods. It selected and funded five external projects, two in-house tasks and one minor grant. At the end of the project, conclusions into fourteen topics, including these funded projects, were summarized by program manager Marc G. Milli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Research Project
Research is " creative and systematic work undertaken to increase the stock of knowledge". It involves the collection, organization and analysis of evidence to increase understanding of a topic, characterized by a particular attentiveness to controlling sources of bias and error. These activities are characterized by accounting and controlling for biases. A research project may be an expansion on past work in the field. To test the validity of instruments, procedures, or experiments, research may replicate elements of prior projects or the project as a whole. The primary purposes of basic research (as opposed to applied research) are documentation, discovery, interpretation, and the research and development (R&D) of methods and systems for the advancement of human knowledge. Approaches to research depend on epistemologies, which vary considerably both within and between humanities and sciences. There are several forms of research: scientific, humanities, artistic, econom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euclidean Space
Euclidean space is the fundamental space of geometry, intended to represent physical space. Originally, that is, in Euclid's Elements, Euclid's ''Elements'', it was the three-dimensional space of Euclidean geometry, but in modern mathematics there are Euclidean spaces of any positive integer dimension (mathematics), dimension, including the three-dimensional space and the ''Euclidean plane'' (dimension two). The qualifier "Euclidean" is used to distinguish Euclidean spaces from other spaces that were later considered in physics and modern mathematics. Ancient History of geometry#Greek geometry, Greek geometers introduced Euclidean space for modeling the physical space. Their work was collected by the Greek mathematics, ancient Greek mathematician Euclid in his ''Elements'', with the great innovation of ''mathematical proof, proving'' all properties of the space as theorems, by starting from a few fundamental properties, called ''postulates'', which either were considered as eviden ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spacecraft Propulsion
Spacecraft propulsion is any method used to accelerate spacecraft and artificial satellites. In-space propulsion exclusively deals with propulsion systems used in the vacuum of space and should not be confused with space launch or atmospheric entry. Several methods of pragmatic spacecraft propulsion have been developed each having its own drawbacks and advantages. Most satellites have simple reliable chemical thrusters (often monopropellant rockets) or resistojet rockets for orbital station-keeping and some use momentum wheels for attitude control. Soviet bloc satellites have used electric propulsion for decades, and newer Western geo-orbiting spacecraft are starting to use them for north–south station-keeping and orbit raising. Interplanetary vehicles mostly use chemical rockets as well, although a few have used ion thrusters and Hall-effect thrusters (two different types of electric propulsion) to great success. Hypothetical in-space propulsion technologies describe the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interstellar Travel
Interstellar travel is the hypothetical travel of spacecraft from one star system, solitary star, or planetary system to another. Interstellar travel is expected to prove much more difficult than interplanetary spaceflight due to the vast difference in the scale of the involved distances. Whereas the distance between any two planets in the Solar System is less than 30 astronomical units (AU), stars are typically separated by hundreds of thousands of AU, causing these distances to typically be expressed instead in light-years. Because of the vastness of these distances, non-generational interstellar travel based on known physics would need to occur at a high percentage of the speed of light; even so, travel times would be long, at least decades and perhaps millennia or longer. As of 2022, five uncrewed spacecraft, all launched and operated by the United States, have achieved the escape velocity required to leave the Solar System as part of missions to explore parts of the out ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
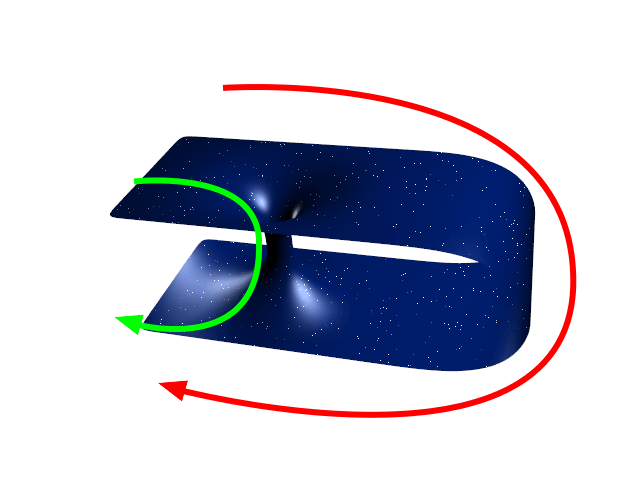
Wormhole
A wormhole (Einstein-Rosen bridge) is a hypothetical structure connecting disparate points in spacetime, and is based on a special Solutions of the Einstein field equations, solution of the Einstein field equations. A wormhole can be visualized as a tunnel with two ends at separate points in spacetime (i.e., different locations, different points in time, or both). Wormholes are consistent with the General relativity, general theory of relativity, but whether wormholes actually exist remains to be seen. Many scientists postulate that wormholes are merely projections of a Four-dimensional space, fourth spatial dimension, analogous to how a two-dimensional (2D) being could experience only part of a three-dimensional (3D) object. Theoretically, a wormhole might connect extremely long distances such as a billion light years, or short distances such as a few meters, or different points in time, or even multiverse, different universes. In 1995, Matt Visser suggested there may be ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Gravity Control Propulsion Research
American interest in "gravity control propulsion research" intensified during the early 1950s. Literature from that period used the terms anti-gravity, anti-gravitation, baricentric, counterbary, electrogravitics (), G-projects, gravitics, gravity control, and gravity propulsion.Gravity Rand Ltd (1956, December). ''The gravitics situation''. In T. Valone (Ed.). (2001, January, 4th ed.) ''Electrogravitics systems: Reports on a new propulsion methodology'' (pp. 42-77). Washington, D.C: Integrity Research Institute. Weyl, A. R. (1957, October). 'Antigravity'. ''Aeronautics'', 37(2), 80-86. (British Aviation Publications). Weyl, A. R. (1959a, January). "Knowledge and possibilities of gravity research" (DTIC No. AD-0830247). W. R. Eichler (Trans.) ''Weltraumfahrt; Zeitschrift für Rakententechnik'', 9, 100-106 (original work published December 1958). Weyl, A. R. (1959b, February). Gravity and the prospects for astronautics. ''Aeronautics'', 59(6), 16-22. (British Aviation Pub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Field Propulsion
Field propulsion is the concept of spacecraft propulsion where no propellant is necessary but instead momentum of the spacecraft is changed by an interaction of the spacecraft with external force fields, such as gravitational and magnetic fields from stars and planets. It is purely speculative and has not yet been demonstrated to be of practical use, or theoretically valid. Types Practical methods Although not presently in wide use for space, there exist proven terrestrial examples of "Field Propulsion", in which electromagnetic fields act upon a conducting medium such as seawater or plasma for propulsion, is known as magnetohydrodynamics or MHD. MHD is similar in operation to electric motors, however rather than using moving parts or metal conductors, fluid or plasma conductors are employed. The EMS-1 and more recently the Yamato 1 are examples of such electromagnetic Field propulsion systems, first described in 1994. There is definitely potential to apply MHD to the space e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AIAA
The American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics (AIAA) is a professional society for the field of aerospace engineering. The AIAA is the U.S. representative on the International Astronautical Federation and the International Council of the Aeronautical Sciences. In 2015, it had more than 30,000 members among aerospace professionals worldwide (a majority are American and/or live in the United States). History The AIAA was founded in 1963 from the merger of two earlier societies: the American Rocket Society (ARS), founded in 1930 as the American Interplanetary Society (AIS), and the Institute of the Aerospace Sciences (IAS), founded in 1932 as the Institute of the Aeronautical Sciences. Paul Johnston was the first executive director of the organization. Jim Harford took his seat after 18 months. The newly-formed structure gathered 47 technical committees and one broad technical publication, the ''AIAA Journal''. The ''AIAA Student Journal'' was also launched in 1963. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Casimir Effect
In quantum field theory, the Casimir effect is a physical force acting on the macroscopic boundaries of a confined space which arises from the quantum fluctuations of the field. It is named after the Dutch physicist Hendrik Casimir, who predicted the effect for electromagnetic systems in 1948. In the same year, Casimir together with Dirk Polder described a similar effect experienced by a neutral atom in the vicinity of a macroscopic interface which is referred to as the Casimir–Polder force. Their result is a generalization of the London–van der Waals force and includes retardation due to the finite speed of light. Since the fundamental principles leading to the London–van der Waals force, the Casimir and the Casimir–Polder force, respectively, can be formulated on the same footing, the distinction in nomenclature nowadays serves a historical purpose mostly and usually refers to the different physical setups. It was not until 1997 that a direct experiment by S. La ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Fluctuation
In quantum physics, a quantum fluctuation (also known as a vacuum state fluctuation or vacuum fluctuation) is the temporary random change in the amount of energy in a point in space, as prescribed by Werner Heisenberg's uncertainty principle. They are minute random fluctuations in the values of the fields which represent elementary particles, such as electric and magnetic fields which represent the electromagnetic force carried by photons, W and Z fields which carry the weak force, and gluon fields which carry the strong force. Vacuum fluctuations appear as virtual particles, which are always created in particle-antiparticle pairs. Since they are created spontaneously without a source of energy, vacuum fluctuations and virtual particles are said to violate the conservation of energy. This is theoretically allowable because the particles annihilate each other within a time limit determined by the uncertainty principle so they are not directly observable. The uncertainty prin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uncertainty Principle
In quantum mechanics, the uncertainty principle (also known as Heisenberg's uncertainty principle) is any of a variety of mathematical inequalities asserting a fundamental limit to the accuracy with which the values for certain pairs of physical quantities of a particle, such as position, ''x'', and momentum, ''p'', can be predicted from initial conditions. Such variable pairs are known as complementary variables or canonically conjugate variables; and, depending on interpretation, the uncertainty principle limits to what extent such conjugate properties maintain their approximate meaning, as the mathematical framework of quantum physics does not support the notion of simultaneously well-defined conjugate properties expressed by a single value. The uncertainty principle implies that it is in general not possible to predict the value of a quantity with arbitrary certainty, even if all initial conditions are specified. Introduced first in 1927 by the German physicist Werner ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Werner Heisenberg
Werner Karl Heisenberg () (5 December 1901 – 1 February 1976) was a German theoretical physicist and one of the main pioneers of the theory of quantum mechanics. He published his work in 1925 in a breakthrough paper. In the subsequent series of papers with Max Born and Pascual Jordan, during the same year, his matrix formulation of quantum mechanics was substantially elaborated. He is known for the uncertainty principle, which he published in 1927. Heisenberg was awarded the 1932 Nobel Prize in Physics "for the creation of quantum mechanics". Heisenberg also made contributions to the theories of the hydrodynamics of turbulent flows, the atomic nucleus, ferromagnetism, cosmic rays, and subatomic particles. He was a principal scientist in the German nuclear weapons program during World War II. He was also instrumental in planning the first West German nuclear reactor at Karlsruhe, together with a research reactor in Munich, in 1957. Following World War II, he was appointed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |