|
Pine Creek (Solomon Creek Tributary)
Pine Creek (also known as Pine Run) is a tributary of Solomon Creek in Luzerne County, Pennsylvania, in the United States. It is approximately long and flows through Bear Creek Township, Laurel Run, and Hanover Township. The watershed of the creek has an area of . The creek is designated as a Coldwater Fishery and a Migratory Fishery and its watershed is inhabited by several species of macroinvertebrates and fish, including trout. A reservoir known as the Pine Run Reservoir is situated on the creek. It is dammed by the Pine Run Dam Number 1. Course Pine Creek begins on a mountain in Bear Creek Township. It flows northwest for a short distance before turning north and flowing off the mountain. After several tenths of a mile, the creek enters the borough of Laurel Run and begins flowing through a valley. It turns west, receives an unnamed tributary from the right and enters Hanover Township. The creek continues west for more than a mile, receiving two unnamed tributaries from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
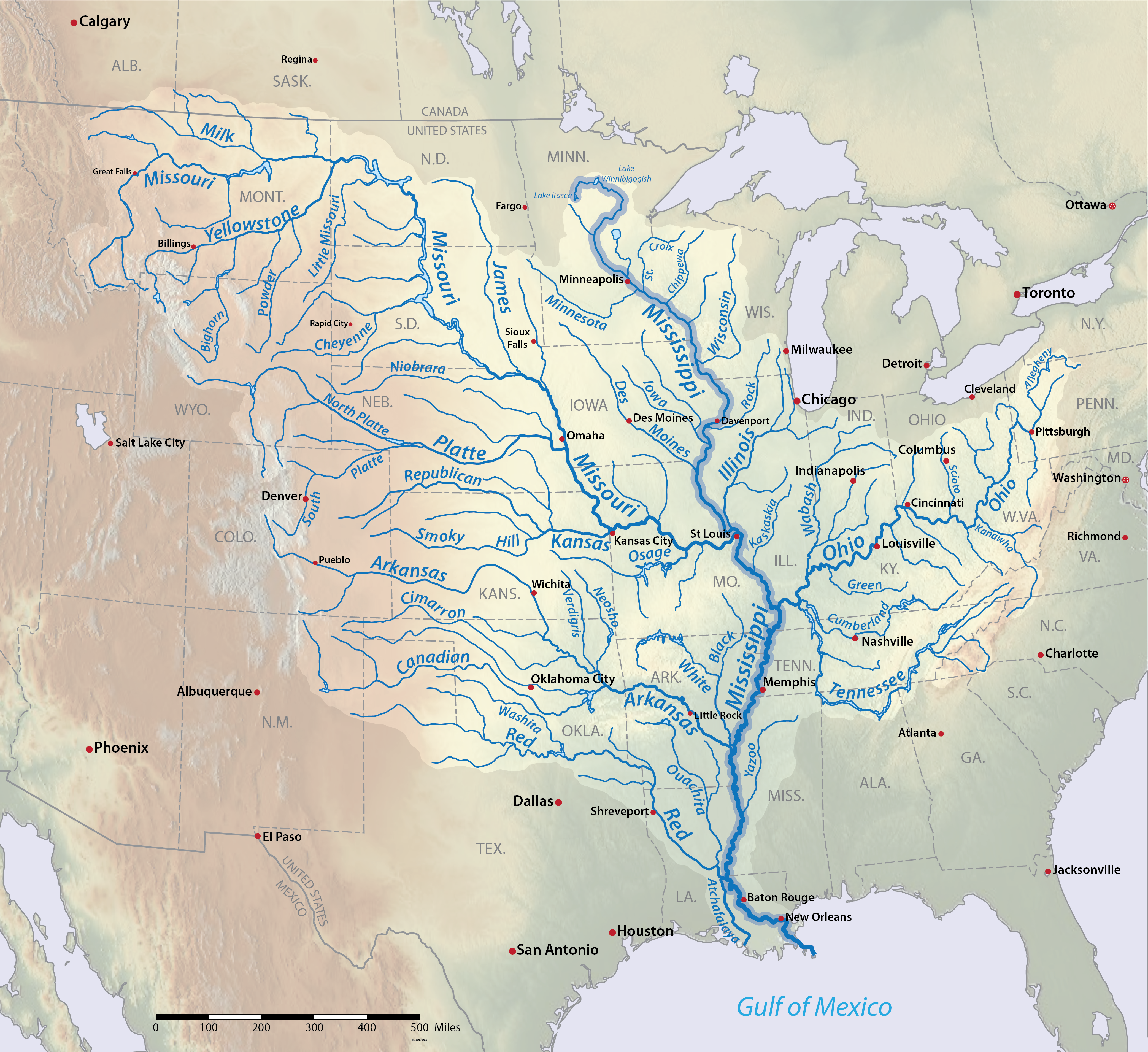
Susquehanna River
The Susquehanna River (; Lenape: Siskëwahane) is a major river located in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States, overlapping between the lower Northeast and the Upland South. At long, it is the longest river on the East Coast of the United States. By watershed area, it is the 16th-largest river in the United States,Susquehanna River Trail Pennsylvania Fish and Boat Commission, accessed March 25, 2010.Susquehanna River , Green Works Radio, accessed March 25, 2010. and also the longest river in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Mouth
A river mouth is where a river flows into a larger body of water, such as another river, a lake/reservoir, a bay/gulf, a sea, or an ocean. At the river mouth, sediments are often deposited due to the slowing of the current reducing the carrying capacity of the water. The water from a river can enter the receiving body in a variety of different ways. The motion of a river is influenced by the relative density of the river compared to the receiving water, the rotation of the earth, and any ambient motion in the receiving water, such as tides or seiches. If the river water has a higher density than the surface of the receiving water, the river water will plunge below the surface. The river water will then either form an underflow or an interflow within the lake. However, if the river water is lighter than the receiving water, as is typically the case when fresh river water flows into the sea, the river water will float along the surface of the receiving water as an overflow. Alon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pennsylvania Code
The ''Pennsylvania Code'' is a publication of the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, listing all rules, regulations, and other administrative documents from the Government of Pennsylvania. Citation Title 1 section 1.2 of the ''Pennsylvania Code'' suggests citation in the following format * The number of the title * The abbreviation "Pa. Code" * The section of the Code (e.g., 1 Pa. Code § 1.2) See also * ''Pennsylvania Bulletin'', a weekly publication of changes to agency rules and regulations * Law of Pennsylvania References External links ''Pennsylvania Code''from pacode.com (Note: Omits some titles, e.g. Title 18) Government of Pennsylvania Pennsylvania Pennsylvania (; ( Pennsylvania Dutch: )), officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, ... Pennsylvania law {{Pennsylvania-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Quality
Water quality refers to the chemical, physical, and biological characteristics of water based on the standards of its usage. It is most frequently used by reference to a set of standards against which compliance, generally achieved through treatment of the water, can be assessed. The most common standards used to monitor and assess water quality convey the health of ecosystems, safety of human contact, extend of water pollution and condition of drinking water. Water quality has a significant impact on water supply and oftentimes determines supply options. Categories The parameters for water quality are determined by the intended use. Work in the area of water quality tends to be focused on water that is treated for potability, industrial/domestic use, or restoration (of an environment/ecosystem, generally for health of human/aquatic life). Human consumption Contaminants that may be in untreated water include microorganisms such as viruses, protozoa and bacteria; inorganic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Supply
Water supply is the provision of water by public utilities, commercial organisations, community endeavors or by individuals, usually via a system of pumps and pipes. Public water supply systems are crucial to properly functioning societies. These systems are what supply drinking water to populations around the globe. Aspects of service quality include continuity of supply, water quality and water pressure. The institutional responsibility for water supply is arranged differently in different countries and regions (urban versus rural). It usually includes issues surrounding policy and regulation, service provision and standardization. The cost of supplying water consists, to a very large extent, of fixed costs (capital costs and personnel costs) and only to a small extent of variable costs that depend on the amount of water consumed (mainly energy and chemicals). Almost all service providers in the world charge tariffs to recover part of their costs. Water supply is a separate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Main Stem
In hydrology, a mainstem (or trunk) is "the primary downstream segment of a river, as contrasted to its tributaries". Water enters the mainstem from the river's drainage basin, the land area through which the mainstem and its tributaries flow.. A drainage basin may also be referred to as a ''watershed'' or ''catchment''. Hydrological classification systems assign numbers to tributaries and mainstems within a drainage basin. In the Strahler number, a modification of a system devised by Robert E. Horton in 1945, channels with no tributaries are called "first-order" streams. When two first-order streams meet, they are said to form a second-order stream; when two second-order streams meet, they form a third-order stream, and so on. In the Horton system, the entire mainstem of a drainage basin was assigned the highest number in that basin. However, in the Strahler system, adopted in 1957, only that part of the mainstem below the tributary of the next highest rank gets the highest num ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geographic Names Information System
The Geographic Names Information System (GNIS) is a database of name and locative information about more than two million physical and cultural features throughout the United States and its territories, Antarctica, and the associated states of the Marshall Islands, Federated States of Micronesia, and Palau. It is a type of gazetteer. It was developed by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) in cooperation with the United States Board on Geographic Names (BGN) to promote the standardization of feature names. Data were collected in two phases. Although a third phase was considered, which would have handled name changes where local usages differed from maps, it was never begun. The database is part of a system that includes topographic map names and bibliographic references. The names of books and historic maps that confirm the feature or place name are cited. Variant names, alternatives to official federal names for a feature, are also recorded. Each feature receives a per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forest
A forest is an area of land dominated by trees. Hundreds of definitions of forest are used throughout the world, incorporating factors such as tree density, tree height, land use, legal standing, and ecological function. The United Nations' Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) defines a forest as, "Land spanning more than 0.5 hectares with trees higher than 5 meters and a canopy cover of more than 10 percent, or trees able to reach these thresholds ''in situ''. It does not include land that is predominantly under agricultural or urban use." Using this definition, '' Global Forest Resources Assessment 2020'' (FRA 2020) found that forests covered , or approximately 31 percent of the world's land area in 2020. Forests are the predominant terrestrial ecosystem of Earth, and are found around the globe. More than half of the world's forests are found in only five countries (Brazil, Canada, China, Russia, and the United States). The largest share of forests (45 percent) are in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Geological Survey
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), formerly simply known as the Geological Survey, is a scientific agency of the United States government. The scientists of the USGS study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, and the natural hazards that threaten it. The organization's work spans the disciplines of biology, geography, geology, and hydrology. The USGS is a fact-finding research organization with no regulatory responsibility. The agency was founded on March 3, 1879. The USGS is a bureau of the United States Department of the Interior; it is that department's sole scientific agency. The USGS employs approximately 8,670 people and is headquartered in Reston, Virginia. The USGS also has major offices near Lakewood, Colorado, at the Denver Federal Center, and Menlo Park, California. The current motto of the USGS, in use since August 1997, is "science for a changing world". The agency's previous slogan, adopted on the occasion of its hundredt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drainage Basin
A drainage basin is an area of land where all flowing surface water converges to a single point, such as a river mouth, or flows into another body of water, such as a lake or ocean. A basin is separated from adjacent basins by a perimeter, the '' drainage divide'', made up of a succession of elevated features, such as ridges and hills. A basin may consist of smaller basins that merge at river confluences, forming a hierarchical pattern. Other terms for a drainage basin are catchment area, catchment basin, drainage area, river basin, water basin, and impluvium. In North America, they are commonly called a watershed, though in other English-speaking places, "watershed" is used only in its original sense, that of a drainage divide. In a closed drainage basin, or endorheic basin, the water converges to a single point inside the basin, known as a sink, which may be a permanent lake, a dry lake, or a point where surface water is lost underground. Drainage basins are similar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
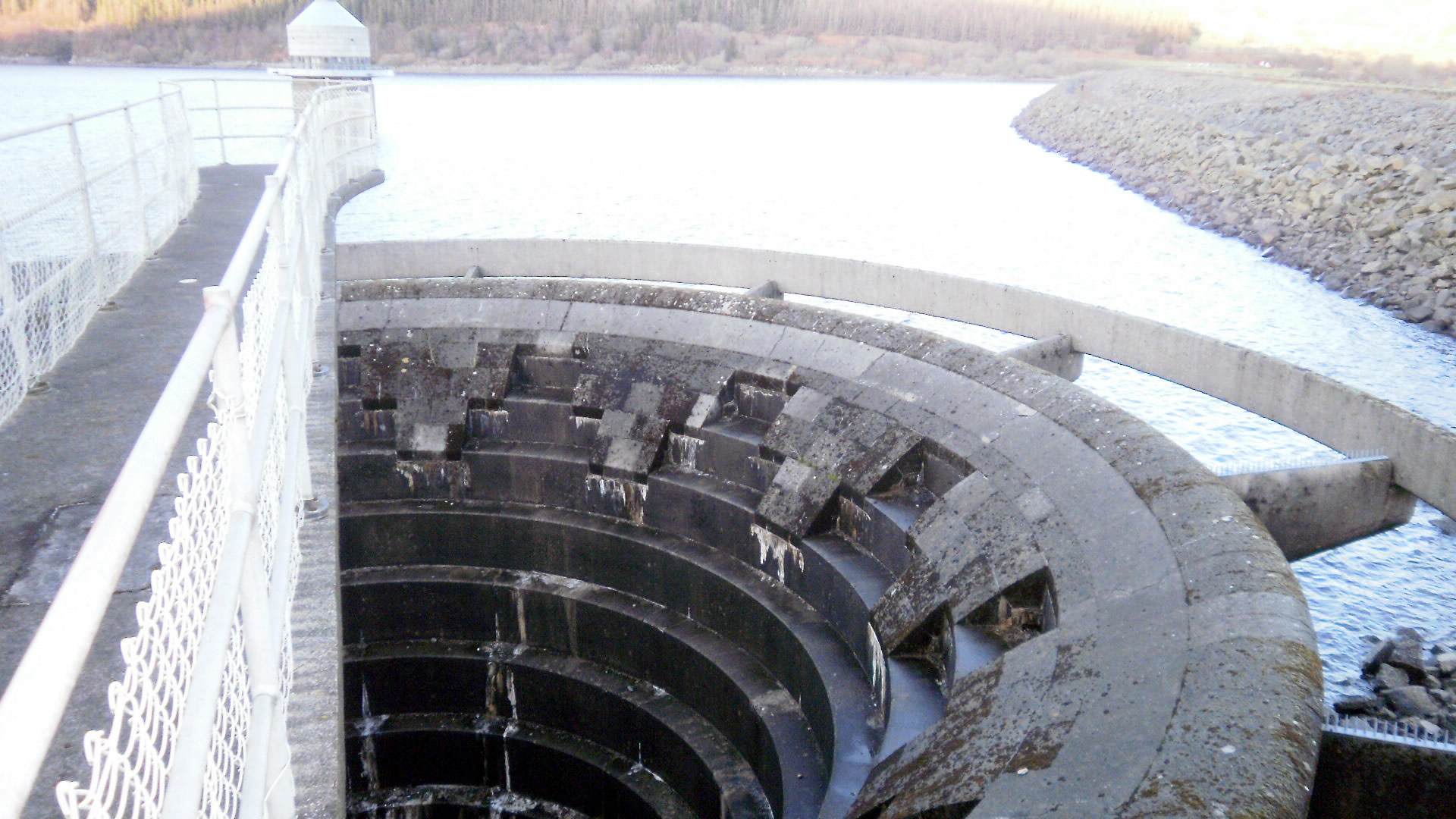
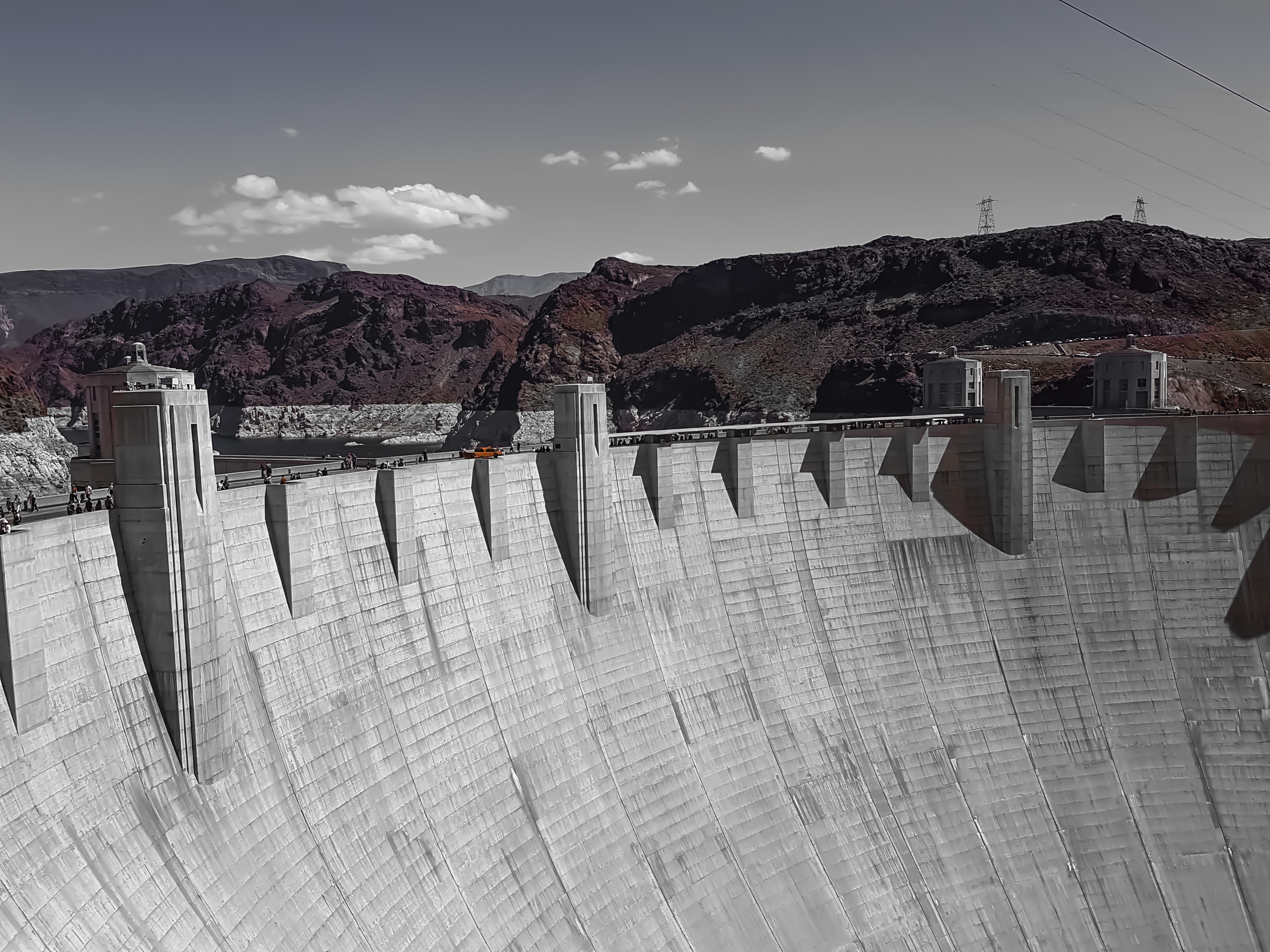
Spillway
A spillway is a structure used to provide the controlled release of water downstream from a dam or levee, typically into the riverbed of the dammed river itself. In the United Kingdom, they may be known as overflow channels. Spillways ensure that water does not damage parts of the structure not designed to convey water. Spillways can include floodgates and fuse plugs to regulate water flow and reservoir level. Such features enable a spillway to regulate downstream flow—by releasing water in a controlled manner before the reservoir is full, operators can prevent an unacceptably large release later. Other uses of the term "spillway" include bypasses of dams and outlets of channels used during high water, and outlet channels carved through natural dams such as moraines. Water normally flows over a spillway only during flood periods, when the reservoir has reached its capacity and water continues entering faster than it can be released. In contrast, an intake tower is a structure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concrete
Concrete is a composite material composed of fine and coarse aggregate bonded together with a fluid cement (cement paste) that hardens (cures) over time. Concrete is the second-most-used substance in the world after water, and is the most widely used building material. Its usage worldwide, ton for ton, is twice that of steel, wood, plastics, and aluminum combined. Globally, the ready-mix concrete industry, the largest segment of the concrete market, is projected to exceed $600 billion in revenue by 2025. This widespread use results in a number of environmental impacts. Most notably, the production process for cement produces large volumes of greenhouse gas emissions, leading to net 8% of global emissions. Other environmental concerns include widespread illegal sand mining, impacts on the surrounding environment such as increased surface runoff or urban heat island effect, and potential public health implications from toxic ingredients. Significant research and development is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)