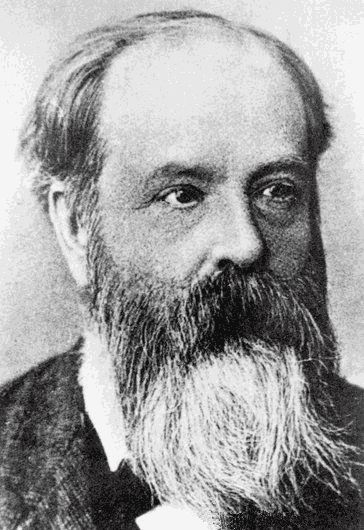|
Physical Society Of London
The Physical Society of London, England, was a scientific society which was founded in 1874. In 1921, it was renamed the Physical Society, and in 1960 it merged with the Institute of Physics (IOP), the combined organisation eventually adopting the name of the latter society. The society was founded due to the efforts of Frederick Guthrie, Professor of Physics at the Royal College of Science, South Kensington, and his assistant, William Fletcher Barrett. They canvassed support for a 'Society for physical research' and on 14 February 1874, the Physical Society of London was formed with an initial membership of 29 people. The Society's first president was John Hall Gladstone. Meetings were held every two weeks, mainly at Imperial College London. From its beginning, the society held open meetings and demonstrations and published '' Proceedings of the Physical Society of London''. The first Guthrie lecture, now known as the Faraday Medal and Prize, was delivered in 1914. In 1921 the so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick Guthrie
Frederick Guthrie FRS FRSE (15 October 1833 – 21 October 1886) was a British physicist and chemist and academic author. He was the son of Alexander Guthrie, a London tradesman, and the younger brother of mathematician Francis Guthrie. Along with William Fletcher Barrett he founded the Physical Society of London (now the Institute of Physics) in 1874 and was president of the society from 1884 until 1886. He believed that science should be based on experimentation rather than discussion. Academic career His academic career started at University College, London, where he studied for three years. He studied chemistry under Thomas Graham and Alexander William Williamson and mathematics under Augustus De Morgan. In 1852, he submitted his brother Francis's observations to De Morgan. In 1854 Guthrie went to Heidelberg to study under Robert Bunsen and then in 1855 obtained a PhD at the University of Marburg under Adolph Wilhelm Hermann Kolbe. In 1856 he joined Edward Frankland, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Bellamy Clifton
Robert Bellamy Clifton Fellow of the Royal Society, FRS (13 March 1836 – 21 February 1921) was a British scientist. Academic career Clifton was educated at University College, London and St John's College, Cambridge where he studied under Sir George Stokes. In 1860 he went to Owens College, Manchester as Professor of Natural Philosophy. In 1865 he was appointed Professor of experimental Natural Philosophy at Oxford University. While at Oxford he designed Clarendon Laboratory and gave research space to Charles Vernon Boys. On 4 June 1868 he became a fellow of the Royal Society. He was president of the Physical Society of London, Physical Society (now Institute of Physics) from 1882 until 1884. From 1868 until his retirement in 1915 he was a Fellow of Merton College, Oxford. Family Clifton's father was the clergyman Robert Cox Clifton. His daughter Catharine Edith was married to the surgeon Henry Souttar. References 1836 births 1921 deaths British physicists British ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Chree
200px, Charles Chree (circa 1900) Charles Chree, FRS (5 May 1860 – 12 August 1928) was a British physicist, an authority on terrestrial magnetism and atmospheric electricity, and for 32 years Superintendent of Kew Observatory. Chree was born in Lintrathen, Forfarshire, Scotland on 5 May 1860, second son to Rev Charles Chree.Obituary Dr Charles Chree, The Times Tuesday Aug 14 1928 He was educated at the Grammar School, Old Aberdeen, the University of Aberdeen where he graduated MA in 1879 and the University of Cambridge where he graduated as Sixth Wrangler (MA, 1883). Chree was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society in 1897, his candidacy citation listing his achievements as: "''Author of the following memoirs, and of many others on analogous subjects - 1. Effects of pressure on the Magnetisation of Cobalt, Phil Trans: 1890 2. Conduction of heat in liquids, Proc: R. Soc: 1887. 3. Stresses and strains in isotropic, elastic, solid ellipsoids, etc, Proc: R. Soc: 1895. 4. A solu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Perry (engineer)
John Perry (14 February 1850 – 4 August 1920) was a pioneering engineer and mathematician from Ireland. Life He was born on 14 February 1850 at Garvagh, County Londonderry, the second son of Samuel Perry and a Scottish-born wife. John's brother James was the County Surveyor in Galway West and co-founded the Galway Electric Light Company. One of his daughters, Alice, was the one of the first women in the world with an engineering degree. Perry worked as Lord Kelvin's assistant at the University of Glasgow, and later became professor of mechanical engineering at Finsbury Technical College. He was a colleague of William Edward Ayrton and John Milne at the Imperial College of Engineering in Tokyo, 1875–79, and was also a Fellow of the Royal Society. He was professor of mathematics at Imperial College in London from 1896 to 1913. In 1900 he was elected president of the Institution of Electrical Engineers, and from 1906–08 served as president of the Physical Society of London ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Henry Poynting
John Henry Poynting FRS (9 September 185230 March 1914) was an English physicist. He was the first professor of physics at Mason Science College from 1880 to 1900, and then the successor institution, the University of Birmingham until his death. Biography Poynting was the youngest son of Thomas Elford Poynting, a Unitarian minister. He was born at the parsonage of the Monton Unitarian Chapel in Eccles, Lancashire (his father serving as minister there from 1846 to 1878.) In his boyhood he was educated at the nearby school operated by his father. From 1867 to 1872 he attended Owens College, now the University of Manchester, where his physics teachers included Osborne Reynolds and Balfour Stewart. From 1872 to 1876 he was a student at Cambridge University, where he attained high honours in mathematics after taking grinds with Edward Routh. In the late 1870s he worked in the Cavendish Laboratory at Cambridge under James Clerk Maxwell. In 1880, he became the first professor of phys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Glazebrook
Sir Richard Tetley Glazebrook (18 September 1854 – 15 December 1935) was an English physicist. Education and early career Glazebrook was born in West Derby, Liverpool, Lancashire, the son of a surgeon. He was educated at Dulwich College until 1870, Liverpool College from 1870 to 1872, and Trinity College, Cambridge, from which he graduated in Mathematics in 1876 and of which he was elected a fellow in 1877. He studied physics under James Clerk Maxwell and John Strutt, 3rd Baron Rayleigh, Lord Rayleigh at the new Cavendish Laboratory and in 1880 was appointed a demonstrator at the laboratory. The following year he was also appointed a college lecturer in mathematics and physics and a university lecturer in mathematics. His research focused on electrical standards and aviation. When defining electrical standards for the unit of resistance, the British Science Association were trying to determine what length a mercury column should be, to express the absolute value of the Ohm. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silvanus P
Silvanus or Sylvanus may refer to: *Silas (Silvanus), disciple, mentioned in four New Testament epistles * Silvanus (monk), one of the Desert Fathers *Silvanus of the Seventy, a traditional figure in Eastern Orthodox tradition assumed to be one of the Seventy Apostles *Silvanus (mythology), a Roman tutelary deity or spirit of woods and fields *Silvanus (name), a surname and given name (and list of people with the name) * Silvanus (''Forgotten Realms''), a fictional deity in the ''Forgotten Realms'' setting of ''Dungeons & Dragons'' * Sylvanus, Michigan, a village * ''Silvanus'' (genus), a genus of beetles See also *''Teachings of Silvanus'', a text from the Nag Hammadi library * Sylvanus Selleck Gristmill, a gristmill built in 1796 in Greenwich, Connecticut * Sylvanus Thayer Award, an award that is given each year by the United States Military Academy at West Point *Silvain (other) *Silvan (other) *Sylvain (other) Sylvain is the French form of Silvanus. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oliver Lodge
Sir Oliver Joseph Lodge, (12 June 1851 – 22 August 1940) was a British physicist and writer involved in the development of, and holder of key patents for, radio. He identified electromagnetic radiation independent of Heinrich Rudolf Hertz, Hertz's proof and at his 1894 Royal Institution lectures ("''The Work of Hertz and Some of His Successors''"), Lodge demonstrated an early radio wave detector he named the "coherer". In 1898 he was awarded the "syntonic" (or tuning) patent by the United States Patent Office. Lodge was Principal of the University of Birmingham from 1900 to 1920. Lodge was also noted for his Spiritualism, Spiritualist beliefs and pseudoscience, pseudoscientifc research into life after death, a topic on which he wrote many books, including the best-selling ''Raymond; or, Life and Death'' (1916), describing what he believed to be detailed messages through a mediumship, medium from his deceased adult son who was killed in World War I. Life Oliver Lodge was b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shelford Bidwell
Shelford Bidwell FRS (6 March 1848 – 18 December 1909) was an English physicist and inventor. He is best known for his work with "telephotography", a precursor to the modern fax machine. Private life He was born in Thetford, Norfolk the eldest son of Shelford Clarke Bidwell, a brewer, and his wife Georgina, the daughter of George Bidwell of Stanton, Norfolk. He entered Caius College, Cambridge, graduating BA (1870), MA (1873) and LLB (1873). Called to the bar from Lincoln's Inn in 1873, he practised as a barrister on the South Eastern Circuit for several years before becoming interested in electronics. He married in 1874 Anna Wilhelmina Evelyn, daughter of Edward Firmstone, rector of Wyke (Regis), the mother church of Weymouth who lived much of later life with his family in Winchester to be close to Winchester Cathedral. Bidwell was the head of a wealthy Victorian family from 1881 to at least 1901, having five servants, at Riverstone, Wimbledon Park Road, Southfields, Lond ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William De Wiveleslie Abney
Sir William de Wiveleslie Abney (24 July 1843 – 3 December 1920) was an English astronomer, chemist, and photographer. Life and career Abney was born in Derby, England, the son of Rev. Edward Abney (1811–1892), vicar of St Alkmund's Church, Derby, and owner of the Firs Estate. William was educated at Rossall School, the Royal Military Academy, Woolwich, and joined the Royal Engineers in 1861, with whom he served in India for several years. Thereafter, and to further his knowledge in photography, he became a chemical assistant at the Chatham School of Military Engineering. Abney was a pioneer of several technical aspects of photography. His father had been an early photographic experimenter and friend of Richard Keene, an early Derby photographer. Keene became a close friend of William and his brother Charles Edward Abney (1850–1914). Both Abney sons subsequently became founder members of the Derby Photographic Society in June 1884. His endeavors in the chemistry of p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur William Rucker
Sir Arthur William Rucker (or Rücker) (23 October 1848, Clapham Park, London, England – 1 November 1915, Yattendon, Berkshire) was a British physicist. Education and career Rucker gained his BA at Brasenose College, Oxford, in 1871, and was a Fellow there from 1871 to 1876. He was Professor of Physics, and the first Cavendish Professor at Yorkshire College, Leeds from 1874 to 1885. Rucker was then a Professor of Physics at the Royal College of Science from 1886 to 1901, when he left to become Principal of the University of London. He received the honorary degree ''Doctor of Science'' (D.Sc.) from the University of Cambridge in May 1902, and from the University of Oxford in June 1902. Royal Society He was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society in 1884. He jointly gave the Royal Society's Bakerian Lecture in 1889, and was awarded the Royal Society's Royal Medal in 1891: "For his researches on liquid films, and his contributions to our knowledge of terrestrial magnetism". He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Francis FitzGerald
Prof George Francis FitzGerald (3 August 1851 – 22 February 1901) was an Irish academic and physicist who served as Erasmus Smith's Professor of Natural and Experimental Philosophy at Trinity College Dublin (TCD) from 1881 to 1901. FitzGerald is known for his work in electromagnetic theory and for the Lorentz–FitzGerald contraction, which became an integral part of Albert Einstein's special theory of relativity. A crater on the far side of the Moon is named after him, as is a building at TCD. Life and work in physics FitzGerald was born at No. 19, Lower Mount Street in Dublin on 3 August 1851 to the Reverend William FitzGerald and his wife Anne Frances Stoney (sister of George Johnstone Stoney and Bindon Blood Stoney). Professor of Moral Philosophy in Trinity and vicar of St Anne's, Dawson Street, at the time of his son's birth, William FitzGerald was consecrated Bishop of Cork, Cloyne and Ross in 1857 and translated to Killaloe and Clonfert in 1862. George returne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |