|
Phosphorus Selenide
Phosphorus selenides are a relatively obscure group of compounds. There have been some studies of the phosphorus - selenium phase diagram and the glassy amorphous phases are reported. The compounds that have been reported are shown below. While some of phosphorus selenides are similar to their sulfide analogues, there are some new forms, molecular and the polymeric ''catena''-. There is also some doubt about the existence of molecular . Crystallographically confirmed compounds Molecular has a norbornane like structure with two phosphorus atoms with oxidation state +3 bridged by two diselenide units (, analogous to disulfide) and one selenide unit (). It was isolated by solvent ( ) extraction from a amorphous phase made from the elements. has been characterised crystallographically and has the same structure as the low temperature form of . It can be prepared from the elements. One preparation is to extract and recrystallise using tetralin. The molecule has the same struct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphorus Sulfides
Phosphorus sulfides comprise a family of inorganic compounds containing only phosphorus and sulfur. These compounds have the formula with ''n'' ≤ 10. Two are of commercial significance, phosphorus pentasulfide (), which is made on a kiloton scale for the production of other organosulfur compounds, and phosphorus sesquisulfide (), used in the production of "strike anywhere matches". There are several other phosphorus sulfides in addition to and . Six of these phosphorus sulfides exist as isomers: . These isomers are distinguished by Greek letter prefixes. The prefix is based on the order of the discovery of the isomers, not their structure. All known molecular phosphorus sulfides contain a tetrahedral array of four phosphorus atoms. is also known but is unstable above −30 °C. Preparation The main method for preparing these compounds is thermolysis of mixtures of phosphorus and sulfur. The product distributions can be analyzed by 31P-NMR spectroscopy. More selectiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
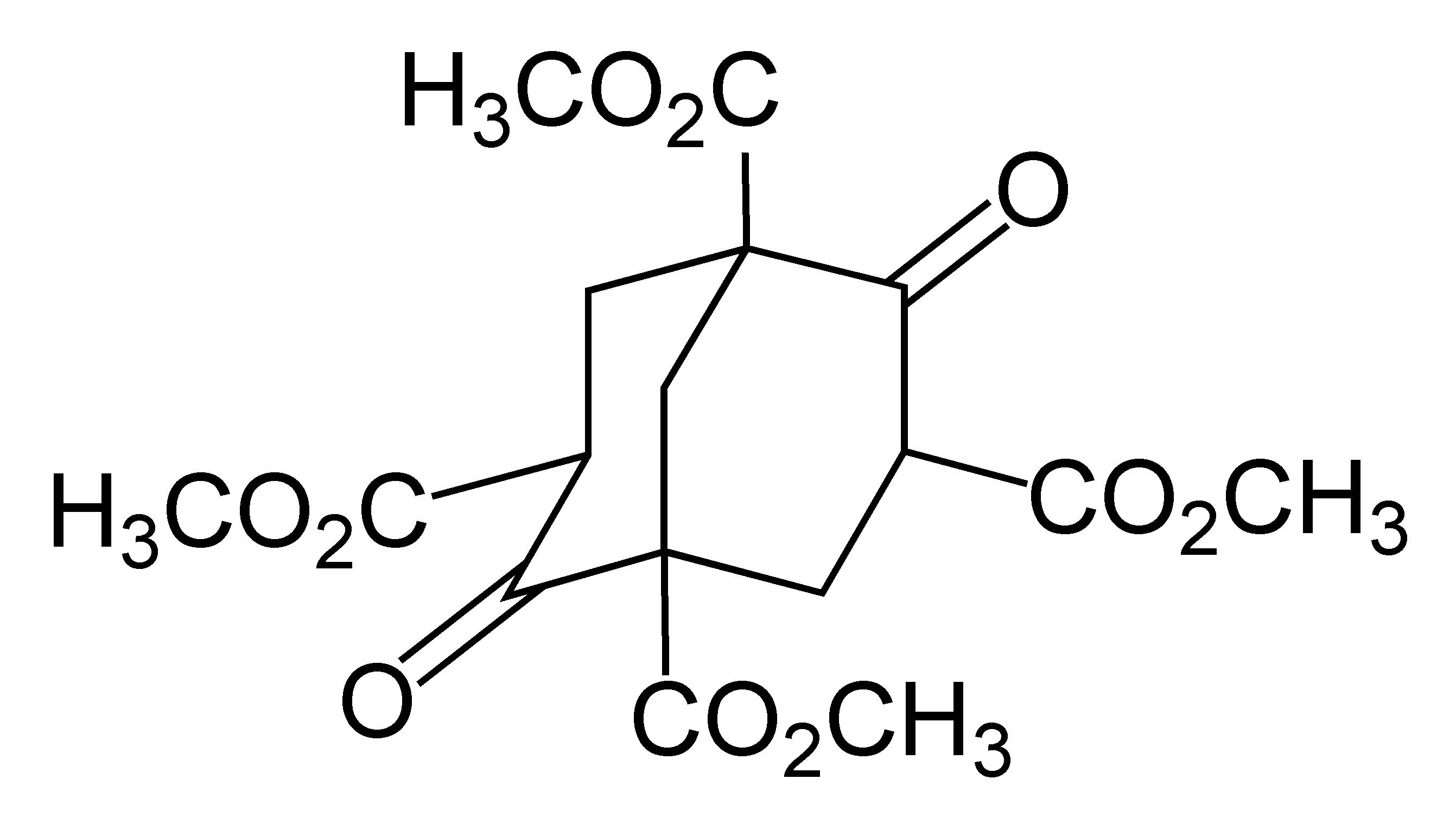
Norbornane
Norbornane (also known as bicyclo .2.1eptane) is an organic compound and a saturated hydrocarbon with chemical formula C7H12. It is a crystalline compound with a melting point of 88 °C. The carbon skeleton is derived from cyclohexane ring with a methylene bridge in the 1,4- position, and is a bridged bicyclic compound. The compound is a prototype of a class of strained bicyclic hydrocarbons. The compound was originally synthesized by reduction of norcamphor. The name norbornane is derived from bornane, which is 1,7,7-trimethylnorbornane, being a derivative of camphor (bornanone). The prefix ''nor'' refers to the stripping of the methyl groups from the parent molecule bornane. See also * 2-Norbornyl cation * Norbornene * Norbornadiene * Bornane * endo-Norborneol * exo-Norborneol * Norcamphor Norcamphor is an organic compound, classified as a bicyclic ketone. It is an analog of camphor, but without the three methyl groups. A colorless solid, it is used as a building block ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diselenide
Diselenide may refer to: *Diselane, H-Se-Se-H *Carbon diselenide, CSe2, a yellow-orange oily liquid with pungent odor * Any organic chemical compound with a selenium-selenium bond, R-Se-Se-R **Diphenyl diselenide, (C6H5)–Se–Se–(C6H5) *Metal dichalcogenides **Manganese diselenide (MnSe2) **Molybdenum diselenide (MoSe2) **Tungsten diselenide Tungsten diselenide is an inorganic compound with the formula WSe2. The compound adopts a hexagonal crystalline structure similar to molybdenum disulfide. Every tungsten atom is covalently bonded to six selenium ligands in a trigonal prismatic c ... (WSe2) ** Titanium diselenide (TiSe2) {{Chemistry index ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disulfide
In biochemistry, a disulfide (or disulphide in British English) refers to a functional group with the structure . The linkage is also called an SS-bond or sometimes a disulfide bridge and is usually derived by the coupling of two thiol groups. In biology, disulfide bridges formed between thiol groups in two cysteine residues are an important component of the secondary and tertiary structure of proteins. ''Persulfide'' usually refers to compounds. In inorganic chemistry disulfide usually refers to the corresponding anion (−S−S−). Organic disulfides Symmetrical disulfides are compounds of the formula . Most disulfides encountered in organo sulfur chemistry are symmetrical disulfides. Unsymmetrical disulfides (also called heterodisulfides) are compounds of the formula . They are less common in organic chemistry, but most disulfides in nature are unsymmetrical. Properties The disulfide bonds are strong, with a typical bond dissociation energy of 60 kcal/mol (251&nbs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Disulfide
Carbon disulfide (also spelled as carbon disulphide) is a neurotoxic, colorless, volatile liquid with the formula and structure . The compound is used frequently as a building block in organic chemistry as well as an industrial and chemical non-polar solvent. It has an "ether-like" odor, but commercial samples are typically contaminated with foul-smelling impurities.. It is of comparable toxicity to carbon monoxide. History In 1796, the German chemist Wilhelm August Lampadius (1772–1842) first prepared carbon disulfide by heating pyrite with moist charcoal. He called it "liquid sulfur" (''flüssig Schwefel''). The composition of carbon disulfide was finally determined in 1813 by the team of the Swedish chemist Jöns Jacob Berzelius (1779–1848) and the Swiss-British chemist Alexander Marcet (1770–1822). Their analysis was consistent with an empirical formula of CS2. Occurrence, manufacture, properties Small amounts of carbon disulfide are released by volcanic eruptio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetralin
Tetralin (1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalene) is a hydrocarbon having the chemical formula C10H12. It is a partially hydrogenated derivative of naphthalene. It is a colorless liquid that is used as a hydrogen-donor solvent. Production Tetralin is produced by the catalytic hydrogenation of naphthalene. Although nickel catalysts are traditionally employed, many variations have been evaluated. Over-hydrogenation converts tetralin into decahydronaphthalene (decalin). Rarely encountered is dihydronaphthalene (dialin). Laboratory methods In a classic named reaction called the Darzens tetralin synthesis, named for Auguste Georges Darzens (1926), derivatives can be prepared by intramolecular electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction of a 1-aryl-4-pentene using concentrated sulfuric acid, Uses Tetralin is used as a hydrogen-donor solvent, for example in coal liquifaction. It functions as a source of H2, which is transferred to the coal. The partially hydrogenated coal is more solu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bromine
Bromine is a chemical element with the symbol Br and atomic number 35. It is the third-lightest element in group 17 of the periodic table (halogens) and is a volatile red-brown liquid at room temperature that evaporates readily to form a similarly coloured vapour. Its properties are intermediate between those of chlorine and iodine. Isolated independently by two chemists, Carl Jacob Löwig (in 1825) and Antoine Jérôme Balard (in 1826), its name was derived from the Ancient Greek (bromos) meaning "stench", referring to its sharp and pungent smell. Elemental bromine is very reactive and thus does not occur as a native element in nature but it occurs in colourless soluble crystalline mineral halide salts, analogous to table salt. In fact, bromine and all the halogens are so reactive that they form bonds in pairs—never in single atoms. While it is rather rare in the Earth's crust, the high solubility of the bromide ion (Br) has caused its accumulation in the oceans. Commercial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Disulfide
Carbon disulfide (also spelled as carbon disulphide) is a neurotoxic, colorless, volatile liquid with the formula and structure . The compound is used frequently as a building block in organic chemistry as well as an industrial and chemical non-polar solvent. It has an "ether-like" odor, but commercial samples are typically contaminated with foul-smelling impurities.. It is of comparable toxicity to carbon monoxide. History In 1796, the German chemist Wilhelm August Lampadius (1772–1842) first prepared carbon disulfide by heating pyrite with moist charcoal. He called it "liquid sulfur" (''flüssig Schwefel''). The composition of carbon disulfide was finally determined in 1813 by the team of the Swedish chemist Jöns Jacob Berzelius (1779–1848) and the Swiss-British chemist Alexander Marcet (1770–1822). Their analysis was consistent with an empirical formula of CS2. Occurrence, manufacture, properties Small amounts of carbon disulfide are released by volcanic eruptio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphorus Pentasulfide
Phosphorus pentasulfide is the inorganic compound with the formula (monomer) or (dimer). This yellow solid is the one of two phosphorus sulfides of commercial value. Samples often appear greenish-gray due to impurities. It is soluble in carbon disulfide but reacts with many other solvents such as alcohols, DMSO, and DMF. Structure and synthesis Its tetrahedral molecular structure is similar to that of adamantane and almost identical to the structure of phosphorus pentoxide. Phosphorus pentasulfide is obtained by the reaction of liquid white phosphorus () with sulfur above 300 °C. The first synthesis of by Berzelius in 1843 was by this method. Alternatively, can be formed by reacting elemental sulfur or pyrite, , with ferrophosphorus, a crude form of (a byproduct of white phosphorus () production from phosphate rock): : : Applications Approximately 150,000 tons of are produced annually. The compound is mainly converted to other derivatives for use as lubrication ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphorus Pentoxide
Phosphorus pentoxide is a chemical compound with molecular formula P4 O10 (with its common name derived from its empirical formula, P2O5). This white crystalline solid is the anhydride of phosphoric acid. It is a powerful desiccant and dehydrating agent. Structure Phosphorus pentoxide crystallizes in at least four forms or polymorphs. The most familiar one, a metastable form (shown in the figure), comprises molecules of P4O10. Weak van der Waals forces hold these molecules together in a hexagonal lattice (However, in spite of the high symmetry of the molecules, the crystal packing is not a close packing). The structure of the P4O10 cage is reminiscent of adamantane with ''T''d symmetry point group. It is closely related to the corresponding anhydride of phosphorous acid, P4O6. The latter lacks terminal oxo groups. Its density is 2.30 g/cm3. It boils at 423 °C under atmospheric pressure; if heated more rapidly it can sublimate. This form can be made by condensing the vap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adamantane
Adamantane is an organic compound with a formula C10H16 or, more descriptively, (CH)4(CH2)6. Adamantane molecules can be described as the fusion of three cyclohexane rings. The molecule is both rigid and virtually stress-free. Adamantane is the most stable isomer of C10H16. The spatial arrangement of carbon atoms in the adamantane molecule is the same as in the diamond crystal. This similarity led to the name ''adamantane'', which is derived from the Greek ''adamantinos'' (relating to steel or diamond). It is a white solid with a camphor-like odor. It is the simplest diamondoid. The discovery of adamantane in petroleum in 1933 launched a new field of chemistry dedicated to the synthesis and properties of polyhedral organic compounds. Adamantane derivatives have found practical application as drugs, polymeric materials, and thermally stable lubricants. History and synthesis In 1924, H. Decker suggested the existence of adamantane, which he called decaterpene. The first attempted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphorus-31 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
Phosphorus-31 NMR spectroscopy is an analytical chemistry technique that uses nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) to study chemical compounds that contain phosphorus. Phosphorus is commonly found in organic compounds and coordination complexes (as phosphines), making it useful to measure 31P NMR spectra routinely. Solution 31P-NMR is one of the more routine NMR techniques because 31P has an isotopic abundance of 100% and a relatively high gyromagnetic ratio. The 31P nucleus also has a spin of , making spectra relatively easy to interpret. The only other highly sensitive NMR-active nuclei spin that are monoisotopic (or nearly so) are 1H and 19F. Operational aspects With a gyromagnetic ratio 40.5% of that for 1H, 31P NMR signals are observed near 202 MHz on an 11.7- Tesla magnet (used for 500 MHz 1H NMR measurements). Chemical shifts are referenced to 85% phosphoric acid, which is assigned the chemical shift of 0, with positive shifts to low field/high frequency. Due to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |