|
Phlebodium Decumanum
''Phlebodium'' is a small genus of ferns in the family Polypodiaceae, subfamily Polypodioideae, according to the Pteridophyte Phylogeny Group classification of 2016 (PPG I). It is native to tropical and subtropical regions of the Americas.Ferns of the World''Phlebodium''Flora of North America''Phlebodium''/ref>Germplasm Resources Information Network''Phlebodium''/ref> Its species were formerly included in ''Polypodium''. They are epiphytic ferns, with a creeping, densely hairy or scaly rhizome bearing fronds at intervals along its length. The fronds are evergreen, persisting for 1–2 years, and are pinnatifid. The sori or groups of spore-cases (sporangia) are borne on the back of the frond. Species , ''Checklist of Ferns and Lycophytes of the World'' accepted the following species: *''Phlebodium areolatum'' (Humb. & Bonpl. ex Willd.) J.Sm., including ''Phlebodium araneosum'' (M.Martens & Galeotti) Mickel & Beitel and ''Phlebodium pseudoaureum'' (Cav.) Lellinger *''Phlebo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Brown (botanist, Born 1773)
Robert Brown (21 December 1773 – 10 June 1858) was a Scottish botanist and paleobotanist who made important contributions to botany largely through his pioneering use of the microscope. His contributions include one of the earliest detailed descriptions of the cell nucleus and cytoplasmic streaming; the observation of Brownian motion; early work on plant pollination and fertilisation, including being the first to recognise the fundamental difference between gymnosperms and angiosperms; and some of the earliest studies in palynology. He also made numerous contributions to plant taxonomy, notably erecting a number of plant families that are still accepted today; and numerous Australian plant genera and species, the fruit of his exploration of that continent with Matthew Flinders. Early life Robert Brown was born in Montrose on 21 December 1773, in a house that existed on the site where Montrose Library currently stands. He was the son of James Brown, a minister in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhizome
In botany and dendrology, a rhizome (; , ) is a modified subterranean plant stem that sends out roots and shoots from its nodes. Rhizomes are also called creeping rootstalks or just rootstalks. Rhizomes develop from axillary buds and grow horizontally. The rhizome also retains the ability to allow new shoots to grow upwards. A rhizome is the main stem of the plant that runs underground horizontally. A stolon is similar to a rhizome, but a stolon sprouts from an existing stem, has long internodes, and generates new shoots at the end, such as in the strawberry plant. In general, rhizomes have short internodes, send out roots from the bottom of the nodes, and generate new upward-growing shoots from the top of the nodes. A stem tuber is a thickened part of a rhizome or stolon that has been enlarged for use as a storage organ. In general, a tuber is high in starch, e.g. the potato, which is a modified stolon. The term "tuber" is often used imprecisely and is sometimes applied to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calaguala
Calaguala is an extract from ''Phlebodium decumanum'' (syn. ''Polypodium decumanum''), a type of fern A fern (Polypodiopsida or Polypodiophyta ) is a member of a group of vascular plants (plants with xylem and phloem) that reproduce via spores and have neither seeds nor flowers. The polypodiophytes include all living pteridophytes except t ... used historically for medicinal purposes. It is also known as kalawalla, and a number of other spellings occur. See also Callawalla (other) References Polypodium {{fern-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phlebodium Decumanum
''Phlebodium'' is a small genus of ferns in the family Polypodiaceae, subfamily Polypodioideae, according to the Pteridophyte Phylogeny Group classification of 2016 (PPG I). It is native to tropical and subtropical regions of the Americas.Ferns of the World''Phlebodium''Flora of North America''Phlebodium''/ref>Germplasm Resources Information Network''Phlebodium''/ref> Its species were formerly included in ''Polypodium''. They are epiphytic ferns, with a creeping, densely hairy or scaly rhizome bearing fronds at intervals along its length. The fronds are evergreen, persisting for 1–2 years, and are pinnatifid. The sori or groups of spore-cases (sporangia) are borne on the back of the frond. Species , ''Checklist of Ferns and Lycophytes of the World'' accepted the following species: *''Phlebodium areolatum'' (Humb. & Bonpl. ex Willd.) J.Sm., including ''Phlebodium araneosum'' (M.Martens & Galeotti) Mickel & Beitel and ''Phlebodium pseudoaureum'' (Cav.) Lellinger *''Phlebo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phlebodium Aureum
''Phlebodium aureum'' (golden polypody, golden serpent fern, cabbage palm fern, gold-foot fern, blue-star fern, hare-foot fern; syn. ''Polypodium aureum'', ''Polypodium leucotomos'') is an epiphytic fern native to tropical and subtropical regions of the Americas. Description It is a rhizomatous fern, with the creeping rhizome 8–15 mm (rarely 30 mm) in diameter, densely covered in the golden-brown scales that give the species its name. The fronds are large and pinnatifid (deeply lobed), from 30–130 cm long and 10–50 cm broad, with up to 35 pinnae; they vary in color from bright green to glaucous green and have undulate margins. Several round sori run along each side of the pinna midrib, and the minute spores are wind-dispersed. The fronds are evergreen in areas with year-round rainfall, semi-evergreen or briefly deciduous in areas with a marked dry season. Distribution It is confined to the eastern side of the continents, extending north into the United States to Florida ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phlebodium Areolatum
''Phlebodium areolatum'', the Virginia blue fern, is a species of epiphytic fern in the family Polypodiaceae. It is native to the New World Tropics and Subtropics; Mexico, Florida, some of the Caribbean islands, Central America, and South America to Argentina, and has been introduced to India. As its synonym ''Phlebodium pseudoaureum'' it has gained the Royal Horticultural Society's Award of Garden Merit The Award of Garden Merit (AGM) is a long-established annual award for plants by the British Royal Horticultural Society (RHS). It is based on assessment of the plants' performance under UK growing conditions. History The Award of Garden Merit .... References Polypodiaceae Ferns of the Americas Flora of Florida Flora of Mexico Flora of Central America Flora of the Dominican Republic Flora of Haiti Flora of Jamaica Flora of the Leeward Islands Flora of Puerto Rico Flora of Trinidad and Tobago Flora of northern South America Flora of western South America Flo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sporangium
A sporangium (; from Late Latin, ) is an enclosure in which spores are formed. It can be composed of a single cell or can be multicellular. Virtually all plants, fungi, and many other lineages form sporangia at some point in their life cycle. Sporangia can produce spores by mitosis, but in nearly all land plants and many fungi, sporangia are the site of meiosis and produce genetically distinct haploid spores. Fungi In some phyla of fungi, the sporangium plays a role in asexual reproduction, and may play an indirect role in sexual reproduction. The sporangium forms on the sporangiophore and contains haploid nuclei and cytoplasm. Spores are formed in the sporangiophore by encasing each haploid nucleus and cytoplasm in a tough outer membrane. During asexual reproduction, these spores are dispersed via wind and germinate into haploid hyphae. Although sexual reproduction in fungi varies between phyla, for some fungi the sporangium plays an indirect role in sexual reprod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sorus
A sorus (pl. sori) is a cluster of sporangia (structures producing and containing spores) in ferns and fungi. A coenosorus (plural coenosori) is a compound sorus composed of multiple, fused sori. Etymology This New Latin word is from Ancient Greek σωρός (''sōrós'' 'stack, pile, heap'). Structure In lichens and other fungi, the sorus is surrounded by an external layer. In some red algae, it may take the form of depression into the thallus. In ferns, the sori form a yellowish or brownish mass on the edge or underside of a fertile frond. In some species, they are protected during development by a scale or film of tissue called the indusium, which forms an umbrella-like cover. Lifecycle significance Sori occur on the sporophyte generation, the sporangia within producing haploid meiospores. As the sporangia mature, the indusium shrivels so that spore release is unimpeded. The sporangia then burst and release the spores. As an aid to identification The shape, arrangemen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
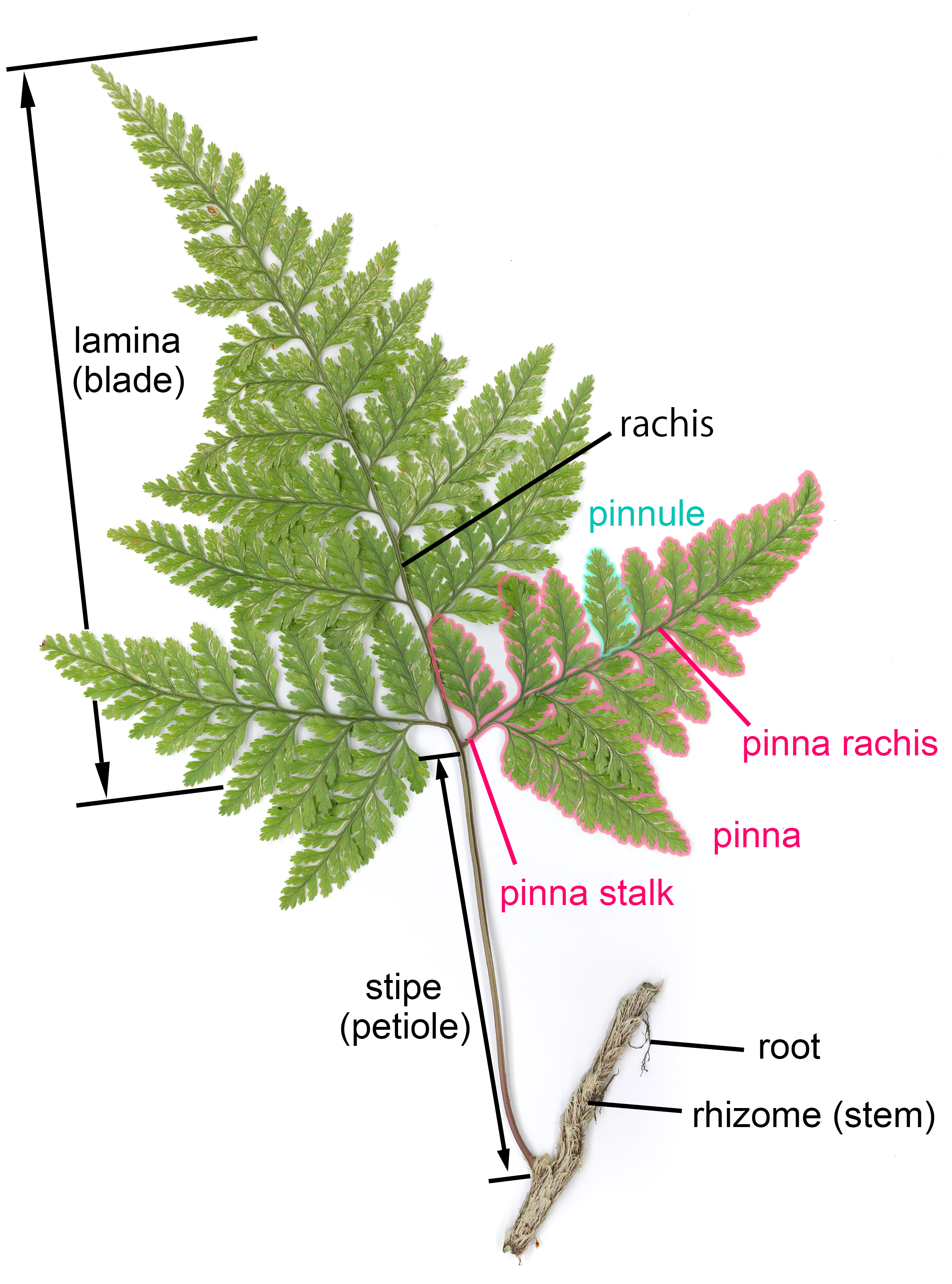
Frond
A frond is a large, divided leaf. In both common usage and botanical nomenclature, the leaves of ferns are referred to as fronds and some botanists restrict the term to this group. Other botanists allow the term frond to also apply to the large leaves of cycads, as well as palms (Arecaceae) and various other flowering plants, such as mimosa or sumac. "Frond" is commonly used to identify a large, compound leaf, but if the term is used botanically to refer to the leaves of ferns and algae it may be applied to smaller and undivided leaves. Fronds have particular terms describing their components. Like all leaves, fronds usually have a stalk connecting them to the main stem. In botany, this leaf stalk is generally called a petiole, but in regard to fronds specifically it is called a stipe, and it supports a flattened blade (which may be called a lamina), and the continuation of the stipe into this portion is called the rachis. The blades may be simple (undivided), pinnatifid ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epiphyte
An epiphyte is an organism that grows on the surface of a plant and derives its moisture and nutrients from the air, rain, water (in marine environments) or from debris accumulating around it. The plants on which epiphytes grow are called phorophytes. Epiphytes take part in nutrient cycles and add to both the diversity and biomass of the ecosystem in which they occur, like any other organism. They are an important source of food for many species. Typically, the older parts of a plant will have more epiphytes growing on them. Epiphytes differ from parasites in that they grow on other plants for physical support and do not necessarily affect the host negatively. An organism that grows on another organism that is not a plant may be called an epibiont. Epiphytes are usually found in the temperate zone (e.g., many mosses, liverworts, lichens, and algae) or in the tropics (e.g., many ferns, cacti, orchids, and bromeliads). Epiphyte species make good houseplants due to their minimal wat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Smith (botanist)
John Smith (1798–1888) was a British botanist who was the first curator at Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew (Kew Gardens), starting in 1841. He had first been employed at the gardens as a stove boy (stoking stoves to warm the greenhouses) in 1822. Along with the directors, Sir William Jackson Hooker and Sir Joseph Hooker, he oversaw the conversion of the gardens from private royal gardens to public gardens when Queen Victoria converted them, possibly saving them from oblivion. He further prevented the gardens from catastrophic decline during the late 19th century when they were neglected in funding priorities. According to the Kew website, "It is significant that when stove-boy-Smith arrived at Kew, 40 species of fern were grown but when Curator Smith retired, there were 1,084." He was born in Pittenweem, Scotland, in 1798. He died 12 February 1888 at Park House, Kew Road The A307 road runs through SW London and NW Surrey. It is primary at the north-east end; the remainder is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polypodium
''Polypodium'' is a genus of ferns in the family Polypodiaceae, subfamily Polypodioideae, according to the Pteridophyte Phylogeny Group classification of 2016 (PPG I). The genus is widely distributed throughout the world, with the highest species diversity in the tropics. The name is derived from Ancient Greek ''poly'' (πολύ) "many" + ''podion'' (πόδιον) "little foot", on account of the foot-like appearance of the rhizome and its branches. They are commonly called polypodies or rockcap ferns, but for many species unique vernacular names exist. They are terrestrial or epiphytic ferns, with a creeping, densely hairy or scaly rhizome bearing fronds at intervals along its length. The species differ in size and general appearance and in the character of the fronds, which are evergreen, persisting for 1–2 years, pinnate or pinnatifid (rarely simple entire), and from 10–80 cm or more long. The sori or groups of spore-cases (sporangia) are borne on the back of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)