|
Phentermine Topiramate
Phentermine ( phenyl- tertiary-butyl amine), with several brand names including Ionamin and Sentis, is a medication used together with diet and exercise to treat obesity. It is taken by mouth for up to a few weeks at a time, after which the benefits subside. It is also available as the combination phentermine/topiramate. Common side effects include a fast heart beat, high blood pressure, trouble sleeping, dizziness, and restlessness. Serious side effects may include abuse but do not include pulmonary hypertension, valvular heart disease as the latter were caused by the fenfluramine component of the fen-phen drug combination. Use is not recommended during pregnancy or breastfeeding, or with SSRIs or MAO inhibitors. It works mainly as an appetite suppressant, likely as a result of being a CNS stimulant. Chemically, phentermine is a substituted amphetamine. Phentermine was approved for medical use in the United States in 1959. It is available as a generic medication. In 2020, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Route
Oral administration is a route of administration where a substance is taken through the mouth. Per os abbreviated to P.O. is sometimes used as a direction for medication to be taken orally. Many medications are taken orally because they are intended to have a systemic effect, reaching different parts of the body via the bloodstream, for example. Oral administration can be easier and less painful than other routes, such as injection. However, the onset of action is relatively low, and the effectiveness is reduced if it is not absorbed properly in the digestive system, or if it is broken down by digestive enzymes before it can reach the bloodstream. Some medications may cause gastrointestinal side effects, such as nausea or vomiting, when taken orally. Oral administration can also only be applied to conscious patients, and patients willing and able to swallow. Terminology ''Per os'' (; ''P.O.'') is an adverbial phrase meaning literally from Latin "through the mouth" or "by mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Substituted Amphetamine
Substituted amphetamines are a class of compounds based upon the amphetamine structure; it includes all derivative compounds which are formed by replacing, or substituting, one or more hydrogen atoms in the amphetamine core structure with substituents. The compounds in this class span a variety of pharmacological subclasses, including stimulants, empathogens, and hallucinogens, among others. Examples of substituted amphetamines are amphetamine (itself), methamphetamine, ephedrine, cathinone, phentermine, mephentermine, bupropion, methoxyphenamine, selegiline, amfepramone (diethylpropion), pyrovalerone, MDMA (ecstasy), and DOM (STP). Some of amphetamine's substituted derivatives occur in nature, for example in the leaves of ''Ephedra'' and khat plants. Amphetamine was first produced at the end of the 19th century. By the 1930s, amphetamine and some of its derivative compounds found use as decongestants in the symptomatic treatment of colds and also occasionally as psychoac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palpitations
Palpitations are perceived abnormalities of the heartbeat characterized by awareness of cardiac muscle contractions in the chest, which is further characterized by the hard, fast and/or irregular beatings of the heart. Symptoms include a rapid pulsation, an abnormally rapid or irregular beating of the heart. Palpitations are a sensory symptom and are often described as a skipped beat, rapid fluttering in the chest, pounding sensation in the chest or neck, or a flip-flopping in the chest. Palpitation can be associated with anxiety and does not necessarily indicate a structural or functional abnormality of the heart, but it can be a symptom arising from an objectively rapid or irregular heartbeat. Palpitation can be intermittent and of variable frequency and duration, or continuous. Associated symptoms include dizziness, shortness of breath, sweating, headaches and chest pain. Palpitation may be associated with coronary heart disease, hyperthyroidism, diseases affecting card ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breast-feeding
Breastfeeding, or nursing, is the process by which human breast milk is fed to a child. Breast milk may be from the breast, or may be expressed by hand or pumped and fed to the infant. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends that breastfeeding begin within the first hour of a baby's life and continue as often and as much as the baby wants. Health organizations, including the World Health Organization, WHO, recommend breastfeeding exclusively for six months. This means that no other foods or drinks, other than vitamin D, are typically given. WHO recommends exclusive breastfeeding for the first 6 months of life, followed by continued breastfeeding with appropriate complementary foods for up to 2 years and beyond. Of the 135 million babies born every year, only 42% are breastfed within the first hour of life, only 38% of mothers practice exclusive breastfeeding during the first six months, and 58% of mothers continue breastfeeding up to the age of two years and beyond. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pregnant
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring develops (gestation, gestates) inside a woman, woman's uterus (womb). A multiple birth, multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins. Pregnancy usually occurs by sexual intercourse, but can also occur through assisted reproductive technology procedures. A pregnancy may end in a Live birth (human), live birth, a miscarriage, an Abortion#Induced, induced abortion, or a stillbirth. Childbirth typically occurs around 40 weeks from the start of the Menstruation#Onset and frequency, last menstrual period (LMP), a span known as the Gestational age (obstetrics), gestational age. This is just over nine months. Counting by Human fertilization#Fertilization age, fertilization age, the length is about 38 weeks. Pregnancy is "the presence of an implanted human embryo or fetus in the uterus"; Implantation (embryology), implantation occurs on average 8–9 days after fertilization. An ''embryo'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glaucoma
Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases that result in damage to the optic nerve (or retina) and cause vision loss. The most common type is open-angle (wide angle, chronic simple) glaucoma, in which the drainage angle for fluid within the eye remains open, with less common types including closed-angle (narrow angle, acute congestive) glaucoma and normal-tension glaucoma. Open-angle glaucoma develops slowly over time and there is no pain. Peripheral vision may begin to decrease, followed by central vision, resulting in blindness if not treated. Closed-angle glaucoma can present gradually or suddenly. The sudden presentation may involve severe eye pain, blurred vision, mid-dilated pupil, redness of the eye, and nausea. Vision loss from glaucoma, once it has occurred, is permanent. Eyes affected by glaucoma are referred to as being glaucomatous. Risk factors for glaucoma include increasing age, high pressure in the eye, a family history of glaucoma, and use of steroid medication. F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism is the condition that occurs due to excessive production of thyroid hormones by the thyroid gland. Thyrotoxicosis is the condition that occurs due to excessive thyroid hormone of any cause and therefore includes hyperthyroidism. Some, however, use the terms interchangeably. Signs and symptoms vary between people and may include irritability, muscle weakness, sleeping problems, a fast heartbeat, heat intolerance, diarrhea, enlargement of the thyroid, hand tremor, and weight loss. Symptoms are typically less severe in the elderly and during pregnancy. An uncommon complication is thyroid storm in which an event such as an infection results in worsening symptoms such as confusion and a high temperature and often results in death. The opposite is hypothyroidism, when the thyroid gland does not make enough thyroid hormone. Graves' disease is the cause of about 50% to 80% of the cases of hyperthyroidism in the United States. Other causes include multinodular goit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiovascular Disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a class of diseases that involve the heart or blood vessels. CVD includes coronary artery diseases (CAD) such as angina and myocardial infarction (commonly known as a heart attack). Other CVDs include stroke, heart failure, hypertensive heart disease, rheumatic heart disease, cardiomyopathy, abnormal heart rhythms, congenital heart disease, valvular heart disease, carditis, aortic aneurysms, peripheral artery disease, thromboembolic disease, and venous thrombosis. The underlying mechanisms vary depending on the disease. It is estimated that dietary risk factors are associated with 53% of CVD deaths. Coronary artery disease, stroke, and peripheral artery disease involve atherosclerosis. This may be caused by high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes mellitus, lack of exercise, obesity, high blood cholesterol, poor diet, excessive alcohol consumption, and poor sleep, among other things. High blood pressure is estimated to account for approximat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
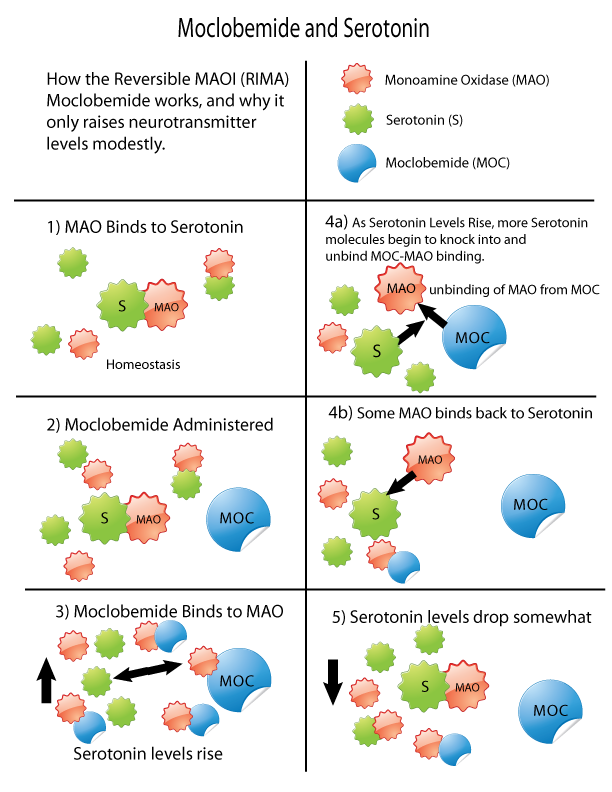
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) are a class of drugs that inhibit the activity of one or both monoamine oxidase enzymes: monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A) and monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B). They are best known as effective antidepressants, especially for treatment-resistant depression and atypical depression. They are also used to treat panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, Parkinson's disease, and several other disorders. Reversible inhibitors of monoamine oxidase A (RIMAs) are a subclass of MAOIs that selectively and reversibly inhibit the MAO-A enzyme. RIMAs are used clinically in the treatment of depression and dysthymia. Due to their reversibility, they are safer in single-drug overdose than the older, irreversible MAOIs, and weaker in increasing the monoamines important in depressive disorder. RIMAs have not gained widespread market share in the United States. Medical uses MAOIs have been found to be effective in the treatment of panic disorder with agoraphobia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sympathomimetic Amine
Sympathomimetic drugs (also known as adrenergic drugs and adrenergic amines) are stimulant compounds which mimic the effects of endogenous agonists of the sympathetic nervous system. Examples of sympathomimetic effects include increases in heart rate, force of cardiac contraction, and blood pressure. The primary endogenous agonists of the sympathetic nervous system are the catecholamines (i.e., epinephrine drenaline norepinephrine oradrenaline and dopamine), which function as both neurotransmitters and hormones. Sympathomimetic drugs are used to treat cardiac arrest and low blood pressure, or even delay premature labor, among other things. These drugs can act through several mechanisms, such as directly activating postsynaptic receptors, blocking breakdown and reuptake of certain neurotransmitters, or stimulating production and release of catecholamines. Mechanisms of action The mechanisms of sympathomimetic drugs can be direct-acting (direct interaction between drug and recep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drug Abuse
Substance abuse, also known as drug abuse, is the use of a drug in amounts or by methods which are harmful to the individual or others. It is a form of substance-related disorder. Differing definitions of drug abuse are used in public health, medical and criminal justice contexts. In some cases, criminal or anti-social behaviour occurs when the person is under the influence of a drug, and long-term personality changes in individuals may also occur. In addition to possible physical, social, and psychological harm, the use of some drugs may also lead to criminal penalties, although these vary widely depending on the local jurisdiction.. Drugs most often associated with this term include: alcohol, amphetamines, barbiturates, benzodiazepines, cannabis, cocaine, hallucinogens (although there is no known ''psychedelic'', one of the three categories of hallucinogens, that has been found to have any addictive potential), methaqualone, and opioids. The exact cause of substance abuse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contraindicated
In medicine, a contraindication is a condition that serves as a reason not to take a certain medical treatment due to the harm that it would cause the patient. Contraindication is the opposite of indication, which is a reason to use a certain treatment. ''Absolute contraindications'' are contraindications for which there are no reasonable circumstances for undertaking a course of action. For example, children and teenagers with viral infections should not be given aspirin because of the risk of Reye syndrome, and a person with an anaphylactic food allergy should never eat the food to which they are allergic. Similarly, a person with hemochromatosis should not be administered iron preparations. ''Relative contraindications'' are contraindications for circumstances in which the patient is at higher risk of complications from treatment, but these risks may be outweighed by other considerations or mitigated by other measures. For example, a pregnant woman should normally avoid gett ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |