|
Pheasant Coucal
The pheasant coucal (''Centropus phasianinus'') is a species of cuckoo in the family Cuculidae. It is found in Australia, Timor and New Guinea. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical moist lowland forests and subtropical or tropical mangrove forests. It has adapted well to canefields in northern Australia. The pheasant coucal is unusual among Australian cuckoos in that it incubates and raises its own young instead of laying its eggs in the nest of another species. Taxonomy The ornithologist John Latham described the pheasant coucal as ''Cuculus phasianinus'' in 1801, based on a drawing by Thomas Watling. Six subspecies are recognised, two of which are found in Australia with an abrupt demarcation between them occurring around the Burdekin River in Central Queensland. South is the nominate subspecies ''phasianinus'', while north is the subspecies ''melanurus'', which is larger in size and has darker and more prominent black bands on its rectrices. The little known subspe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Latham (ornithologist)
John Latham (27 June 1740 – 4 February 1837) was an English physician, naturalist and author. His main works were ''A General Synopsis of Birds'' (1781–1801) and ''General History of Birds'' (1821–1828). He was able to examine specimens of Australian birds which reached England in the last twenty years of the 18th century, and was responsible for providing English names for many of them. He named some of Australia's most famous birds, including the emu, sulphur-crested cockatoo, wedge-tailed eagle, superb lyrebird, Australian magpie, magpie-lark and pheasant coucal. He was also the first to describe the hyacinth macaw. Latham has been called the "grandfather" of Australian ornithology. Biography John Latham was born on 27 June 1740 at Eltham in northwest Kent. He was the eldest son of John Latham (died 1788), a surgeon, and his mother, who was a descendant of the Sothebys, in Yorkshire. He was educated at Merchant Taylors' School and then studied anatomy under William Hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kai Coucal
The Kai coucal (''Centropus spilopterus'') is a species of cuckoo in the family Cuculidae. It is endemic to the Kai Islands of Indonesia. It was formerly considered a subspecies of the pheasant coucal (''C. phasianus''). References Kai coucal Birds of the Kai Islands Kai coucal Kai coucal The Kai coucal (''Centropus spilopterus'') is a species of cuckoo in the family Cuculidae. It is endemic to the Kai Islands of Indonesia. It was formerly considered a subspecies of the pheasant coucal The pheasant coucal (''Centropus phasianinu ... Taxonomy articles created by Polbot {{cuculiformes-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birds Of New Guinea
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweight skeleton. Birds live worldwide and range in size from the bee hummingbird to the ostrich. There are about ten thousand living species, more than half of which are passerine, or "perching" birds. Birds have whose development varies according to species; the only known groups without wings are the extinct moa and elephant birds. Wings, which are modified forelimbs, gave birds the ability to fly, although further evolution has led to the loss of flight in some birds, including ratites, penguins, and diverse endemic island species. The digestive and respiratory systems of birds are also uniquely adapted for flight. Some bird species of aquatic environments, particularly seabirds and some waterbirds, have further evolved for swimming. Birds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birds Of Australia
Australia and its offshore islands and territories have 898 recorded bird species as of 2014. Of the recorded birds, 165 are considered vagrant or accidental visitors, of the remainder over 45% are classified as Australian endemics: found nowhere else on earth. It has been suggested that up to 10% of Australian bird species may go extinct by the year 2100 as a result of climate change. Australian species range from the tiny weebill to the huge, flightless emu. Many species of Australian birds will immediately seem familiar to visitors from the Northern Hemisphere: Australian wrens look and act much like northern wrens, and Australian robins seem to be close relatives of the northern robins. However, the majority of Australian passerines are descended from the ancestors of the crow family, and the close resemblance is misleading: the cause is not genetic relatedness but convergent evolution. For example, almost any land habitat offers a nice home for a small bird that specia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centropus
A coucal is one of about 30 species of birds in the cuckoo family. All of them belong in the subfamily Centropodinae and the genus ''Centropus''. Unlike many Old World cuckoos, coucals are not brood parasites, though they do have their own reproductive peculiarity: all members of the genus are (to varying degrees) sex-role reversed, so that the smaller male provides most of the parental care. At least one coucal species, the black coucal, is polyandrous. Some species (''Centropus phasianinus'') have the male investing more in incubation and parental care. Taxonomy The genus ''Centropus'' was introduced in 1811 by the German zoologist Johann Karl Wilhelm Illiger. The type species was subsequently designated as the Senegal coucal by George Robert Gray in 1840. The genus name combines the Ancient Greek ''kentron'' meaning "spur" or "spike" with ''pous'' meaning "foot". Description Many coucals have a long claw on their hind toe (hallux). The feet have minute spurs and this is respon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Understory
In forestry and ecology, understory (American English), or understorey (Commonwealth English), also known as underbrush or undergrowth, includes plant life growing beneath the forest canopy without penetrating it to any great extent, but above the forest floor. Only a small percentage of light penetrates the canopy so understory vegetation is generally shade-tolerant. The understory typically consists of trees stunted through lack of light, other small trees with low light requirements, saplings, shrubs, vines and undergrowth. Small trees such as holly and dogwood are understory specialists. In temperate deciduous forests, many understory plants start into growth earlier in the year than the canopy trees, to make use of the greater availability of light at that particular time of year. A gap in the canopy caused by the death of a tree stimulates the potential emergent trees into competitive growth as they grow upwards to fill the gap. These trees tend to have straight trunks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centropus Phasianinus -Daintree, Queensland, Australia-8
A coucal is one of about 30 species of birds in the cuckoo family. All of them belong in the subfamily Centropodinae and the genus ''Centropus''. Unlike many Old World cuckoos, coucals are not brood parasites, though they do have their own reproductive peculiarity: all members of the genus are (to varying degrees) sex-role reversed, so that the smaller male provides most of the parental care. At least one coucal species, the black coucal, is polyandrous. Some species (''Centropus phasianinus'') have the male investing more in incubation and parental care. Taxonomy The genus ''Centropus'' was introduced in 1811 by the German zoologist Johann Karl Wilhelm Illiger. The type species was subsequently designated as the Senegal coucal by George Robert Gray in 1840. The genus name combines the Ancient Greek ''kentron'' meaning "spur" or "spike" with ''pous'' meaning "foot". Description Many coucals have a long claw on their hind toe (hallux). The feet have minute spurs and this is respon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Field Guide To The Birds Of Australia (Simpson & Day)
The Simpson and Day ''Field Guide to the Birds of Australia'' is one of the main national bird field guides used by Australian birders, which over the years has evolved through several revised and updated editions. Total sales exceed 500,000 copies.Penguin Books. History The book was first published in 1984 by Lloyd O’Neil as ''The Birds of Australia'', in hardcover format with a dust jacket, 285 mm high by 215 mm wide and weighing 1.7 kg. It contained illustrations by Nicolas Day of 758 species on 128 colour plates. It was divided into three main sections, a key to bird families, the field information section with the plates opposite the relevant species descriptions and distribution maps, and the “handbook” with more detailed information on avian biology. The endpapers featured life-size profile drawings of the bills of albatrosses and petrels to aid the identification of beach-washed seabirds.Simpson & Day (1984). Although the dust jacket and tit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pheasant
Pheasants ( ) are birds of several genera within the family (biology), family Phasianidae in the order (biology), order Galliformes. Although they can be found all over the world in introduced (and captive) populations, the pheasant genera native range is restricted to Eurasia. The classification "pheasant" is Paraphyly, paraphyletic, as birds referred to as pheasants are included within both the subfamilies Phasianinae and Peafowl, Pavoninae, and in many cases are more closely related to smaller phasianids, grouse, and turkey (formerly classified in Perdicinae, Grouse, Tetraoninae, and Meleagridinae) than to other pheasants. Pheasants are characterised by strong sexual dimorphism, males being highly decorated with bright colours and adornments such as wattle (anatomy), wattles. Males are usually larger than females and have longer tails. Males play no part in rearing the young. A pheasant's call or cry can be recognised due to the fact it sounds like a rusty sink or valve b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Ornithologists' Union
The International Ornithologists' Union, formerly known as the International Ornithological Committee, is a group of about 200 international ornithologists, and is responsible for the International Ornithological Congress and other international ornithological activities, undertaken by its standing committees. International Ornithological Congress The International Ornithological Congress series forms the oldest and largest international series of meetings of ornithologists. It is organised by the International Ornithologists' Union. The first meeting was in 1884; subsequent meetings were irregular until 1926 since when meetings have been held every four years, except for two missed meetings during and in the immediate aftermath of the Second World War. Meetings See also * '' Birds of the World: Recommended English Names'', a book written by Frank Gill Frank Gill may refer to: * Frank Gill (Australian footballer) (1908–1970), Australian rules footballer with Carlton * Fran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guinea. Indonesia is the world's largest archipelagic state and the 14th-largest country by area, at . With over 275 million people, Indonesia is the world's fourth-most populous country and the most populous Muslim-majority country. Java, the world's most populous island, is home to more than half of the country's population. Indonesia is a presidential republic with an elected legislature. It has 38 provinces, of which nine have special status. The country's capital, Jakarta, is the world's second-most populous urban area. Indonesia shares land borders with Papua New Guinea, East Timor, and the eastern part of Malaysia, as well as maritime borders with Singapore, Vietnam, Thailand, the Philippines, Australia, Palau, and India ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
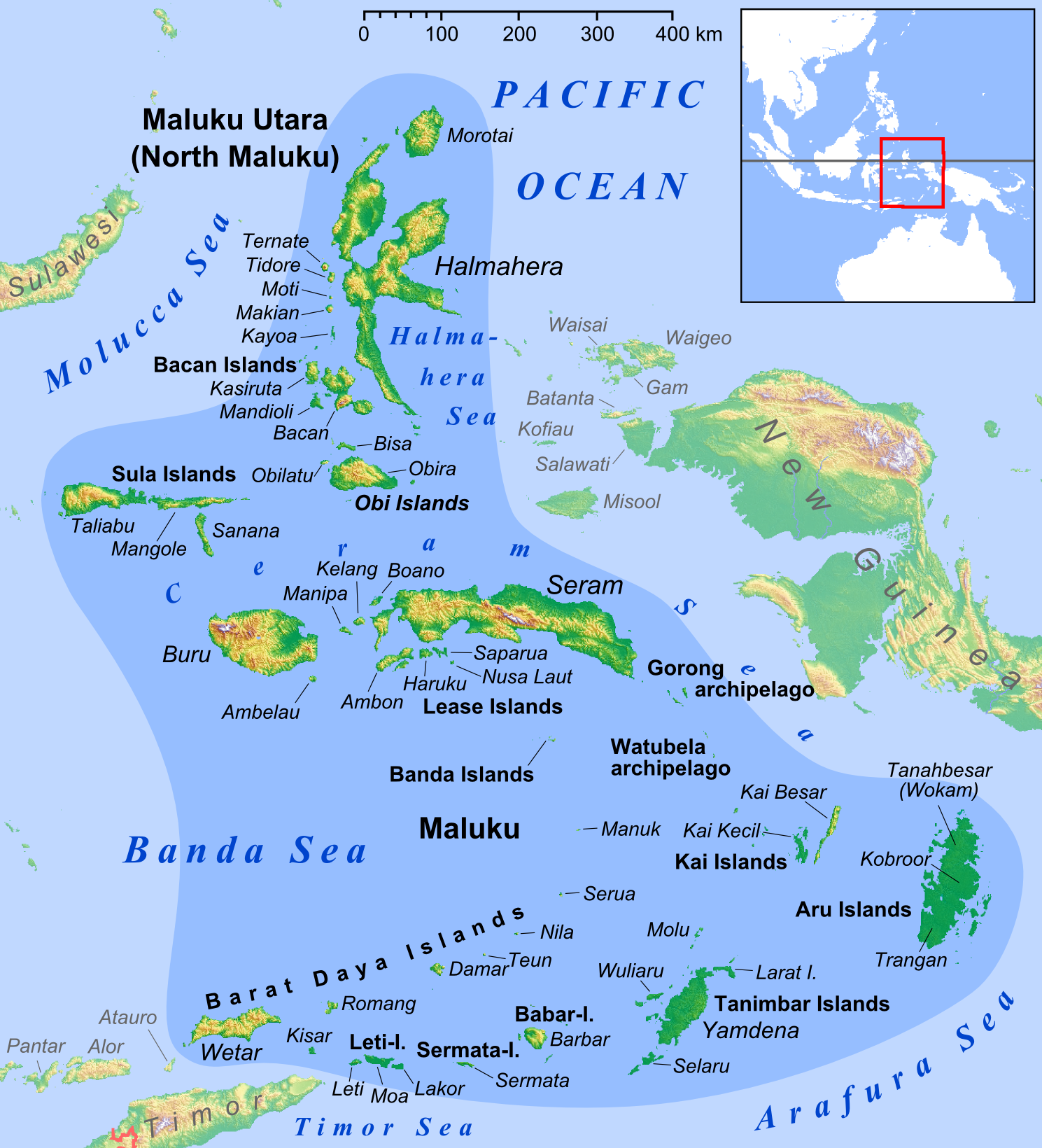
Kai Islands
The Kai Islands (also Kei Islands) of Indonesia are a group of islands in the southeastern part of the Maluku Islands, located in the province of Maluku (province), Maluku. The Moluccas have been known as the Spice Islands due to regionally specific plants such as nutmeg, mace (spice), mace, and cloves that originally intrigued the European nations of the 16th century. Though originally Melanesians, Melanesian, many islanders were exterminated in the 17th century during the Dutch–Portuguese War, spice wars, particularly in the Banda Islands. A second influx of Austronesian peoples, Austronesian immigrants began in the early 20th century under the Dutch East Indies, Dutch and continued in the Indonesian era. Administrative divisions The Kai Islands consist of the two distinct second-tier administrations, both in Maluku Province. The Southeast Maluku Regency (Maluku Tenggara) is sub-divided into eleven administrative Districts of Indonesia, districts (''kecamatan''). Though ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_(8967632085).jpg)
.jpg)
_in_Hyderabad_W_IMG_8962.jpg)