|
Pharyngeal Consonant
A pharyngeal consonant is a consonant that is articulated primarily in the pharynx. Some phoneticians distinguish upper pharyngeal consonants, or "high" pharyngeals, pronounced by retracting the root of the tongue in the mid to upper pharynx, from (ary)epiglottal consonants, or "low" pharyngeals, which are articulated with the aryepiglottic folds against the epiglottis at the entrance of the larynx, as well as from epiglotto-pharyngeal consonants, with both movements being combined. Stops and trills can be reliably produced only at the epiglottis, and fricatives can be reliably produced only in the upper pharynx. When they are treated as distinct places of articulation, the term ''radical consonant'' may be used as a cover term, or the term '' guttural consonants'' may be used instead. Pharyngeal consonants can trigger effects on neighboring vowels. Instead of uvulars, which nearly always trigger retraction, pharyngeals tend to trigger lowering. For example, in Moroccan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Place Of Articulation
In articulatory phonetics, the place of articulation (also point of articulation) of a consonant is an approximate location along the vocal tract where its production occurs. It is a point where a constriction is made between an active and a passive articulator. Active articulators are organs capable of voluntary movement which create the constriction, while passive articulators are so called because they are normally fixed and are the parts with which an active articulator makes contact. Along with the manner of articulation and phonation, the place of articulation gives the consonant its distinctive sound. Since vowels are produced with an open vocal tract, the point where their production occurs cannot be easily determined. Therefore, they are not described in terms of a place of articulation but by the relative positions in vowel space. This is mostly dependent on their formant frequencies and less on the specific tongue position and lip rounding. The terminology used in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voiced Epiglottal Trill
The voiced epiglottal or pharyngeal trill, or voiced epiglottal fricative,John Esling (2010) "Phonetic Notation", in Hardcastle, Laver & Gibbon (eds) ''The Handbook of Phonetic Sciences'', 2nd ed., p 695. is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is . Few languages distinguish between pharyngeal and epiglottal fricatives/trills, and in fact the fricatives in Arabic are routinely described as "pharyngeal". However, according to Peter Ladefoged, the Aghul spoken in the village of Burkikhan, Dagestan has both (as well as an epiglottal stop), as presented ithese audio files Features Features of the voiced epiglottal trill/fricative: Occurrence See also * Index of phonetics articles A * Acoustic phonetics * Active articulator * Affricate * Airstream mechanism * Alexander John Ellis * Alexander Melville Bell * Alfred C. Gimson * Allophone * Alveolar approximant () ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voiceless Upper-pharyngeal Plosive
The voiceless upper-pharyngeal plosive or stop is a rare consonant. Pharyngeal consonants are typically pronounced at two regions of the pharynx, upper and lower. The lower region is epiglottal, so the upper region is often abbreviated as merely 'pharyngeal'. Among widespread speech sounds in the world's languages, the upper pharynx produces a voiceless fricative and a voiced sound that ranges from fricative to (more commonly) approximant, . The epiglottal region produces the plosive as well as sounds that range from fricative to trill, and . Because the latter pair is most often trilled and rarely simply fricative, these consonants have been classified together as simply pharyngeal, and distinguished as plosive, fricative/approximant and trill. Features Features of the voiceless upper-pharyngeal stop: Occurrence No language is known to have a phonemic upper pharyngeal plosive. The Nǁng language (Nǀuu) is claimed to have an upper pharyngeal place of articulatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
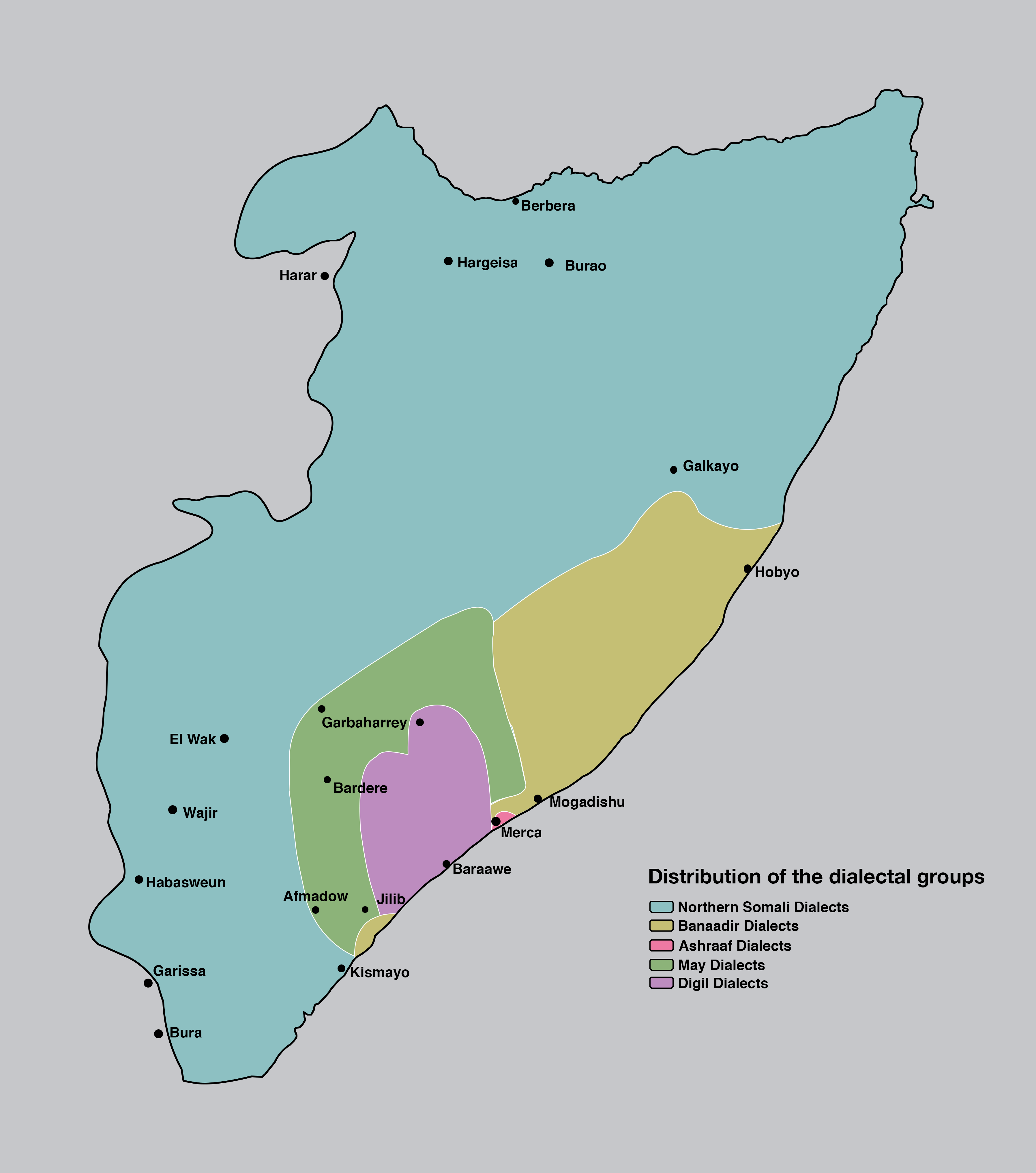
Somali Language
Somali is an Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language belonging to the Cushitic languages, Cushitic branch, primarily spoken by the Somalis, Somali people, native to Greater Somalia. It is an official language in Somalia, Somaliland, and Ethiopia; one of the two national languages in Djibouti; and a recognised minority language in Kenya. Somali is officially written in the Latin script (Somali Latin alphabet), with the Arabic script (Wadaad's writing) and several local scripts (Osmanya script, Osmanya, Kaddare script, Kaddare and Gadabuursi Somali Script, Borama scripts) being informally used.Lewis, I.M. (1958)The Gadabuursi Somali Script ''Bulletin of the School of Oriental and African Studies'', University of London, Vol. 21, pp. 134–156. Classification Somali is classified within the Cushitic branch of the Afroasiatic family, specifically, Lowland East Cushitic languages, Lowland East Cushitic in addition to Afar language, Afar and Saho language, Saho. Somali is the bes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voiced Epiglottal Affricate
The voiced epiglottal affricate ( in IPA) is a rare affricate consonant An affricate is a consonant that begins as a stop and releases as a fricative, generally with the same place of articulation (most often coronal). It is often difficult to decide if a stop and fricative form a single phoneme or a consonant pai ... that is initiated as an epiglottal stop and released as a voiced epiglottal fricative . It has not been reported to occur phonemically in any language. Features Features of the voiced epiglottal affricate: Occurrence Notes References * {{DEFAULTSORT:Voiced Epiglottal Affricate Affricates Pulmonic consonants Voiced oral consonants Central consonants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haida Language
Haida (', ', ', ') is the language of the Haida people, spoken in the Haida Gwaii archipelago off the coast of western Canada and on Prince of Wales Island in Alaska. An endangered language, Haida currently has 24 native speakers, though revitalization efforts are underway. At the time of the European arrival at in 1774, it is estimated that Haida speakers numbered about 15,000. Epidemics soon led to a drastic reduction in the Haida population, which became limited to three villages: Masset, Skidegate, and Hydaburg. Positive attitudes towards assimilation combined with the ban on speaking Haida in residential schools led to a sharp decline in the use of the Haida language among the Haida people, and today almost all ethnic Haida use English to communicate. Classification of the Haida language is a matter of controversy, with some linguists placing it in the Na-Dené language family and others arguing that it is a language isolate. Haida itself is split between Northern a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voiceless Epiglottal Affricate
The voiceless epiglottal affricate ( in IPA) is a rare affricate consonant An affricate is a consonant that begins as a stop and releases as a fricative, generally with the same place of articulation (most often coronal). It is often difficult to decide if a stop and fricative form a single phoneme or a consonant pai ... that is initiated as an epiglottal stop and released as a voiceless epiglottal fricative . It has not been reported to occur phonemically in any language except in the Hydaburg dialect of the Haida language. Features Features of the voiceless epiglottal affricate: Occurrence Notes References * {{DEFAULTSORT:Voiceless Epiglottal Affricate Affricates Pulmonic consonants Voiceless oral consonants Central consonants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dargwa Language
Dargwa (, ''dargan mez'') is a Northeast Caucasian languages, Northeast Caucasian language spoken by the Dargins, Dargin people in the Russian republic Dagestan. This article discusses the literary dialect of the dialect continuum constituting the Dargin languages. It is based on the Aqusha dialect, Aqusha and Urakhi dialect, Urakhi dialects of Northern Dargin. Classification Dargwa is part of a Northeast Caucasian dialect continuum, the Dargin languages. The other languages in this dialect continuum (such as Kaitag language, Kajtak, Kubachi language, Kubachi, Itsari language, Itsari, and Chirag language, Chirag) are often considered variants of Dargwa, but also sometimes considered separate languages by certain scholars. Korjakov (2012) concludes that Southwestern Dargwa is closer to Kajtak than it is to North-Central Dargwa. Geographic distribution According to the Russian Census (2002), 2002 Census, there are 429,347 speakers of Dargwa proper in Dagestan, 7,188 in neighbo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epiglottal Ejective
The epiglottal or pharyngeal ejective is a rare type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is . Features Features of the pharyngeal ejective: Occurrence A pharyngeal ejective has been reported in certain Dargin languages, a branch of the Northeast Caucasian family. See also * List of phonetics topics A * Acoustic phonetics * Active articulator * Affricate * Airstream mechanism * Alexander John Ellis * Alexander Melville Bell * Alfred C. Gimson * Allophone * Alveolar approximant () * Alveolar click () * Alveolar consonant * Alveolar e ... References {{IPA navigation Ejectives Epiglottal consonants Oral consonants Central consonants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Danish Phonology
The phonology of Danish is similar to that of the other closely related Scandinavian languages, Swedish and Norwegian, but it also has distinct features setting it apart. For example, Danish has a suprasegmental feature known as stød which is a kind of laryngeal phonation that is used phonemically. It also exhibits extensive lenition of plosives, which is noticeably more common than in the neighboring languages. Because of these and a few other features, spoken Danish can be challenging for Norwegians and Swedes to understand without training, although they can easily read written Danish. Consonants Danish has at least 17 consonant phonemes: occur only syllable-initially and only syllable-finally. is phonemically and is the syllable-final allophone of . also occurs syllable-initially in English loans, along with , but syllable-initial is in free variation with and these are not considered part of the phonological inventory of Danish. occurs only before sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharyngeal Approximant
The voiced pharyngeal approximant or fricative is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is , and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is ?\. Epiglottals and epiglotto-pharyngeals are often mistakenly taken to be pharyngeal. Although traditionally placed in the fricative row of the IPA chart, is usually an approximant. The IPA symbol itself is ambiguous, but no language is known to make a phonemic distinction between fricatives and approximants at this place of articulation. The IPA letter is caseless. Capital and lower-case are pending at Unicode U+A7CE and U+A7CF. Features Features of the voiced pharyngeal approximant fricative: Occurrence Pharyngeal consonants are not widespread. Sometimes, a pharyngeal approximant develops from a uvular approximant. Many languages that have been described as having pharyngeal fricatives or approximants turn out on closer inspection ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dahalo Language
Dahalo is an endangered Cushitic language spoken by around 500600 Dahalo people on the coast of Kenya, near the mouth of the Tana River. Dahalo is unusual among the world's languages in using all four airstream mechanisms found in human language: clicks, implosives, ejectives, and pulmonic consonants. While the language is known primarily as "''Dahalo''" to linguists, the term itself is an exonym supposedly used by Aweer speakers that itself essentially means “stupid” or “worthless.” The speakers themselves refer to the language as . Overview The Dahalo, former elephant hunters, are dispersed among Swahili and other Bantu peoples, with no villages of their own, and are bilingual in those languages. Children no longer learn the language, which would make it moribund, and it may be extinct. Dahalo has a highly diverse sound system using all four airstream mechanisms found in human language: clicks, ejectives, and implosives, as well as the universal pulmonic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |