|
Peter Finke
Peter Finke (born 1944) is a German theoretical physicist who participated in Project-706, Pakistan's clandestine nuclear research project. A close associate and friend of the famous Pakistani nuclear engineer Munir Ahmad Khan (late), he is citizen of both Pakistan and Germany. He is one of the European scientists who participated in Project-706 in the 1970s. Finke is, perhaps, better known in much of the world for his involvement in the development of Beryllium reflector technology as well as selling this technology to Pakistan in the late 1980s. In 1989, Finke was arrested in Germany by the Interpol Police because of his involvement in nuclear proliferation. However, Germany dropped the allegations due to lack of evidence. Finke was sentenced to jail by the German court in 1989 because of violation of Germany's export control laws. Biography Nuclear Proliferation During the 1970s, Finke was working as a director at Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt where he carried ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bonn
The federal city of Bonn ( lat, Bonna) is a city on the banks of the Rhine in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia, with a population of over 300,000. About south-southeast of Cologne, Bonn is in the southernmost part of the Rhine-Ruhr region, Germany's largest metropolitan area, with over 11 million inhabitants. It is a university city and the birthplace of Ludwig van Beethoven. Founded in the 1st century BC as a Roman settlement in the province Germania Inferior, Bonn is one of Germany's oldest cities. It was the capital city of the Electorate of Cologne from 1597 to 1794, and residence of the Archbishops and Prince-electors of Cologne. From 1949 to 1990, Bonn was the capital of West Germany, and Germany's present constitution, the Basic Law, was declared in the city in 1949. The era when Bonn served as the capital of West Germany is referred to by historians as the Bonn Republic. From 1990 to 1999, Bonn served as the seat of government – but no longer capital – ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Engineer
Nuclear engineering is the branch of engineering concerned with the application of breaking down atomic nuclei ( fission) or of combining atomic nuclei (fusion), or with the application of other sub-atomic processes based on the principles of nuclear physics. In the sub-field of nuclear fission, it particularly includes the design, interaction, and maintenance of systems and components like reactors, power plants, or weaponry. The field also includes the study of medical and other applications of radiation, particularly Ionizing radiation, nuclear safety, heat/thermodynamics transport, nuclear fuel, or other related technology (e.g., radioactive waste disposal) and the problems of nuclear proliferation. This field also includes chemical engineering and electrical engineering. Professional areas The United States currently generates about 20% of its electricity from nuclear power plants. Nuclear engineers in this field generally work, directly or indirectly, in the nucle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tritium
Tritium ( or , ) or hydrogen-3 (symbol T or H) is a rare and radioactive isotope of hydrogen with half-life about 12 years. The nucleus of tritium (t, sometimes called a ''triton'') contains one proton and two neutrons, whereas the nucleus of the common isotope hydrogen-1 (''protium'') contains one proton and zero neutrons, and that of hydrogen-2 (''deuterium'') contains one proton and one neutron. Naturally occurring tritium is extremely rare on Earth. The atmosphere has only trace amounts, formed by the interaction of its gases with cosmic rays. It can be produced artificially by irradiating lithium metal or lithium-bearing ceramic pebbles in a nuclear reactor and is a low-abundance byproduct in normal operations of nuclear reactors. Tritium is used as the energy source in radioluminescent lights for watches, gun sights, numerous instruments and tools, and even novelty items such as self-illuminating key chains. It is used in a medical and scientific setting as a radioacti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Munir Ahmed Khan
Munir Ahmad Khan ( ur, ; 20 May 1926 – 22 April 1999), , was a Pakistani nuclear reactor physicist who is credited, among others, with being the "father of the atomic bomb program" of Pakistan for their leading role in developing their nation's nuclear weapons during the successive years after the war with India in 1971. From 1972 to 1991, Khan served as the chairman of the Pakistan Atomic Energy Commission (PAEC) who directed and oversaw the completion of the clandestine bomb program from its earliest efforts to develop the atomic weapons to their ultimate nuclear testings in May 1998. His early career was mostly spent in the International Atomic Energy Agency and he used his position to help establish the International Centre for Theoretical Physics in Italy and an annual conference on physics in Pakistan. As chair of PAEC, Khan was a proponent of the nuclear arms race with India whose efforts were directed towards concentrated production of reactor-grade to weapon-gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abdul Qadeer Khan
Abdul Qadeer Khan, (; ur, ; 1 April 1936 – 10 October 2021), known as A. Q. Khan, was a Pakistani nuclear physicist and metallurgical engineer. He was a key figure in Pakistan’s nuclear weapons program and is colloquially known as the "Father of Pakistan's atomic weapons program". He is a national hero in Pakistan. An ''émigré (Muhajir)'' from India who migrated to Pakistan in 1952, Khan was educated in the metallurgical engineering departments of Western European technical universities where he pioneered studies in phase transitions of metallic alloys, uranium metallurgy, and isotope separation based on gas centrifuges. After learning of India's "Smiling Buddha" nuclear test in 1974, Khan joined his nation's clandestine efforts to develop atomic weapons when he founded the Khan Research Laboratories (KRL) in 1976 and was both its chief scientist and director for many years. In January 2004, Khan was subjected to a debriefing by the Musharraf administration ov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Reactor Technology
A nuclear reactor is a device used to initiate and control a fission nuclear chain reaction or nuclear fusion reactions. Nuclear reactors are used at nuclear power plants for electricity generation and in nuclear marine propulsion. Heat from nuclear fission is passed to a working fluid (water or gas), which in turn runs through steam turbines. These either drive a ship's propellers or turn electrical generators' shafts. Nuclear generated steam in principle can be used for industrial process heat or for district heating. Some reactors are used to produce isotopes for medical and industrial use, or for production of weapons-grade plutonium. , the International Atomic Energy Agency reports there are 422 nuclear power reactors and 223 nuclear research reactors in operation around the world. In the early era of nuclear reactors (1940s), a reactor was known as a nuclear pile or atomic pile (so-called because the graphite moderator blocks of the first reactor were placed into a tall pi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pakistan Atomic Energy Commission
Pakistan Atomic Energy Commission (PAEC) (Urdu: ) is a federally funded independent governmental agency, concerned with research and development of nuclear power, promotion of nuclear science, energy conservation and the peaceful usage of nuclear technology. Since its establishment in 1956, the PAEC has overseen the extensive development of nuclear infrastructure to support the economical uplift of Pakistan by founding institutions that focus on development on food irradiation and on nuclear medicine radiation therapy for cancer treatment. The PAEC organizes conferences and directs research at the country's leading universities. Since the 1960s, the PAEC is also a scientific research partner and sponsor of the European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN), where Pakistani scientists have contributed to developing particle accelerators and research on high-energy physics. PAEC scientists regularly pay visits to CERN while taking part in projects led by CERN. Until 2001, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siddique Ahmad Butt
Siddique may refer to: Mononym * Siddique (actor), Indian actor * Siddique (director), Indian director and script writer Given name * Siddique ul-Islam (1970–2007), Bangladeshi terrorist * Siddique Salik (1935–1988), Pakistani general and author * Siddique Umer (born 1982), Pakistani sport shooter Middle name *Ammar Siddique Khan, Pakistani politician member of the Provincial Assembly of the Punjab *Mian Ghulam Siddique Mekan (1844-1905), Muslim Scholar, Sufi of Qadri order and poet *Ramzan Siddique Bhatti, Pakistani politician and member of the Provincial Assembly of the Punjab Surname *AAMS Arefin Siddique or Abu Ahsan Mohammad Shamsul Arefin Siddique (born 1953), Bangladeshi academic *Ab Siddique (1927-2012), Bangladeshi politician *Abubakar Siddique (born 1936), Bangladeshi poet, novelist, short story writer and critic * Abubakar Boniface Siddique also Abubakar Saddique Boniface) (born 1960), Ghanaian politician and government minister *Abdul Kader Siddique, Bangladeshi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Physicist
Nuclear physics is the field of physics that studies atomic nuclei and their constituents and interactions, in addition to the study of other forms of nuclear matter. Nuclear physics should not be confused with atomic physics, which studies the atom as a whole, including its electrons. Discoveries in nuclear physics have led to applications in many fields. This includes nuclear power, nuclear weapons, nuclear medicine and magnetic resonance imaging, industrial and agricultural isotopes, ion implantation in materials engineering, and radiocarbon dating in geology and archaeology. Such applications are studied in the field of nuclear engineering. Particle physics evolved out of nuclear physics and the two fields are typically taught in close association. Nuclear astrophysics, the application of nuclear physics to astrophysics, is crucial in explaining the inner workings of stars and the origin of the chemical elements. History The history of nuclear physics as a discipline ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beryllium
Beryllium is a chemical element with the symbol Be and atomic number 4. It is a steel-gray, strong, lightweight and brittle alkaline earth metal. It is a divalent element that occurs naturally only in combination with other elements to form minerals. Notable gemstones high in beryllium include beryl ( aquamarine, emerald) and chrysoberyl. It is a relatively rare element in the universe, usually occurring as a product of the spallation of larger atomic nuclei that have collided with cosmic rays. Within the cores of stars, beryllium is depleted as it is fused into heavier elements. Beryllium constitutes about 0.0004 percent by mass of Earth's crust. The world's annual beryllium production of 220 tons is usually manufactured by extraction from the mineral beryl, a difficult process because beryllium bonds strongly to oxygen. In structural applications, the combination of high flexural rigidity, thermal stability, thermal conductivity and low density (1.85 times that of water) ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Technology
Nuclear technology is technology that involves the nuclear reactions of atomic nuclei. Among the notable nuclear technologies are nuclear reactors, nuclear medicine and nuclear weapons. It is also used, among other things, in smoke detectors and gun sights. History and scientific background Discovery The vast majority of common, natural phenomena on Earth only involve gravity and electromagnetism, and not nuclear reactions. This is because atomic nuclei are generally kept apart because they contain positive electrical charges and therefore repel each other. In 1896, Henri Becquerel was investigating phosphorescence in uranium salts when he discovered a new phenomenon which came to be called radioactivity. He, Pierre Curie and Marie Curie began investigating the phenomenon. In the process, they isolated the element radium, which is highly radioactive. They discovered that radioactive materials produce intense, penetrating rays of three distinct sorts, which they labeled al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
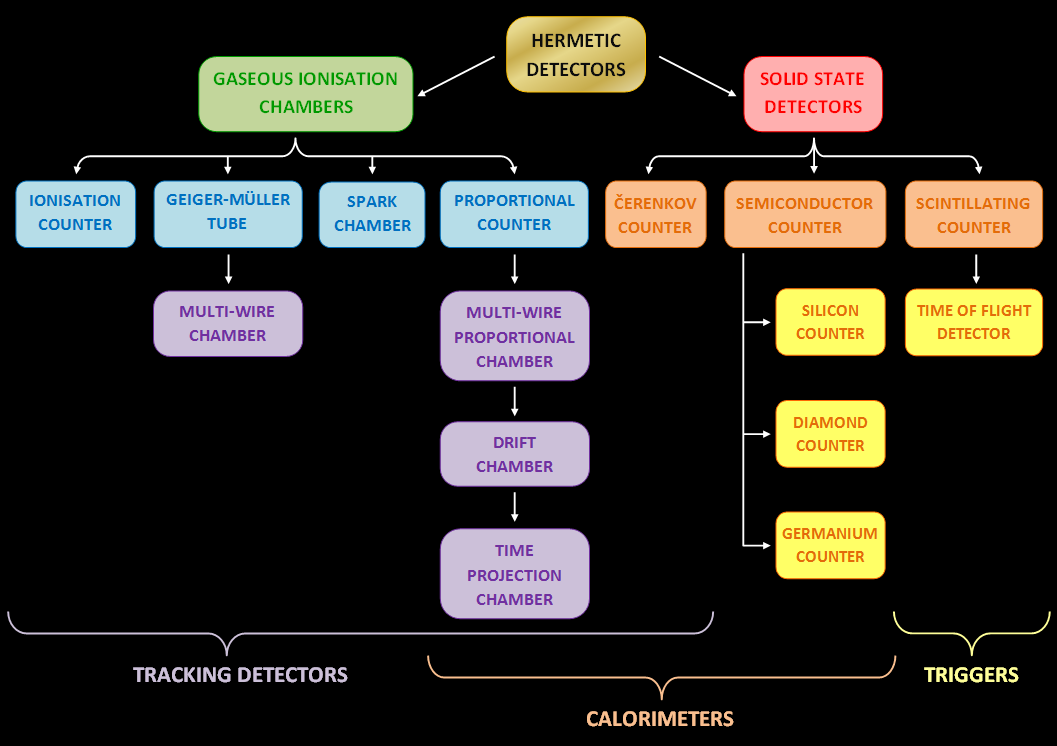
Particle Detector
In experimental and applied particle physics, nuclear physics, and nuclear engineering, a particle detector, also known as a radiation detector, is a device used to detect, track, and/or identify ionizing particles, such as those produced by nuclear decay, cosmic radiation, or reactions in a particle accelerator. Detectors can measure the particle energy and other attributes such as momentum, spin, charge, particle type, in addition to merely registering the presence of the particle. Examples and types Many of the detectors invented and used so far are ionization detectors (of which gaseous ionization detectors and semiconductor detectors are most typical) and scintillation detectors; but other, completely different principles have also been applied, like Čerenkov light and transition radiation. Historical examples *Bubble chamber * Wilson cloud chamber (diffusion chamber) * Photographic plate ;Detectors for radiation protection The following types of particle detector ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |