|
Perceptual Coding
Psychoacoustics is the branch of psychophysics involving the scientific study of the perception of sound by the human auditory system. It is the branch of science studying the psychological responses associated with sound including noise, speech, and music. Psychoacoustics is an interdisciplinary field including psychology, acoustics, electronic engineering, physics, biology, physiology, and computer science. Background Hearing is not a purely mechanical phenomenon of wave propagation, but is also a sensory and perceptual event. When a person hears something, that something arrives at the ear as a mechanical sound wave traveling through the air, but within the ear it is transformed into neural action potentials. These nerve pulses then travel to the brain where they are perceived. Hence, in many problems in acoustics, such as for audio processing, it is advantageous to take into account not just the mechanics of the environment, but also the fact that both the ear and the brain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychophysics
Psychophysics is the field of psychology which quantitatively investigates the relationship between physical stimulus (physiology), stimuli and the sensation (psychology), sensations and perceptions they produce. Psychophysics has been described as "the scientific study of the relation between stimulus and Sensation (psychology), sensation" or, more completely, as "the analysis of perceptual processes by studying the effect on a subject's experience or behaviour of systematically varying the properties of a stimulus along one or more physical dimensions". ''Psychophysics'' also refers to a general class of methods that can be applied to study a perceptual system. Modern applications rely heavily on threshold measurement, ideal observer analysis, and Detection theory, signal detection theory. Psychophysics has widespread and important practical applications. For instance, in the realm of digital signal processing, insights from psychophysics have guided the development of models a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loudness
In acoustics, loudness is the subjectivity, subjective perception of sound pressure. More formally, it is defined as the "attribute of auditory sensation in terms of which sounds can be ordered on a scale extending from quiet to loud". The relation of physical attributes of sound to perceived loudness consists of physical, physiological and psychological components. The study of apparent loudness is included in the topic of psychoacoustics and employs methods of psychophysics. In different industries, loudness may have different meanings and different measurement standards. Some definitions, such as ITU-R BS.1770 refer to the relative loudness of different segments of electronically reproduced sounds, such as for broadcasting and cinema. Others, such as ISO 532A (Stevens loudness, measured in sones), ISO 532B (Eberhard Zwicker, Zwicker loudness), DIN 45631 and ASA/ANSI S3.4, have a more general scope and are often used to characterize loudness of environmental noise. More modern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decibel
The decibel (symbol: dB) is a relative unit of measurement equal to one tenth of a bel (B). It expresses the ratio of two values of a Power, root-power, and field quantities, power or root-power quantity on a logarithmic scale. Two signals whose level (logarithmic quantity), levels differ by one decibel have a power ratio of 101/10 (approximately ) or root-power ratio of 101/20 (approximately ). The strict original usage above only expresses a relative change. However, the word decibel has since also been used for expressing an Absolute scale, absolute value that is relative to some fixed reference value, in which case the dB symbol is often suffixed with letter codes that indicate the reference value. For example, for the reference value of 1 volt, a common suffix is "#Voltage, V" (e.g., "20 dBV"). As it originated from a need to express power ratios, two principal types of scaling of the decibel are used to provide consistency depending on whether the scaling refer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sound Pressure Level
Sound pressure or acoustic pressure is the local pressure deviation from the ambient (average or equilibrium) atmospheric pressure, caused by a sound wave. In air, sound pressure can be measured using a microphone, and in water with a hydrophone. The International System of Units, SI unit of sound pressure is the Pascal (unit), pascal (Pa). Mathematical definition A sound wave in a transmission medium causes a deviation (sound pressure, a ''dynamic'' pressure) in the local ambient pressure, a ''static'' pressure. Sound pressure, denoted ''p'', is defined by p_\text = p_\text + p, where * ''p''total is the total pressure, * ''p''stat is the static pressure. Sound measurements Sound intensity In a sound wave, the complementary variable to sound pressure is the particle velocity. Together, they determine the sound intensity of the wave. ''Sound intensity'', denoted I and measured in Watt, W·Metre, m−2 in SI units, is defined by \mathbf I = p \mathbf v, where * ''p'' is th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micropascal
The pascal (symbol: Pa) is the unit of pressure in the International System of Units (SI). It is also used to quantify internal pressure, stress, Young's modulus, and ultimate tensile strength. The unit, named after Blaise Pascal, is an SI coherent derived unit defined as one newton per square metre (N/m2). It is also equivalent to 10 barye (10 Ba) in the CGS system. Common multiple units of the pascal are the hectopascal (1 hPa = 100 Pa), which is equal to one millibar, and the kilopascal (1 kPa = 1000 Pa), which is equal to one centibar. The unit of measurement called '' standard atmosphere (atm)'' is defined as . Meteorological observations typically report atmospheric pressure in hectopascals per the recommendation of the World Meteorological Organization, thus a standard atmosphere (atm) or typical sea-level air pressure is about 1013 hPa. Reports in the United States typically use inches of mercury or millibars (hectopascals). In Canada, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
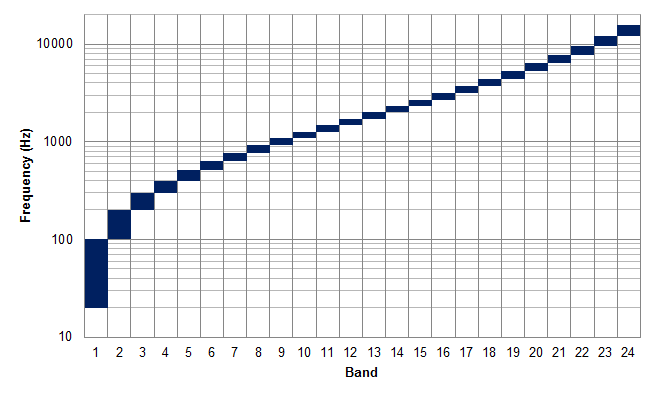
Bark Scale
The Bark scale is a psychoacoustical scale proposed by Eberhard Zwicker in 1961. It is named after Heinrich Barkhausen, who proposed the first subjective measurements of loudness.Zwicker, E. (1961),Subdivision of the audible frequency range into critical bands, ''The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America'', Volume 33, Issue 2, p. 248 (1961). One definition of the term is "a frequency scale on which equal distances correspond with perceptually equal distances. Above about 500 Hz this scale is more or less equal to a logarithmic frequency axis. Below 500 Hz the Bark scale becomes more and more linear." The scale ranges from 1 to 24 and corresponds to the first 24 critical bands of hearing. It is related to, but somewhat less popular than, the mel scale, a perceptual scale of pitches judged by listeners to be equal in distance from one another. Bark scale critical bands Since the direct measurements of the critical bands are subject to er ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mel Scale
The mel scale (after the word ''melody'') is a perceptual scale of pitches judged by listeners to be equal in distance from one another. The reference point between this scale and normal frequency measurement is defined by assigning a perceptual pitch of 1000 mels to a 1000 Hz tone, 40 dB above the listener's threshold. Above about 500 Hz, increasingly large intervals are judged by listeners to produce equal pitch increments. Formula A formula (O'Shaughnessy 1987) to convert ''f'' hertz into ''m'' mels is m = 2595 \log_\left(1 + \frac\right). History and other formulas The formula from O'Shaughnessy's book can be expressed with different logarithmic bases: m = 2595 \log_\left(1 + \frac\right) = 1127 \ln\left(1 + \frac\right). The corresponding inverse expressions are f = 700\left(10^\frac - 1\right) = 700\left(e^\frac - 1\right). There were published curves and tables on psychophysical pitch scales since Steinberg's 1937 curves based on just-noticeable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Logarithmic Scale
A logarithmic scale (or log scale) is a method used to display numerical data that spans a broad range of values, especially when there are significant differences among the magnitudes of the numbers involved. Unlike a linear Scale (measurement), scale where each unit of distance corresponds to the same increment, on a logarithmic scale each unit of length is a multiple of some base value raised to a power, and corresponds to the multiplication of the previous value in the scale by the base value. In common use, logarithmic scales are in base 10 (unless otherwise specified). A logarithmic scale is Nonlinear system, nonlinear, and as such numbers with equal distance between them such as 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 are not equally spaced. Equally spaced values on a logarithmic scale have exponents that increment uniformly. Examples of equally spaced values are 10, 100, 1000, 10000, and 100000 (i.e., 101, 102, 103, 104, 105) and 2, 4, 8, 16, and 32 (i.e., 21, 22, 23, 24, 25). Exponential growt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semitone
A semitone, also called a minor second, half step, or a half tone, is the smallest musical interval commonly used in Western tonal music, and it is considered the most dissonant when sounded harmonically. It is defined as the interval between two adjacent notes in a 12-tone scale (or half of a whole step), visually seen on a keyboard as the distance between two keys that are adjacent to each other. For example, C is adjacent to C; the interval between them is a semitone. In a 12-note approximately equally divided scale, any interval can be defined in terms of an appropriate number of semitones (e.g. a whole tone or major second is 2 semitones wide, a major third 4 semitones, and a perfect fifth 7 semitones). In music theory, a distinction is made between a diatonic semitone, or minor second (an interval encompassing two different staff positions, e.g. from C to D) and a chromatic semitone or augmented unison (an interval between two notes at the same staff position, e.g. f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beat (acoustics)
In acoustics, a beat is an interference pattern between two sounds of slightly different frequencies, ''perceived'' as a periodic variation in volume whose rate is the difference of the two frequencies. With tuning instruments that can produce sustained tones, beats can be readily recognized. Tuning two tones to a unison will present a peculiar effect: when the two tones are close in pitch but not identical, the difference in frequency generates the beating. The volume varies as in a tremolo as the sounds alternately interfere constructively and destructively. As the two tones gradually approach unison, the beating slows down and may become so slow as to be imperceptible. As the two tones get further apart, their beat frequency starts to approach the range of human pitch perception, the beating starts to sound like a note, and a combination tone is produced. Mathematics and physics of beat tones This phenomenon is best known in acoustics or music, though it can be found in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sense Of Touch
The somatosensory system, or somatic sensory system is a subset of the sensory nervous system. The main functions of the somatosensory system are the perception of external stimuli, the perception of internal stimuli, and the regulation of body position and balance (proprioception). It is believed to act as a pathway between the different sensory modalities within the body. As of 2024 debate continued on the underlying mechanisms, correctness and validity of the somatosensory system model, and whether it impacts emotions in the body. The somatosensory system has been thought of as having two subdivisions; *one for the detection of mechanosensory information related to touch. Mechanosensory information includes that of light touch, vibration, pressure and tension in the skin. Much of this information belongs to the sense of touch which is a general somatic sense in contrast to the special senses of sight, smell, taste, hearing, and balance. * one for the nociception det ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perceived Human Hearing
Perception () is the organization, identification, and interpretation of sensory information in order to represent and understand the presented information or environment. All perception involves signals that go through the nervous system, which in turn result from physical or chemical stimulation of the sensory system.Goldstein (2009) pp. 5–7 Vision involves light striking the retina of the eye; smell is mediated by odor molecules; and hearing involves pressure waves. Perception is not only the passive receipt of these signals, but it is also shaped by the recipient's learning, memory, expectation, and attention. Gregory, Richard. "Perception" in Gregory, Zangwill (1987) pp. 598–601. Sensory input is a process that transforms this low-level information to higher-level information (e.g., extracts shapes for object recognition). The following process connects a person's concepts and expectations (or knowledge) with restorative and selective mechanisms, such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |