|
Pentaerythritol Tetranitrate
Pentaerythritol tetranitrate (PETN), also known as PENT, PENTA, (ПЕНТА, primarily in Russian) TEN, corpent, or penthrite (or, rarely and primarily in German, as nitropenta), is an explosive material. It is the nitrate ester of pentaerythritol, and is structurally very similar to nitroglycerin. Penta refers to the five carbon atoms of the neopentane skeleton. PETN is a very powerful explosive material with a relative effectiveness factor of 1.66. When mixed with a plasticizer, PETN forms a plastic explosive. Along with RDX it is the main ingredient of Semtex. PETN is also used as a vasodilator drug to treat certain heart conditions, such as for management of angina. History Pentaerythritol tetranitrate was first prepared and patented in 1894 by the explosives manufacturer Rheinisch-Westfälische Sprengstoff A.G. of Cologne, Germany. The production of PETN started in 1912, when the improved method of production was patented by the German government. PETN was used by the Ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Explosive Material
An explosive (or explosive material) is a reactive substance that contains a great amount of potential energy that can produce an explosion if released suddenly, usually accompanied by the production of light, heat, sound, and pressure. An explosive charge is a measured quantity of explosive material, which may either be composed solely of one ingredient or be a mixture containing at least two substances. The potential energy stored in an explosive material may, for example, be * chemical energy, such as nitroglycerin or grain dust * pressurized gas, such as a gas cylinder, aerosol can, or BLEVE * nuclear energy, such as in the fissile isotopes uranium-235 and plutonium-239 Explosive materials may be categorized by the speed at which they expand. Materials that detonate (the front of the chemical reaction moves faster through the material than the speed of sound) are said to be "high explosives" and materials that deflagrate are said to be "low explosives". Explosives ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
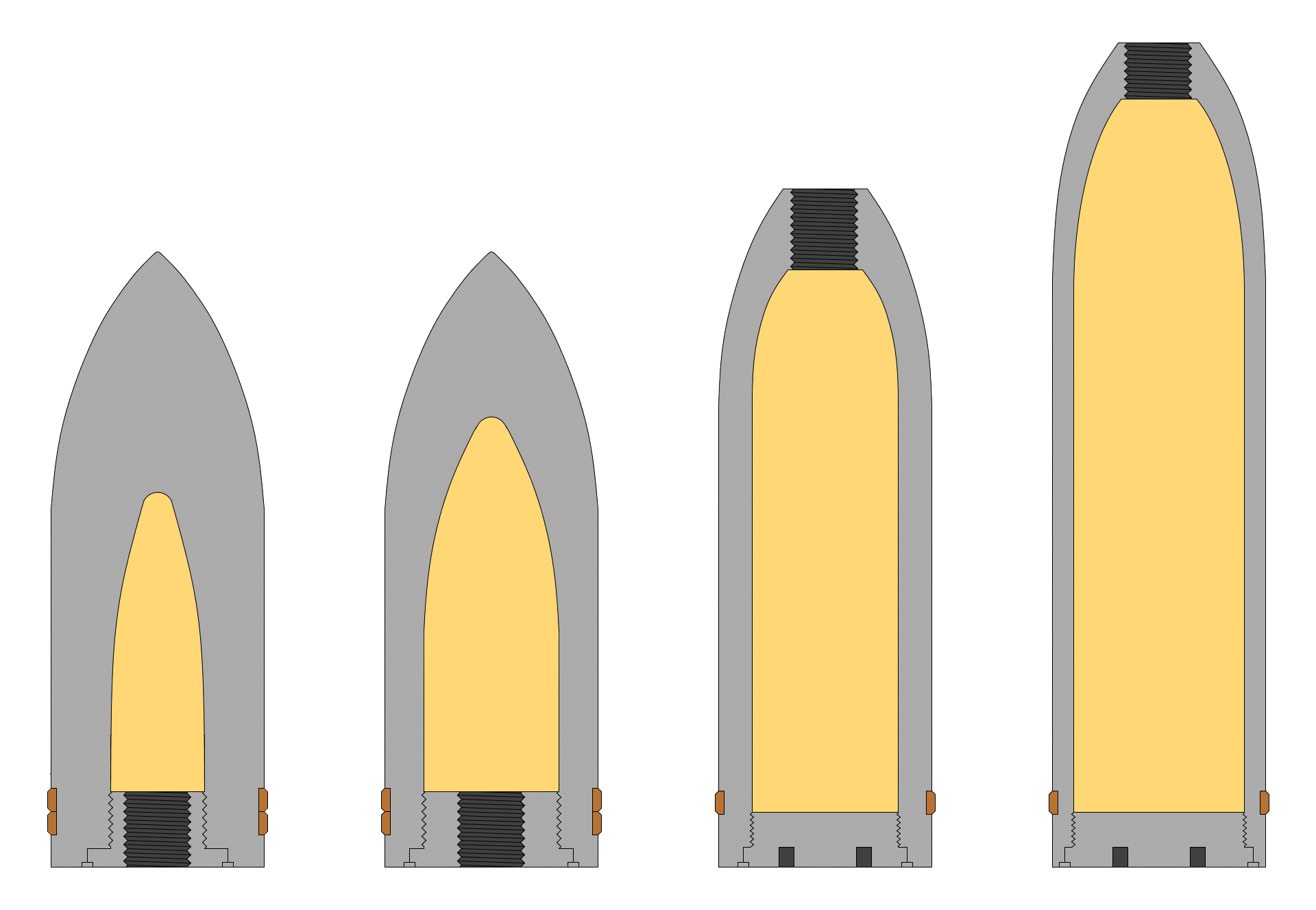
Mine Shell
A mine shell (from the German term ''Minengeschoß'', "mine shot"), also known as High-Explosive, High-Capacity (HEHC) in British military nomenclature, is a military explosive shell type characterized by thin (usually steel) shell walls and a correspondingly high quantity of explosives, much higher than the traditional high explosive shell type per caliber, meaning that mine shells trade fragmentation effect (due to the thinner shell walls) for a higher pressure wave effect when comparing to traditional high explosive shells. Mine shells were originally developed during the mid to late 1800s against fortresses prior to rebar but got a new role during World War II against air targets as reinforced fortresses had made the original use of the type obsolete around World War I. Effect, construction and use The mine shell is a more explosive version of the common high-explosive and high-explosive fragmentation shells, relying on inflicting damage primarily through the blast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrolysis
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile. Biological hydrolysis is the cleavage of biomolecules where a water molecule is consumed to effect the separation of a larger molecule into component parts. When a carbohydrate is broken into its component sugar molecules by hydrolysis (e.g., sucrose being broken down into glucose and fructose), this is recognized as saccharification. Hydrolysis reactions can be the reverse of a condensation reaction in which two molecules join into a larger one and eject a water molecule. Thus hydrolysis adds water to break down, whereas condensation builds up by removing water. Types Usually hydrolysis is a chemical process in which a molecule of water is added to a substance. Sometimes this addition causes both the substance and water molecule to split into two parts. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reagent
In chemistry, a reagent ( ) or analytical reagent is a substance or compound added to a system to cause a chemical reaction, or test if one occurs. The terms ''reactant'' and ''reagent'' are often used interchangeably, but reactant specifies a substance ''consumed'' in the course of a chemical reaction. ''Solvents'', though involved in the reaction mechanism, are usually not called reactants. Similarly, ''catalysts'' are not consumed by the reaction, so they are not reactants. In biochemistry, especially in connection with enzyme-catalyzed reactions, the reactants are commonly called substrates. Definitions Organic chemistry In organic chemistry, the term "reagent" denotes a chemical ingredient (a compound or mixture, typically of inorganic or small organic molecules) introduced to cause the desired transformation of an organic substance. Examples include the Collins reagent, Fenton's reagent, and Grignard reagents. Analytical chemistry In analytical chemistry, a reagent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetryl
2,4,6-Trinitrophenylmethylnitramine commonly referred to as tetryl ( C7 H5 N5 O8) is an explosive compound used to make detonators and explosive booster charges. Tetryl is a nitramine booster explosive, though its use has been largely superseded by RDX. Tetryl is a sensitive secondary high explosive used as a booster, a small charge placed next to the detonator in order to propagate detonation into the main explosive charge. Chemical properties Tetryl is a yellow crystalline solid powder material, practically insoluble in water but soluble in acetone, benzene and other solvents. When tetryl is heated, it first melts, then decomposes and explodes. It burns readily and is more easily detonated than ammonium picrate or TNT, being about as sensitive as picric acid. It is detonated by friction, shock, or spark. It remains stable at all temperatures which may be encountered in storage. It is generally used in the form of pressed pellets, and has been approved as the standard burs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trinitrotoluene
Trinitrotoluene (), more commonly known as TNT, more specifically 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene, and by its preferred IUPAC name 2-methyl-1,3,5-trinitrobenzene, is a chemical compound with the formula C6H2(NO2)3CH3. TNT is occasionally used as a reagent in chemical synthesis, but it is best known as an explosive material with convenient handling properties. The explosive yield of TNT is considered to be the standard comparative convention of bombs and asteroid impacts. In chemistry, TNT is used to generate charge transfer salts. History TNT was first prepared in 1863 by German chemist Julius Wilbrand and originally used as a yellow dye. Its potential as an explosive was not recognized for three decades, mainly because it was too difficult to detonate because it was less sensitive than alternatives. Its explosive properties were first discovered in 1891 by another German chemist, Carl Häussermann. TNT can be safely poured when liquid into shell cases, and is so insensitive t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitro Compound
In organic chemistry, nitro compounds are organic compounds that contain one or more nitro functional groups (). The nitro group is one of the most common explosophores (functional group that makes a compound explosive) used globally. The nitro group is also strongly electron-withdrawing. Because of this property, bonds alpha (adjacent) to the nitro group can be acidic. For similar reasons, the presence of nitro groups in aromatic compounds retards electrophilic aromatic substitution but facilitates nucleophilic aromatic substitution. Nitro groups are rarely found in nature. They are almost invariably produced by nitration reactions starting with nitric acid. Synthesis Preparation of aromatic nitro compounds Aromatic nitro compounds are typically synthesized by nitration. Nitration is achieved using a mixture of nitric acid and sulfuric acid, which produce the nitronium ion (), which is the electrophile: + The nitration product produced on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aromaticity
In chemistry, aromaticity is a chemical property of cyclic (ring-shaped), ''typically'' planar (flat) molecular structures with pi bonds in resonance (those containing delocalized electrons) that gives increased stability compared to saturated compounds having single bonds, and other geometric or connective non-cyclic arrangements with the same set of atoms. Aromatic rings are very stable and do not break apart easily. Organic compounds that are not aromatic are classified as aliphatic compounds—they might be cyclic, but only aromatic rings have enhanced stability. The term ''aromaticity'' with this meaning is historically related to the concept of having an aroma, but is a distinct property from that meaning. Since the most common aromatic compounds are derivatives of benzene (an aromatic hydrocarbon common in petroleum and its distillates), the word ''aromatic'' occasionally refers informally to benzene derivatives, and so it was first defined. Nevertheless, man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eutectic System
A eutectic system or eutectic mixture ( ) is a homogeneous mixture that has a melting point lower than those of the constituents. The lowest possible melting point over all of the mixing ratios of the constituents is called the ''eutectic temperature''. On a phase diagram, the eutectic temperature is seen as the eutectic point (see plot on the right). Non-eutectic mixture ratios would have different melting temperatures for their different constituents, since one component's lattice will melt at a lower temperature than the other's. Conversely, as a non-eutectic mixture cools down, each of its components would solidify (form a lattice) at a different temperature, until the entire mass is solid. Not all binary alloys have eutectic points, since the valence electrons of the component species are not always compatible, in any mixing ratio, to form a new type of joint crystal lattice. For example, in the silver-gold system the melt temperature (liquidus) and freeze temperature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimethylformamide
Dimethylformamide is an organic compound with the formula ( CH3)2NC(O)H. Commonly abbreviated as DMF (although this initialism is sometimes used for dimethylfuran, or dimethyl fumarate), this colourless liquid is miscible with water and the majority of organic liquids. DMF is a common solvent for chemical reactions. Dimethylformamide is odorless, but technical-grade or degraded samples often have a fishy smell due to impurity of dimethylamine. Dimethylamine degradation impurities can be removed by sparging samples with an inert gas such as argon or by sonicating the samples under reduced pressure. As its name indicates, it is structurally related to formamide, having two methyl groups in the place of the two hydrogens. DMF is a polar (hydrophilic) aprotic solvent with a high boiling point. It facilitates reactions that follow polar mechanisms, such as SN2 reactions. Structure and properties As for most amides, the spectroscopic evidence indicates partial double bond cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetone
Acetone (2-propanone or dimethyl ketone), is an organic compound with the formula . It is the simplest and smallest ketone (). It is a colorless, highly volatile and flammable liquid with a characteristic pungent odour. Acetone is miscible with water and serves as an important organic solvent in its own right, in industry, home, and laboratory. About 6.7 million tonnes were produced worldwide in 2010, mainly for use as a solvent and production of methyl methacrylate (and from that PMMA) as well as bisphenol A.Acetone World Petrochemicals report, January 2010Stylianos Sifniades, Alan B. Levy, "Acetone" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2005. It is a common building block in |
Carbon Tetrachloride
Carbon tetrachloride, also known by many other names (such as tetrachloromethane, also recognised by the IUPAC, carbon tet in the cleaning industry, Halon-104 in firefighting, and Refrigerant-10 in HVACR) is an organic compound with the chemical formula CCl4. It is a colourless liquid with a "sweet" smell that can be detected at low levels. It is practically incombustible at lower temperatures. It was formerly widely used in fire extinguishers, as a precursor to refrigerants and as a cleaning agent, but has since been phased out because of environmental and safety concerns. Exposure to high concentrations of carbon tetrachloride (including vapor) can affect the central nervous system and degenerate the liver and kidneys. Prolonged exposure can be fatal. Properties In the carbon tetrachloride molecule, four chlorine atoms are positioned symmetrically as corners in a tetrahedral configuration joined to a central carbon atom by single covalent bonds. Because of this symmetric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.png)

