|
Pediments Of The Parthenon
The pediments of the Parthenon are the two sets of statues (around fifty) in Pentelic marble originally located as the pedimental sculpture on the east and west facades of the Parthenon on the Acropolis of Athens. They were probably made by several artists, including Agoracritos. The master builder was probably Phidias. They were probably lifted into place by 432 BC, having been carved on the ground. Pausanias, a Greek geographer, described their subjects: to the east, the birth of Athena, and to the west the quarrel between her and Poseidon to become the tutelary deity of Athens. The pediments were very damaged by time and military conflicts. Considered the archetype of classical sculpture, or even the embodiment of ideal beauty, several of the statues were removed from the building by Lord Elgin's agents in the early nineteenth century and transported to the British Museum in London. Some statues and many fragments are kept at the Acropolis Museum in Athens. Other groups of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
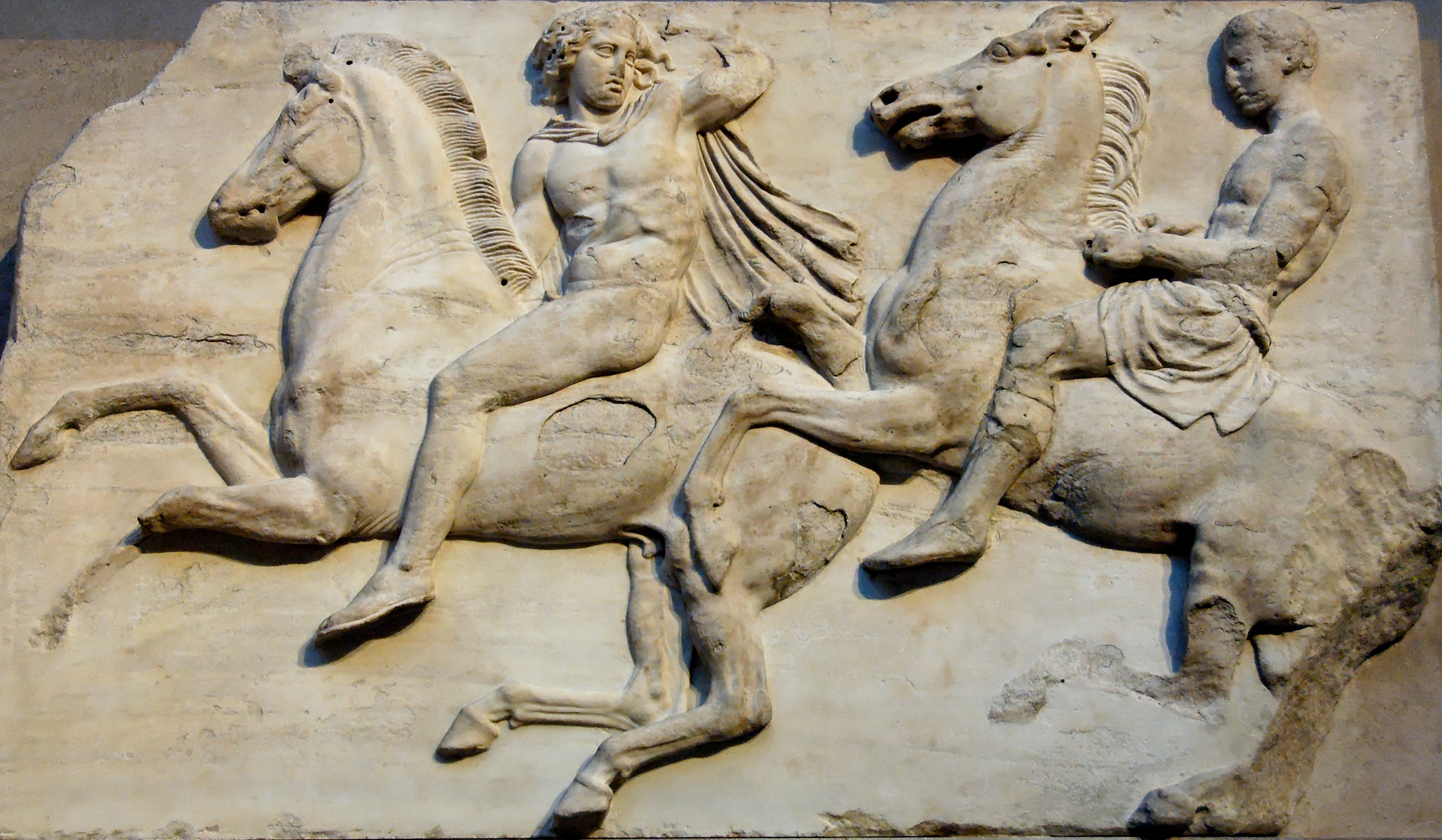
Dionysos Pediment Parthenon BM
In ancient Greek religion and myth, Dionysus (; grc, Διόνυσος ) is the god of the grape-harvest, winemaking, orchards and fruit, vegetation, fertility, insanity, ritual madness, religious ecstasy, festivity, and theatre. The Romans called him Bacchus ( or ; grc, Βάκχος ) for a frenzy he is said to induce called ''bakkheia''. As Dionysus Eleutherios ("the liberator"), his wine, music, and ecstatic dance free his followers from self-conscious fear and care, and subvert the oppressive restraints of the powerful. His ''thyrsus'', a fennel-stem sceptre, sometimes wound with ivy and dripping with honey, is both a beneficent wand and a weapon used to destroy those who oppose his cult and the freedoms he represents. Those who partake of his mysteries are believed to become possessed and empowered by the god himself. His origins are uncertain, and his cults took many forms; some are described by ancient sources as Thracian, others as Greek. In Orphic religion, he was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parthenon Frieze
The Parthenon frieze is the high-relief Pentelic marble sculpture created to adorn the upper part of the Parthenon’s naos. It was sculpted between c. 443 and 437 BC, most likely under the direction of Pheidias. Of the 160 meters (524 ft) of the original frieze, 128 meters (420 ft) survives—some 80 percent. The rest is known only from the drawings attributed to French artist Jacques Carrey in 1674, thirteen years before the Venetian bombardment that ruined the temple. At present, the majority of the frieze is at the British Museum in London (forming the major part of the Elgin Marbles); the largest proportion of the rest is at the Acropolis Museum in Athens, and the remainder of fragments shared between six other institutions. Casts of the frieze may be found in the Beazley archive at the Ashmolean Museum at Oxford, at the Spurlock Museum in Urbana, in the Skulpturhalle at Basel and elsewhere. Construction Plutarch’s ''Life of Pericles'', 13.4–9, informs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
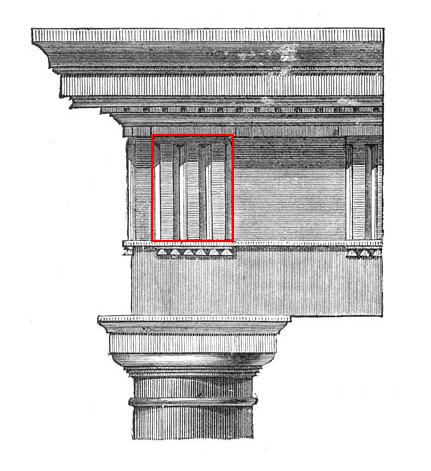
Metope (architecture)
In classical architecture, a metope (μετόπη) is a rectangular architectural element that fills the space between two triglyphs in a Doric order, Doric frieze, which is a decorative band of alternating triglyphs and metopes above the architrave of a building of the Doric order. Metopes often had painted or sculptural decoration; the most famous example are the 92 metopes of the Parthenon marbles some of which depict the battle between the Centaurs and the Lapiths. The painting on most metopes has been lost, but sufficient traces remain to allow a close idea of their original appearance. In terms of structure, metopes may be carved from a single block with a triglyph (or triglyphs), or they may be cut separately and slide into slots in the triglyph blocks as at the Temple of Aphaea. Sometimes the metopes and friezes were cut from different stone, so as to provide color contrast. Although they tend to be close to square in shape, some metopes are noticeably larger in heigh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triglyphs
Triglyph is an architectural term for the vertically channeled tablets of the Doric frieze in classical architecture, so called because of the angular channels in them. The rectangular recessed spaces between the triglyphs on a Doric frieze are called metopes. The raised spaces between the channels themselves (within a triglyph) are called ''femur'' in Latin or ''meros'' in Greek. In the strict tradition of classical architecture, a set of guttae, the six triangular "pegs" below, always go with a triglyph above (and vice versa), and the pair of features are only found in entablatures of buildings using the Doric order. The absence of the pair effectively converts a building from being in the Doric order to being in the Tuscan order. The triglyph is largely thought to be a tectonic and skeuomorphic representation in stone of the wooden beam ends of the typical primitive hut, as described by Vitruvius and Renaissance writers. The wooden beams were notched in three separate place ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doric Order
The Doric order was one of the three orders of ancient Greek and later Roman architecture; the other two canonical orders were the Ionic and the Corinthian. The Doric is most easily recognized by the simple circular capitals at the top of columns. Originating in the western Doric region of Greece, it is the earliest and, in its essence, the simplest of the orders, though still with complex details in the entablature above. The Greek Doric column was fluted or smooth-surfaced, and had no base, dropping straight into the stylobate or platform on which the temple or other building stood. The capital was a simple circular form, with some mouldings, under a square cushion that is very wide in early versions, but later more restrained. Above a plain architrave, the complexity comes in the frieze, where the two features originally unique to the Doric, the triglyph and gutta, are skeuomorphic memories of the beams and retaining pegs of the wooden constructions that preceded stone Do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Pediments Of The Parthenon
West or Occident is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from east and is the direction in which the Sun sets on the Earth. Etymology The word "west" is a Germanic word passed into some Romance languages (''ouest'' in French, ''oest'' in Catalan, ''ovest'' in Italian, ''oeste'' in Spanish and Portuguese). As in other languages, the word formation stems from the fact that west is the direction of the setting sun in the evening: 'west' derives from the Indo-European root ''*wes'' reduced from ''*wes-pero'' 'evening, night', cognate with Ancient Greek ἕσπερος hesperos 'evening; evening star; western' and Latin vesper 'evening; west'. Examples of the same formation in other languages include Latin occidens 'west' from occidō 'to go down, to set' and Hebrew מַעֲרָב maarav 'west' from עֶרֶב erev 'evening'. Navigation To go west using a compass for navigation (in a place where magnetic north is the same dire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attic Talent
The Attic talent (a talent of the Attic standard), also known as the Athenian talent or Greek talent ( el, τάλαντον, ''talanton''), is an ancient unit of weight equal to about , as well as a unit of value equal to this amount of pure silver.The exact mass of a talent was 25.992kg. Herodotus, Robin Waterfield and Carolyn Dewald, ''The Histories'' (1998), p. 593. A talent was originally intended to be the mass of water required to fill an amphora, about .Talent (Biblical Hebrew), Unit of Measure ''unitconversion.org''. History The earliest known Athenian coins range between the years of 545 BC to 515 BC. However, Athenians had already adopted the |
Epidaurus
Epidaurus ( gr, Ἐπίδαυρος) was a small city (''polis'') in ancient Greece, on the Argolid Peninsula at the Saronic Gulf. Two modern towns bear the name Epidavros: ''Palaia Epidavros'' and ''Nea Epidavros''. Since 2010 they belong to the new municipality of Epidaurus, part of the regional unit of Argolis. The seat of the municipality is the town Lygourio. The nearby sanctuary and ancient theatre were inscribed on the UNESCO World Heritage List in 1988 because of their exemplary architecture and importance in the development and spread of healing sanctuaries and cults across the ancient Greek and Roman worlds. Name and etymology The name “Epidaurus” is of Greek origin. It was named after the hero Epidauros, son of Apollo. According to Strabo, the city was originally named Ἐπίκαρος (Epíkaros) under the Carians, (Aristotle claimed that Caria, as a naval empire, occupied Epidaurus and Hermione) before taking the name Ἐπίταυρος (Epítauros) when the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asclepeion
Asclepieia ( grc, Ἀσκληπιεῖον ''Asklepieion''; Ἀσκλαπιεῖον in Doric dialect; Latin ''aesculapīum'') were healing temples located in ancient Greece (and in the wider Hellenistic and Roman world), dedicated to Asclepius, the first doctor-demigod in Greek mythology. Asclepius was said to have been such a skilled doctor that he could even raise people from the dead. So stemming from the myth of his great healing powers, pilgrims would flock to temples built in his honor in order to seek spiritual and physical healing. Asclepieia included carefully controlled spaces conducive to healing and fulfilled several of the requirements of institutions created for healing. Treatment at these temples largely centered around promoting healthy lifestyles, with a particular emphasis on a person's spiritual needs. Characteristic of the Asclepieion was the practice of '' incubatio'', also known as 'temple sleep.' This was a process by which patients would go to sleep in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Praxiteles
Praxiteles (; el, Πραξιτέλης) of Athens, the son of Cephisodotus the Elder, was the most renowned of the Attica sculptors of the 4th century BC. He was the first to sculpt the nude female form in a life-size statue. While no indubitably attributable sculpture by Praxiteles is extant, numerous copies of his works have survived; several authors, including Pliny the Elder, wrote of his works; and coins engraved with silhouettes of his various famous statuary types from the period still exist. A supposed relationship between Praxiteles and his beautiful model, the Thespian courtesan Phryne, has inspired speculation and interpretation in works of art ranging from painting ( Gérôme) to comic opera ( Saint-Saëns) to shadow play ( Donnay). Some writers have maintained that there were two sculptors of the name Praxiteles. One was a contemporary of Pheidias, and the other his more celebrated grandson. Though the repetition of the same name in every other generation is commo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcamenes
Alcamenes ( grc, Ἀλκαμένης) was an ancient Greek sculptor of Lemnos and Athens, who flourished in the 2nd half of the 5th century BC. He was a younger contemporary of Phidias and noted for the delicacy and finish of his works, among which a Hephaestus and an Aphrodite of the Gardens were conspicuous. Pausanias says that he was the author of one of the pediments of the temple of Zeus at Olympia, but this seems a chronological and stylistic impossibility. Pausanias also refers to a statue of Ares by Alcamenes that was erected on the Athenian agora, which some have related to the Ares Borghese. However, the temple of Ares to which he refers had only been moved from Acharnes and re-sited in the Agora in Augustus's time, and statues known to derive from Alcamenes' statue show the god in a breastplate, so the identification of Alcamenes' Ares with the Ares Borghese is not secure. At Pergamum there was discovered in 1903 a Hellenistic copy of the head of the Hermes "Propyla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leipzig
Leipzig ( , ; Upper Saxon: ) is the most populous city in the German state of Saxony. Leipzig's population of 605,407 inhabitants (1.1 million in the larger urban zone) as of 2021 places the city as Germany's eighth most populous, as well as the second most populous city in the area of the former East Germany after (East) Berlin. Together with Halle (Saale), the city forms the polycentric Leipzig-Halle Conurbation. Between the two cities (in Schkeuditz) lies Leipzig/Halle Airport. Leipzig is located about southwest of Berlin, in the southernmost part of the North German Plain (known as Leipzig Bay), at the confluence of the White Elster River (progression: ) and two of its tributaries: the Pleiße and the Parthe. The name of the city and those of many of its boroughs are of Slavic origin. Leipzig has been a trade city since at least the time of the Holy Roman Empire. The city sits at the intersection of the Via Regia and the Via Imperii, two important medieval trad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |