|
Pediculus Mjobergi
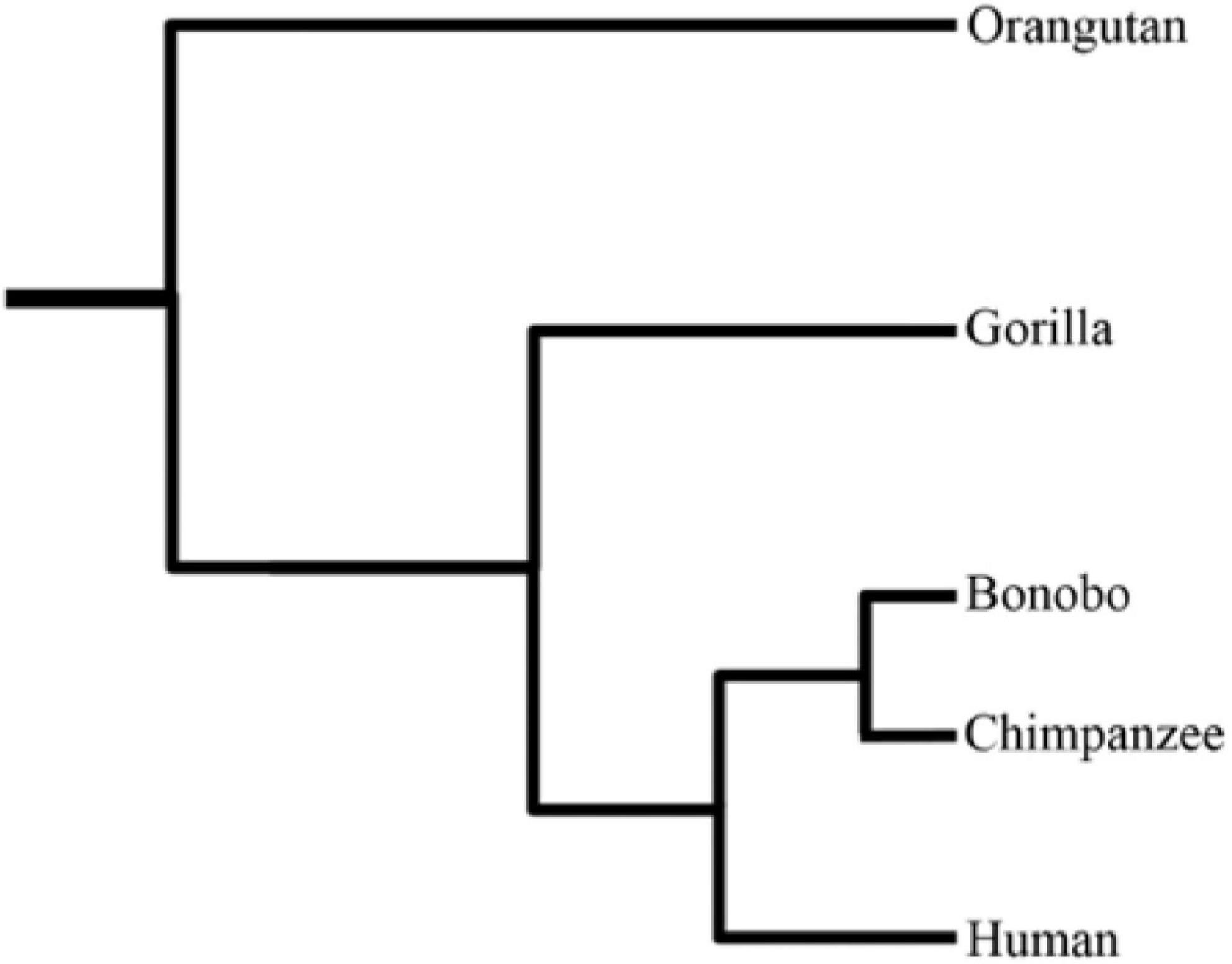
''Pediculus'' is a genus of sucking lice, the sole genus in the family Pediculidae. ''Pediculus'' species are ectoparasites of primates. Species include: *''Pediculus clavicornis'' Nitzsch, 1864 *''Pediculus humanus'' Linnaeus, 1758 **''Pediculus humanus humanus'' Linnaeus, 1758 – the body louse **''Pediculus humanus capitis'' De Geer, 1767 – the head louse *''Pediculus mjobergi'' Ferris, 1916 *''Pediculus schaeffi'' Fahrenholz, 1910 Humans are the hosts of ''Pediculus humanus''. Chimpanzees and bonobos host ''Pediculus shaeffi''. Various New World monkeys in the families Cebidae and Atelidae The Atelidae are one of the five families of New World monkeys now recognised. It was formerly included in the family Cebidae. Atelids are generally larger monkeys; the family includes the howler, spider, woolly, and woolly spider monkeys (t ... host ''Pediculus mjobergi''. References Lice {{louse-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Head Louse
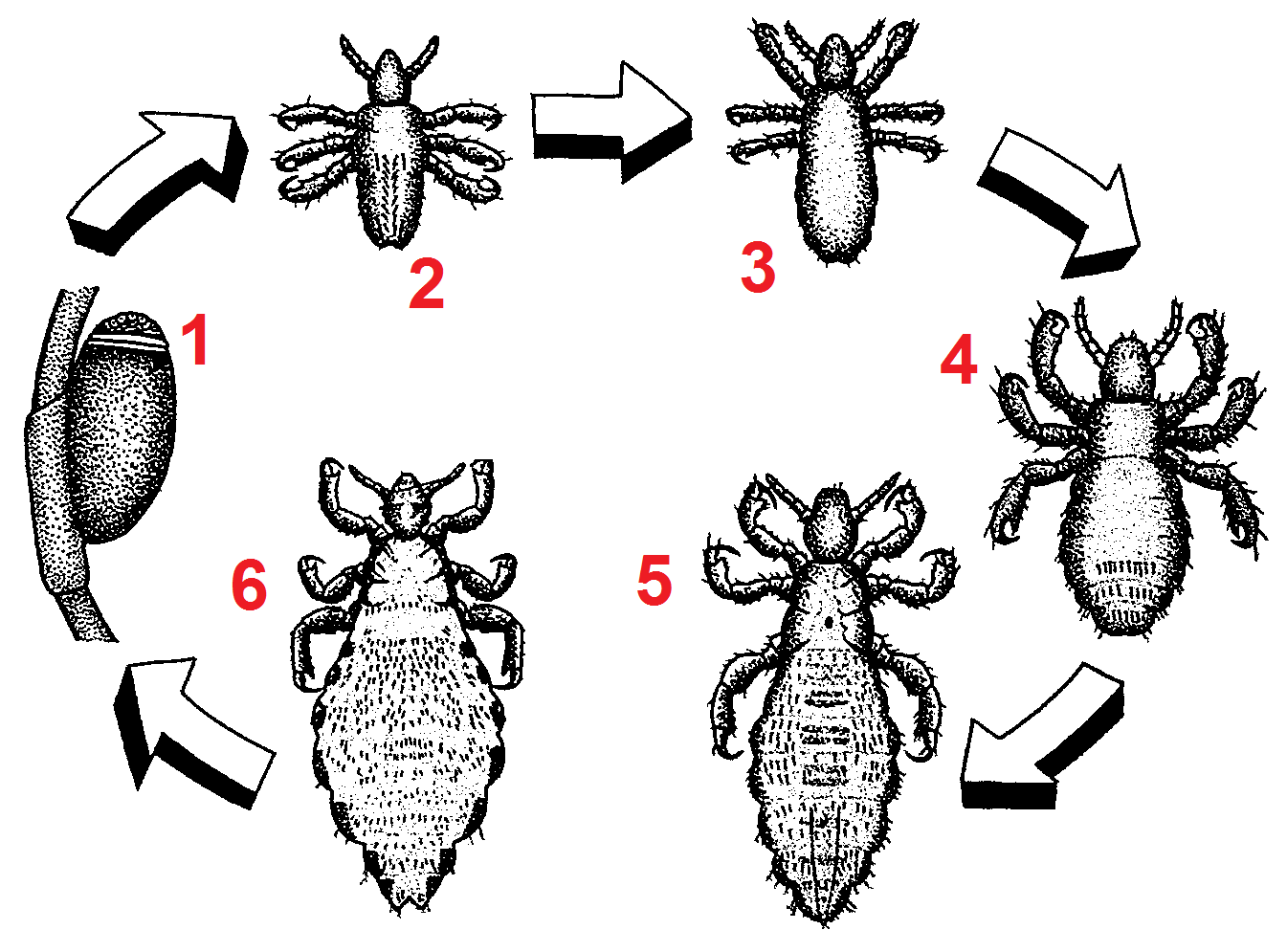
The head louse (''Pediculus humanus capitis'') is an obligate ectoparasite of humans. Head lice are wingless insects that spend their entire lives on the human scalp and feeding exclusively on human blood. Humans are the only known hosts of this specific parasite, while chimpanzees and bonobos host a closely related species, ''Pediculus schaeffi''. Other species of lice infest most orders of mammals and all orders of birds. Lice differ from other hematophagic ectoparasites such as fleas in spending their entire lifecycle on a host. Head lice cannot fly, and their short, stumpy legs render them incapable of jumping, or even walking efficiently on flat surfaces. The non-disease-carrying head louse differs from the related disease-carrying body louse (''Pediculus humanus humanus'') in preferring to attach eggs to scalp hair rather than to clothing. The two subspecies are morphologically almost identical, but do not normally interbreed. From genetic studies, they are thought to h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pediculus Humanus Capitis
The head louse (''Pediculus humanus capitis'') is an obligate ectoparasite of humans. Head lice are wingless insects that spend their entire lives on the human scalp and feeding exclusively on human blood. Humans are the only known hosts of this specific parasite, while chimpanzees and bonobos host a closely related species, ''Pediculus schaeffi''. Other species of lice infest most orders of mammals and all orders of birds. Lice differ from other hematophagic ectoparasites such as fleas in spending their entire lifecycle on a host. Head lice cannot fly, and their short, stumpy legs render them incapable of jumping, or even walking efficiently on flat surfaces. The non-disease-carrying head louse differs from the related disease-carrying body louse (''Pediculus humanus humanus'') in preferring to attach eggs to scalp hair rather than to clothing. The two subspecies are morphologically almost identical, but do not normally interbreed. From genetic studies, they are thought to hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cebidae
The Cebidae are one of the five families of New World monkeys now recognised. Extant members are the capuchin and squirrel monkeys. These species are found throughout tropical and subtropical South and Central America. Characteristics Cebid monkeys are arboreal animals that only rarely travel on the ground. They are generally small monkeys, ranging in size up to that of the brown capuchin, with a body length of 33 to 56 cm, and a weight of 2.5 to 3.9 kilograms. They are somewhat variable in form and coloration, but all have the wide, flat, noses typical of New World monkeys. They are omnivorous, mostly eating fruit and insects, although the proportions of these foods vary greatly between species. They have the dental formula: Females give birth to one or two young after a gestation period of between 130 and 170 days, depending on species. They are social animals, living in groups of between five and forty individuals, with the smaller species typically forming larger g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
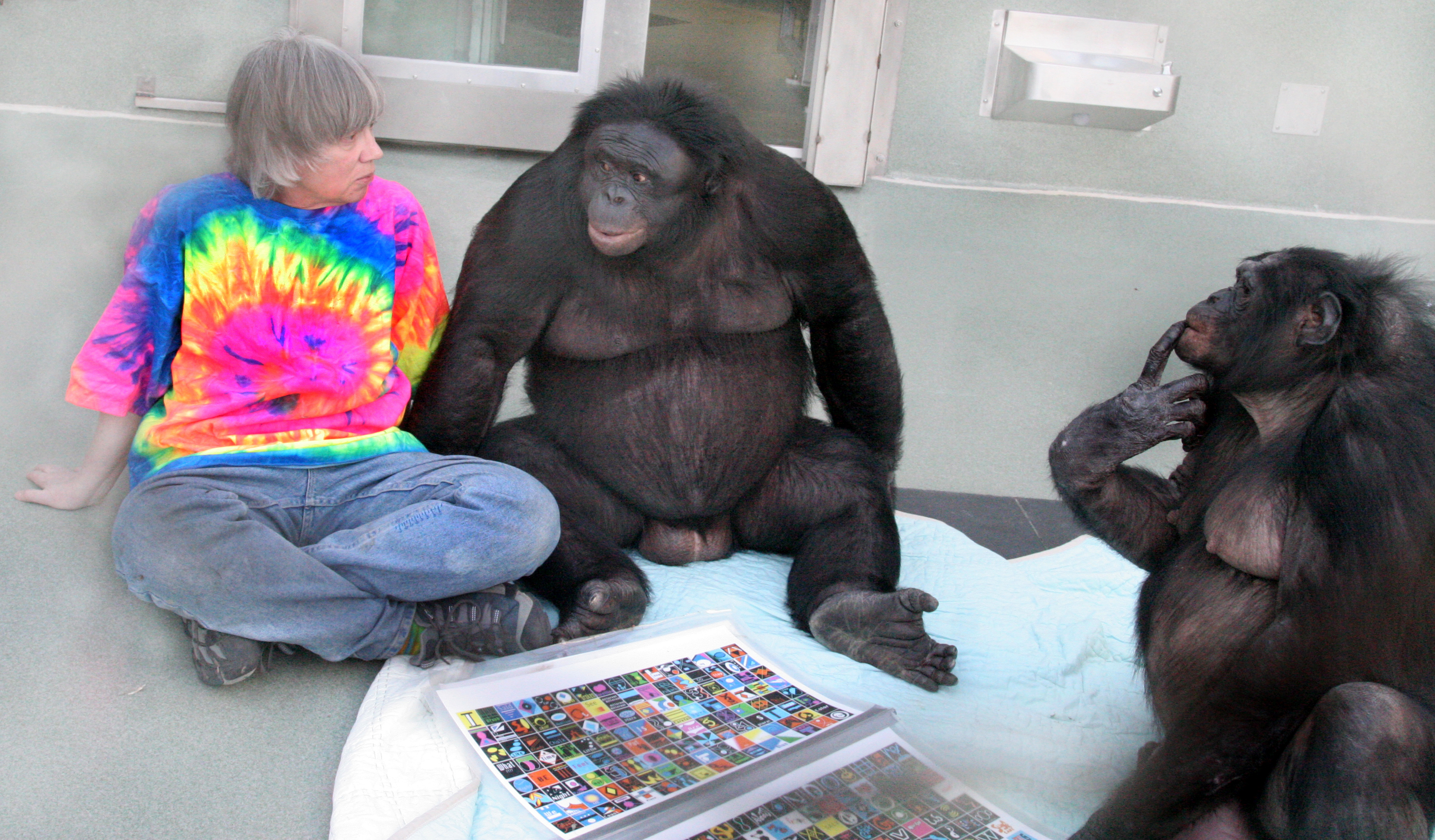
Bonobo
The bonobo (; ''Pan paniscus''), also historically called the pygmy chimpanzee and less often the dwarf chimpanzee or gracile chimpanzee, is an endangered great ape and one of the two species making up the genus '' Pan,'' the other being the common chimpanzee (''Pan troglodytes''). While bonobos are now recognized as a distinct species in their own right, they were initially thought to be a subspecies of chimpanzee (''Pan troglodytes)'' due to the physical similarities between the two species. Taxonomically, the members of the chimpanzee/bonobo subtribe Panina (composed entirely by the genus '' Pan'') are collectively termed ''panins''. The bonobo is distinguished by relatively long legs, pink lips, dark face, tail-tuft through adulthood, and parted long hair on its head. The bonobo is found in a area of the Congo Basin in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Central Africa. The species is frugivorous and inhabits primary and secondary forests, including seasonally inundated sw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chimpanzee
The chimpanzee (''Pan troglodytes''), also known as simply the chimp, is a species of great ape native to the forest and savannah of tropical Africa. It has four confirmed subspecies and a fifth proposed subspecies. When its close relative the bonobo was more commonly known as the pygmy chimpanzee, this species was often called the common chimpanzee or the robust chimpanzee. The chimpanzee and the bonobo are the only species in the genus ''Pan''. Evidence from fossils and DNA sequencing shows that ''Pan'' is a sister taxon to the human lineage and is humans' closest living relative. The chimpanzee is covered in coarse black hair, but has a bare face, fingers, toes, palms of the hands, and soles of the feet. It is larger and more robust than the bonobo, weighing for males and for females and standing . The chimpanzee lives in groups that range in size from 15 to 150 members, although individuals travel and forage in much smaller groups during the day. The species lives in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pediculus Schaeffi
''Pediculus'' is a genus of sucking lice, the sole genus in the family Pediculidae. ''Pediculus'' species are ectoparasites of primates. Species include: *''Pediculus clavicornis'' Nitzsch, 1864 *''Pediculus humanus'' Linnaeus, 1758 **''Pediculus humanus humanus'' Linnaeus, 1758 – the body louse **''Pediculus humanus capitis'' De Geer, 1767 – the head louse *''Pediculus mjobergi'' Ferris, 1916 *''Pediculus schaeffi'' Fahrenholz, 1910 Humans are the hosts of ''Pediculus humanus''. Chimpanzees and bonobos host ''Pediculus shaeffi''. Various New World monkeys in the families Cebidae and Atelidae The Atelidae are one of the five families of New World monkeys now recognised. It was formerly included in the family Cebidae. Atelids are generally larger monkeys; the family includes the howler, spider, woolly, and woolly spider monkeys (t ... host ''Pediculus mjobergi''. References Lice {{louse-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pediculus Mjobergi
''Pediculus'' is a genus of sucking lice, the sole genus in the family Pediculidae. ''Pediculus'' species are ectoparasites of primates. Species include: *''Pediculus clavicornis'' Nitzsch, 1864 *''Pediculus humanus'' Linnaeus, 1758 **''Pediculus humanus humanus'' Linnaeus, 1758 – the body louse **''Pediculus humanus capitis'' De Geer, 1767 – the head louse *''Pediculus mjobergi'' Ferris, 1916 *''Pediculus schaeffi'' Fahrenholz, 1910 Humans are the hosts of ''Pediculus humanus''. Chimpanzees and bonobos host ''Pediculus shaeffi''. Various New World monkeys in the families Cebidae and Atelidae The Atelidae are one of the five families of New World monkeys now recognised. It was formerly included in the family Cebidae. Atelids are generally larger monkeys; the family includes the howler, spider, woolly, and woolly spider monkeys (t ... host ''Pediculus mjobergi''. References Lice {{louse-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles De Geer
Baron Charles de Geer (the family is usually known as De Geer with a capitalized "De" and is pronounced "de yer"); Finspång in Risinge 30 January 1720 – Stockholm 7 March 1778) was a Swedish industrialist and entomologist. Life De Geer, who came from a family with strong Dutch connections, grew up in Utrecht from the age of three. He returned to Sweden at the age of 19. He had inherited the entailed manor and important iron-works of Leufsta (Lövsta) in Uppland from his childless uncle and namesake and would substantially increased the wealth of the estate. Ever since he had received a present of some silk worms at the age of eight, he had an interest in entomology and became a respected amateur entomologist at an early age. His major work was the ''Mémoires pour servir à l'histoire des insectes'' (eight volumes, 1752-1778). He was elected a member of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences already in 1739, at the age of nineteen, and a corresponding member of the Fren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pediculus Humanus Humanus
The body louse (''Pediculus humanus humanus'', also known as ''Pediculus humanus corporis'') is a hematophagic ectoparasite louse that infests humans. It is one of three lice which infest humans, the other two being the head louse, and the crab louse or pubic louse. Despite the name, body lice do not directly live on the host. They lay their eggs on fibres of clothing and only come into contact with the host whenever they need to feed. Since body lice cannot jump or fly, they spread by direct contact with another person or more rarely by contact with clothing or bed sheets that are infested. Body lice are disease vectors and can transmit pathogens that cause human diseases such as epidemic typhus, trench fever, and relapsing fever. In developed countries, infestations are only a problem in areas of poverty where there is poor body hygiene, crowded living conditions, and a lack of access to clean clothing. Outbreaks can also occur in situations where large groups of people ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family (taxonomy), family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. ''Panthera leo'' (lion) and ''Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomy (biology), taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pediculus Humanus
''Pediculus humanus'' is a species of louse that infects humans. It comprises two subspecies: *''Pediculus humanus humanus'' Linnaeus, 1758 – body louse *''Pediculus humanus capitis'' De Geer, 1767 – head louse The head louse (''Pediculus humanus capitis'') is an obligate ectoparasite of humans. Head lice are wingless insects that spend their entire lives on the human scalp and feeding exclusively on human blood. Humans are the only known hosts of th ... References External links * Lice Insects described in 1758 Parasitic arthropods of humans Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus {{louse-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pediculus Clavicornis
''Pediculus'' is a genus of sucking lice, the sole genus in the family Pediculidae. ''Pediculus'' species are ectoparasites of primates. Species include: *''Pediculus clavicornis'' Nitzsch, 1864 *''Pediculus humanus'' Linnaeus, 1758 **''Pediculus humanus humanus'' Linnaeus, 1758 – the body louse **''Pediculus humanus capitis'' De Geer, 1767 – the head louse *''Pediculus mjobergi'' Ferris, 1916 *''Pediculus schaeffi'' Fahrenholz, 1910 Humans are the hosts of ''Pediculus humanus''. Chimpanzees and bonobos host ''Pediculus shaeffi''. Various New World monkeys in the families Cebidae and Atelidae The Atelidae are one of the five families of New World monkeys now recognised. It was formerly included in the family Cebidae. Atelids are generally larger monkeys; the family includes the howler, spider, woolly, and woolly spider monkeys (t ... host ''Pediculus mjobergi''. References Lice {{louse-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |