|
Patagosaurus Fariasi
''Patagosaurus'' (meaning "Patagonia lizard") is an extinct genus of eusauropod dinosaur from the Middle-Late Toarcian of Patagonia, Argentina. It was first found in deposits of the Cañadón Asfalto Formation, which date to around 179 to 177 million years ago. Although originally twelve specimens were assigned to the taxon, at least one of them may belong to a different genus. ''Patagosaurus'' probably lived alongside genera as ''Piatnitzkysaurus'', ''Condorraptor'' and ''Volkheimeria''. Since ''Patagosaurus'' is known from many specimens, including at least one juvenile, its anatomy and growth are fairly well understood. Both ages exhibit the typical features of a sauropod, a long neck, small head, a long tail and being quadrupedal. The juvenile exhibits features different from the adult in regions like the mandible, pectoral girdle, pelvis and hindlimb, although overall their anatomy is quite similar. The many known specimens help fill in gaps in the anatomy of the genus, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toarcian
The Toarcian is, in the ICS' geologic timescale, an age and stage in the Early or Lower Jurassic. It spans the time between 182.7 Ma (million years ago) and 174.1 Ma. It follows the Pliensbachian and is followed by the Aalenian. The Toarcian Age began with the Toarcian turnover, the extinction event that sets its fossil faunas apart from the previous Pliensbachian age. It is believed to have ended with a global cooling event known as the Comptum Cooling Event, although whether it represented a worldwide event is controversial. Stratigraphic definitions The Toarcian takes its name from the city of Thouars, just south of Saumur in the Loire Valley of France. The stage was introduced by French palaeontologist Alcide d'Orbigny in 1842, after examining rock strata of this age in a quarry near Thouars. In Europe this period is represented by the upper part of the Lias. The base of the Toarcian is defined as the place in the stratigraphic record where the ammonite genus '' Eoda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pelvis
The pelvis (plural pelves or pelvises) is the lower part of the trunk, between the abdomen and the thighs (sometimes also called pelvic region), together with its embedded skeleton (sometimes also called bony pelvis, or pelvic skeleton). The pelvic region of the trunk includes the bony pelvis, the pelvic cavity (the space enclosed by the bony pelvis), the pelvic floor, below the pelvic cavity, and the perineum, below the pelvic floor. The pelvic skeleton is formed in the area of the back, by the sacrum and the coccyx and anteriorly and to the left and right sides, by a pair of hip bones. The two hip bones connect the spine with the lower limbs. They are attached to the sacrum posteriorly, connected to each other anteriorly, and joined with the two femurs at the hip joints. The gap enclosed by the bony pelvis, called the pelvic cavity, is the section of the body underneath the abdomen and mainly consists of the reproductive organs (sex organs) and the rectum, while the pelvic f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camarasaurus
''Camarasaurus'' ( ) was a genus of quadrupedal, herbivorous dinosaurs and is the most common North American sauropod fossil. Its fossil remains have been found in the Morrison Formation, dating to the Late Jurassic epoch (Kimmeridgian to Tithonian stages), between 155 and 145 million years ago. ''Camarasaurus'' presented a distinctive cranial profile of a blunt snout and an arched skull that was remarkably square, typical of basal Macronarians. The name means "chambered lizard", referring to the hollow chambers, known as pleurocoels, in its cervical vertebrae (Greek (') meaning "vaulted chamber", or anything with an arched cover, and (') meaning "lizard". ''Camarasaurus'' contains four species that are commonly recognized as valid: ''Camarasaurus grandis'', '' Camarasaurus lentus'', '' Camarasaurus lewisi'', and ''Camarasaurus supremus''. ''C. supremus'', the type species, is the largest and geologically youngest of the four. ''Camarasaurus'' is the type genus of Camarasau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diplodocus
''Diplodocus'' (, , or ) was a genus of diplodocid sauropod dinosaurs, whose fossils were first discovered in 1877 by S. W. Williston. The generic name, coined by Othniel Charles Marsh in 1878, is a neo-Latin term derived from Greek διπλός (''diplos'') "double" and δοκός (''dokos'') "beam", in reference to the double-beamed chevron bones located in the underside of the tail, which were then considered unique. The genus of dinosaurs lived in what is now mid-western North America, at the end of the Jurassic period. It is one of the more common dinosaur fossils found in the middle to upper Morrison Formation, between about 154 and 152 million years ago, during the late Kimmeridgian Age. The Morrison Formation records an environment and time dominated by gigantic sauropod dinosaurs, such as ''Apatosaurus'', ''Barosaurus'', ''Brachiosaurus'', ''Brontosaurus'', and '' Camarasaurus''. Its great size may have been a deterrent to the predators ''Allosaurus'' and ''Cerato ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synapomorphy
In phylogenetics, an apomorphy (or derived trait) is a novel character or character state that has evolved from its ancestral form (or plesiomorphy). A synapomorphy is an apomorphy shared by two or more taxa and is therefore hypothesized to have evolved in their most recent common ancestor. ) In cladistics, synapomorphy implies homology. Examples of apomorphy are the presence of erect gait, fur, the evolution of three middle ear bones, and mammary glands in mammals but not in other vertebrate animals such as amphibians or reptiles, which have retained their ancestral traits of a sprawling gait and lack of fur. Thus, these derived traits are also synapomorphies of mammals in general as they are not shared by other vertebrate animals. Etymology The word —coined by German entomologist Willi Hennig—is derived from the Ancient Greek words (''sún''), meaning "with, together"; (''apó''), meaning "away from"; and (''morphḗ''), meaning "shape, form". Clade analysis T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amygdalodon
''Amygdalodon'' (; "almond tooth" for its almond shaped teeth) was a genus of basal sauropod from the Middle Jurassic of Argentina. The type species is ''Amygdalodon patagonicus''. Fossils of ''Amygdalodon'' have been found in the Toarcian Cerro Carnerero Formation of the Jurassic (about 180-172 million years ago). Very little is known about it, but it is one of the few Jurassic dinosaurs from South America found thus far. Discovery The holotype (MLP 46-VIII-21-1) consists of some vertebrae, ribs, four complete and three partial teeth, and a partial pelvis and shoulder-blade, of which was discovered in 1936. The type species, ''Amygdalodon patagonicus'', was described by Cabrera in Argentina in 1947.A. Cabrera. 1947. Un saurópodo nuevo del Jurásico de Patagonia. Instituto del Museo de la Universidad Nacional de La Plata, ''Notas del Museo de La Plata, Paleontología'' 12(95):1–17 Until 1936 sauropod fossils from Argentina were completely unknown then, prompted by Piatnitzky' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
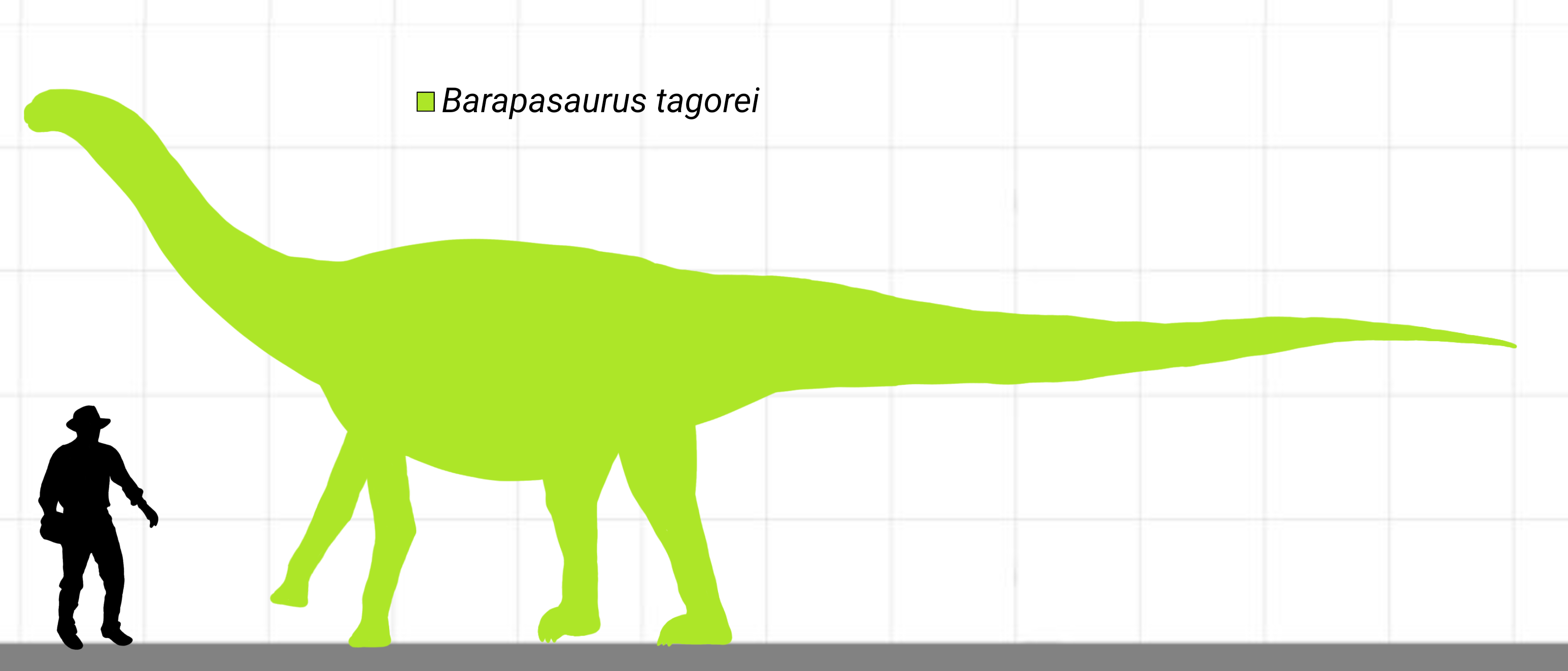
Barapasaurus
''Barapasaurus'' ( ) is a genus of basal sauropod dinosaur from Early Jurassic rocks of India. The only species is ''B. tagorei''. ''Barapasaurus'' comes from the lower part of the Kota Formation, that dates back to the Sinemurian and Pliensbachian stages of the early Jurassic. It is therefore one of the earliest known sauropods. ''Barapasaurus'' is known from approximately 300 bones from at least six individuals, so that the skeleton is almost completely known except for the anterior cervical vertebrae and the skull. This makes ''Barapasaurus'' one of the most completely known sauropods from the early Jurassic. Etymology The name ''Barapasaurus'' ("big-legged lizard") is derived from ''bara'' meaning 'big' and ''pa'' meaning 'leg' in several Indian languages including Bengali; the Greek word ''sauros'' means 'lizard'. This name was used as a ''nomen nudum'' since a femur measuring over 1.7 m was unearthed at 1961. The specific name ''tagorei'' means 'Tagore's', which honors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basal (phylogenetics)
In phylogenetics, basal is the direction of the ''base'' (or root) of a phylogenetic tree#Rooted tree, rooted phylogenetic tree or cladogram. The term may be more strictly applied only to nodes adjacent to the root, or more loosely applied to nodes regarded as being close to the root. Note that extant taxa that lie on branches connecting directly to the root are not more closely related to the root than any other extant taxa. While there must always be two or more equally "basal" clades sprouting from the root of every cladogram, those clades may differ widely in taxonomic rank, Phylogenetic diversity, species diversity, or both. If ''C'' is a basal clade within ''D'' that has the lowest rank of all basal clades within ''D'', ''C'' may be described as ''the'' basal taxon of that rank within ''D''. The concept of a 'key innovation' implies some degree of correlation between evolutionary innovation and cladogenesis, diversification. However, such a correlation does not make a given ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cetiosaurus
''Cetiosaurus'' () meaning 'whale lizard', from the Greek '/ meaning 'sea monster' (later, 'whale') and '/ meaning 'lizard', is a genus of herbivorous sauropod dinosaur from the Middle Jurassic Period, living about 168 million years ago in what is now Europe. ''Cetiosaurus'' was in 1842 the first sauropod from which bones were described and is the most complete sauropod found in England. It was so named because its describer, Sir Richard Owen, supposed it was a marine creature, initially an extremely large crocodile, and did not recognise it for a land-dwelling dinosaur. Because of the early description many species would be named in the genus, eventually eighteen of them. Most of these have now been placed in other genera or are understood to be dubious names, based on poor fossil material. The last is true also of the original type species, ''Cetiosaurus medius'', and so ''C. oxoniensis'' was officially made the new type species in 2014. ''C. oxoniensis'' is based on three mor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ischium
The ischium () forms the lower and back region of the (''os coxae''). Situated below the ilium and behind the pubis, it is one of three regions whose fusion creates the . The superior portion of this region forms approximately one-third of the acetabulum. |
Forelimb
A forelimb or front limb is one of the paired articulated appendages (limbs) attached on the cranial ( anterior) end of a terrestrial tetrapod vertebrate's torso. With reference to quadrupeds, the term foreleg or front leg is often used instead. In bipedal animals with an upright posture (e.g. humans and some primates), the term upper limb is often used. A forelimb is not to be confused with a forearm, which is a distal portion of the human upper limb between the elbow and the wrist. All vertebrate forelimbs are homologous, meaning that they all evolved from the same structures. For example, the flipper of a turtle or of a dolphin, the arm of a human, the foreleg of a horse, and the wings of both bats and birds are ultimately homologous, despite the large differences between them. Specific uses of the forelimbs may be analogous if they evolved from different sub-structures of the forelimb, such as the flippers of turtles and dolphins, and the wings of birds and bats. Evolu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robustness (morphology)
In biology, robustness is used to describe a taxon with a stronger and heavier build (morphology) when compared to a related gracile taxon. The terms are used in contrast to one another. The term is used by physical anthropologists and paleoanthropologists to refer to a big-boned and muscular body. For example, members of the genus ''Sapajus'' have robust body types and are called the robust capuchin monkeys while members of the genus ''Cebus'' have gracile body types and are called the gracile capuchin monkeys. Male and female members of the same species may display sexual dimorphism and have robust and gracile morphologies. The terms "robust" vs. "gracile" are used in the context of human evolution, to distinguish: *"robust" vs. "gracile" australopithecines, see '' Paranthropus'' *"robust" archaic humans vs. "gracile" anatomically modern humans *"robust" early modern humans (Cro-Magnon) vs. "gracile" Epipaleolithic In archaeology, the Epipalaeolithic or Epipaleolithic (some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |