|
Patagonotothen Guntheri
''Patagonotothen guntheri'', the yellowfin notothen, is a species of notothen found in the Argentinian region of Patagonia, the Falkland Islands, the Burdwood Bank and the Shag Rocks (where it is found in abundance) west of South Georgia on the continental shelf at depths of 120-250 m (394-820 ft), but may be found in waters deeper than 250 m in the Argentinian region. Etymology This species was named in honor of Mr. E. R. Gunther, a fisheries biologist of the Discovery investigations. Description This species is a small notothen with lemon yellow caudal, pectoral and pelvic fins. The anal and dorsal fins are also yellow. All fins are lighter at the tips and the body is generally colored gray, with the snout and the top of the head being darker. 2 or 3 dark stripes extend across the cheek, and a horizontal stripe may be present above the eye. This species attains a maximum length of 23 cm (9 inches). Up to 9 cross-bars may form on the body after preservation. This species is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patagonotothen
''Patagonotothen'' is a genus of marine ray-finned fishes, belonging to the family Nototheniidae, the notothens or cod icefishes. They are native to the southeast Pacific Ocean, southern Atlantic Ocean and the Southern Ocean. Taxonomy ''Patagonotothen'' was first formally described in 1976 by the Soviet ichthyologist Arkady Vladimirovich Balushkin with ''Notothenia tessellata'', which had been described in 1845 by the Scottish naturalist, Arctic explorer and naval surgeon John Richardson with a type locality of the Falkland Islands, as the type species. Some authorities place this genus in the subfamily Nototheniinae, but the 5th edition of ''Fishes of the World'' does not include subfamilies in the Nototheniidae. The genus name is a compound of ''Patago'', a reference to Patagonia, and ''notothen'', indicating that this genus is part of the family Nototheniidae. Species The 15 recognized species in this genus are: * '' Patagonotothen brevicauda'' (Lönnberg, 1905) (Patagon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Roxborough Norman
John Roxborough Norman (1898, Wandsworth, London – 26 May 1944, Berkhamsted, Hertfordshire) was an English ichthyologist. He started as a clerk in a bank. His lifetime affliction with rheumatic fever began during his military service during the First World War. He entered the British Museum in 1921 where he worked for Charles Tate Regan (1878-1943). From 1939 to 1944, he was in charge of the Natural History Museum at Tring as the Curator of Zoology. Norman was the author of, among others, ''A History of Fishes'' (1931) and ''A Draft Synopsis of the Orders, Families and Genera of Recent Fishes'' (1957). He was considered closer to Albert Günther (1830-1914) than to Regan. See also *:Taxa named by John Roxborough Norman References Aldemaro Romero Home Page (Archived on 14 September 2006) *Translated from the French Wikipedia article 1898 births 1944 deaths English ichthyologists People from Wandsworth 20th-century British zoologists British military personnel of World War ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anal Fin
Fins are distinctive anatomical features composed of bony spines or rays protruding from the body of a fish. They are covered with skin and joined together either in a webbed fashion, as seen in most bony fish, or similar to a flipper, as seen in sharks. Apart from the tail or caudal fin, fish fins have no direct connection with the spine and are supported only by muscles. Their principal function is to help the fish swim. Fins located in different places on the fish serve different purposes such as moving forward, turning, keeping an upright position or stopping. Most fish use fins when swimming, flying fish use pectoral fins for gliding, and frogfish use them for crawling. Fins can also be used for other purposes; male sharks and mosquitofish use a modified fin to deliver sperm, thresher sharks use their caudal fin to stun prey, reef stonefish have spines in their dorsal fins that inject venom, anglerfish use the first spine of their dorsal fin like a fishing rod to lu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxa Named By John Roxborough Norman
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; plural taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and given a particular ranking, especially if and when it is accepted or becomes established. It is very common, however, for taxonomists to remain at odds over what belongs to a taxon and the criteria used for inclusion. If a taxon is given a formal scientific name, its use is then governed by one of the nomenclature codes specifying which scientific name is correct for a particular grouping. Initial attempts at classifying and ordering organisms (plants and animals) were set forth in Carl Linnaeus's system in '' Systema Naturae'', 10th edition (1758), as well as an unpublished work by Bernard and Antoine Laurent de Jussieu. The idea of a unit-based system of biological classification was first made widely available in 1805 in the i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commercial Fisheries
Commercial fishing is the activity of catching fish and other seafood for commercial profit, mostly from wild fisheries. It provides a large quantity of food to many countries around the world, but those who practice it as an industry must often pursue fish far into the ocean under adverse conditions. Large-scale commercial fishing is also known as industrial fishing. The major fishing industries are not only owned by major corporations but by small families as well. In order to adapt to declining fish populations and increased demand, many commercial fishing operations have reduced the sustainability of their harvest by fishing further down the food chain. This raises concern for fishery managers and researchers, who highlight how further they say that for those reasons, the sustainability of the marine ecosystems could be in danger of collapsing. Commercial fishermen harvest a wide variety of animals. However, a very small number of species support the majority of the world' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
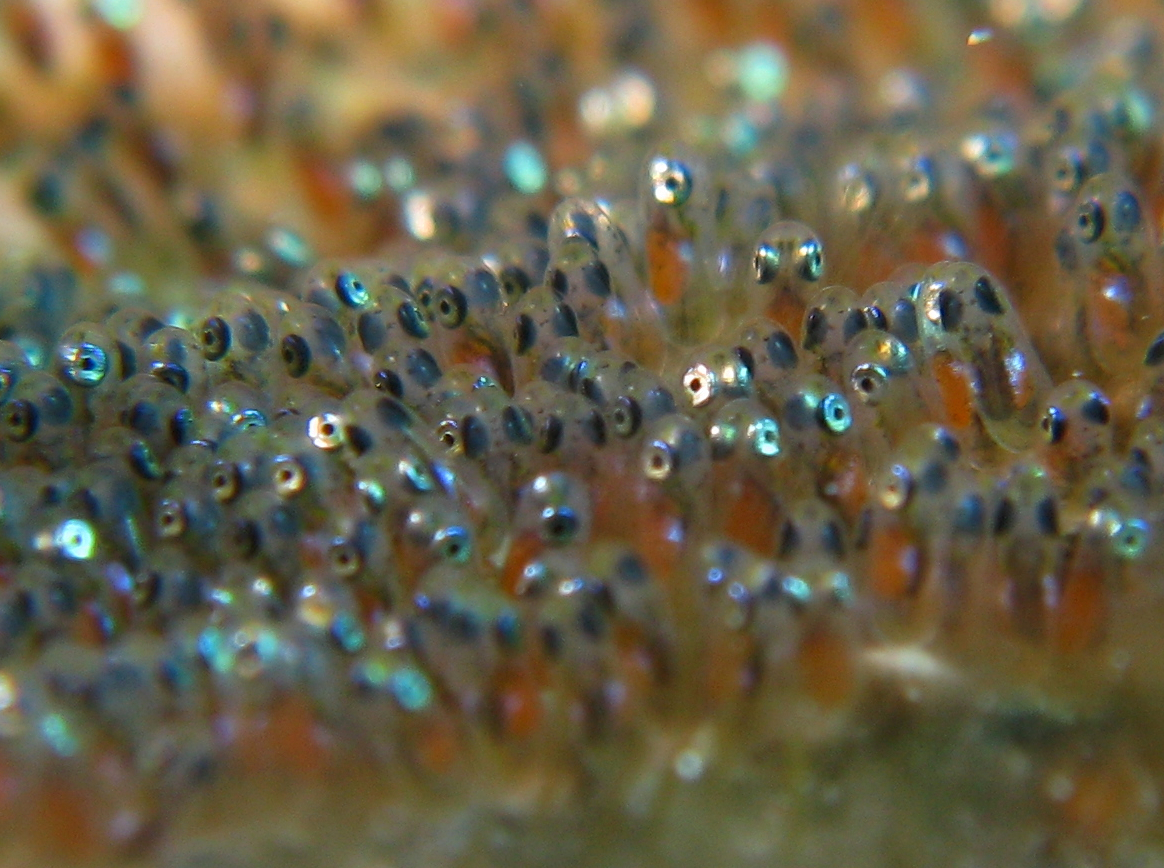
Spawn (biology)
Spawn is the Egg cell, eggs and Spermatozoa, sperm released or deposited into water by aquatic animals. As a verb, ''to spawn'' refers to the process of releasing the eggs and sperm, and the act of both sexes is called spawning. Most aquatic animals, except for aquatic mammals and marine reptile, reptiles, reproduce through the process of spawning. Spawn consists of the reproductive cells (gametes) of many aquatic animals, some of which will become fertilized and produce offspring. The process of spawning typically involves females releasing Ovum, ova (unfertilized eggs) into the water, often in large quantities, while males simultaneously or sequentially release spermatozoa (milt) to fertilize the eggs. Most fish reproduce by spawning, as do most other aquatic animals, including crustaceans such as crabs and shrimps, molluscs such as oysters and squid, echinoderms such as sea urchins and sea cucumbers, amphibians such as frogs and newts, aquatic insects such as mayflies and mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphipoda
Amphipoda is an order of malacostracan crustaceans with no carapace and generally with laterally compressed bodies. Amphipods range in size from and are mostly detritivores or scavengers. There are more than 9,900 amphipod species so far described. They are mostly marine animals, but are found in almost all aquatic environments. Some 1,900 species live in fresh water, and the order also includes the terrestrial sandhoppers such as ''Talitrus saltator''. Etymology and names The name ''Amphipoda'' comes, via New Latin ', from the Greek roots 'on both/all sides' and 'foot'. This contrasts with the related Isopoda, which have a single kind of thoracic leg. Particularly among anglers, amphipods are known as ''freshwater shrimp'', ''scuds'', or ''sideswimmers''. Description Anatomy The body of an amphipod is divided into 13 segments, which can be grouped into a head, a thorax and an abdomen. The head is fused to the thorax, and bears two pairs of antennae and one pair of s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
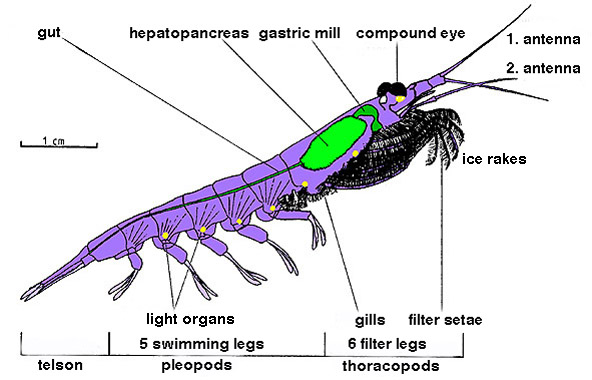
Krill
Krill are small crustaceans of the order Euphausiacea, and are found in all the world's oceans. The name "krill" comes from the Norwegian Norwegian, Norwayan, or Norsk may refer to: *Something of, from, or related to Norway, a country in northwestern Europe * Norwegians, both a nation and an ethnic group native to Norway * Demographics of Norway *The Norwegian language, including ... word ', meaning "small fry of fish", which is also often attributed to species of fish. Krill are considered an important trophic level connection – near the bottom of the food chain. They feed on phytoplankton and (to a lesser extent) zooplankton, yet also are the main source of food for many larger animals. In the Southern Ocean, one species, the Antarctic krill, ''Euphausia superba'', makes up an estimated biomass (ecology), biomass of around 379,000,000 tonnes, making it among the species with the largest total biomass. Over half of this biomass is eaten by whales, Pinniped, seals, pen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benthopelagic Fish
Demersal fish, also known as groundfish, live and feed on or near the bottom of seas or lakes (the demersal zone).Walrond Carl . "Coastal fish - Fish of the open sea floor"Te Ara - the Encyclopedia of New Zealand. Updated 2 March 2009 They occupy the sea floors and lake beds, which usually consist of mud, sand, gravel or rocks. In coastal waters they are found on or near the continental shelf, and in deep waters they are found on or near the continental slope or along the continental rise. They are not generally found in the deepest waters, such as abyssal depths or on the abyssal plain, but they can be found around seamounts and islands. The word ''demersal'' comes from the Latin ''demergere'', which means ''to sink''. Demersal fish are bottom feeders. They can be contrasted with pelagic fish which live and feed away from the bottom in the open water column. Demersal fish fillets contain little fish oil (one to four percent), whereas pelagic fish can contain up to 30 perc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gill Raker
Gill rakers in fish are bony or cartilaginous processes that project from the branchial arch (gill arch) and are involved with suspension feeding tiny prey. They are not to be confused with the gill filaments that compose the fleshy part of the gill used for gas exchange. Rakers are usually present in two rows, projecting from both the anterior and posterior side of each gill arch. Rakers are widely varied in number, spacing, and form. By preventing food particles from exiting the spaces between the gill arches, they enable the retention of food particles in filter feeders. The structure and spacing of gill rakers in fish determines the size of food particles trapped, and correlates with feeding behavior. Fish with densely spaced, elongated, comb-like gill rakers are efficient at filtering tiny prey, whereas carnivores and omnivores often have more widely spaced gill rakers with secondary projections. Because gill raker characters often vary between closely related taxa, they are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patagonotothen Brevicauda
''Patagonotothen brevicauda'', the Patagonian rockcod, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, belonging to the family Nototheniidae, the notothens or cod icefishes. It is native to oceans of the Patagonian region, including Tierra del Fuego, the Strait of Magellan, the Beagle Channel and the Falkland Islands. Taxonomy Described in 1905 by Swedish naturalist Einar Lönnberg with the nominate species name ''Patagonotothen brevicauda brevicauda'', the population from the Shag Rocks was described as ''P. brevicauda shagenisis'' by Soviet ichthyologists A.V. Balushkin and Y.Y. Permetin in 1982. This taxon is regarded as a valid species by both FishBase and Catalog of Fishes, '' Patagonotothen shagensis''. Description This species is a relatively small notothen, reaching a maximum length of up to . The depressed body is generally brownish. A series of yellowish-and-dark bands transverse the body. The bases of the pectoral fins are outlined by dark lines, which are pale, as are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
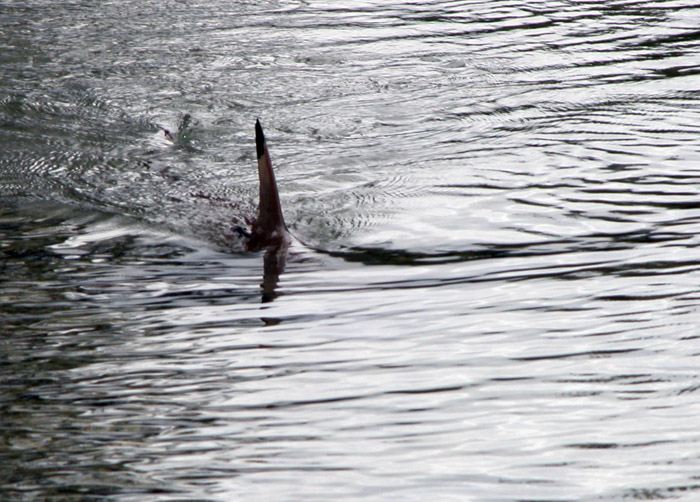
Dorsal Fin
A dorsal fin is a fin located on the back of most marine and freshwater vertebrates within various taxa of the animal kingdom. Many species of animals possessing dorsal fins are not particularly closely related to each other, though through convergent evolution they have independently evolved external superficial fish-like body plans adapted to their marine environments, including most numerously fish, but also mammals such as cetaceans (whales, dolphins, and porpoises), and even extinct ancient marine reptiles such as various known species of ichthyosaurs. Most species have only one dorsal fin, but some have two or three. Wildlife biologists often use the distinctive nicks and wear patterns which develop on the dorsal fins of large cetaceans to identify individuals in the field. The bony or cartilaginous bones that support the base of the dorsal fin in fish are called ''pterygiophores''. Functions The main purpose of the dorsal fin is to stabilize the animal against rollin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)