|
Participle (Ancient Greek)
The Ancient Greek participle is a non-finite nominal verb form declined for gender, number and case (thus, it is a verbal adjective) and has many functions in Ancient Greek. It can be active, middle or passive and can be used in the present, future, aorist and perfect tense; these tenses normally represent not absolute time but only time relative to the main verb of the sentence. In general, as it shows no personal endings, its main use is to express an action or situation that accompanies the action or situation expressed by the main verb. Terminology The Greek grammarians called a participle a μετοχή 'participation, share', because it shares the properties of a verb and of an adjective. Latin calqued the word as ''participium'', from which English gets ''participle''. Uses of the participle Three main syntactic uses of the participle can be distinguished: (a) the participle as a modifier of a noun (attributive participle) (b) the participle used as an obligatory argume ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Participle
In linguistics, a participle (; abbr. ) is a nonfinite verb form that has some of the characteristics and functions of both verbs and adjectives. More narrowly, ''participle'' has been defined as "a word derived from a verb and used as an adjective, as in a ''laughing face''". "Participle" is a traditional grammatical term from Greek and Latin that is widely used for corresponding verb forms in European languages and analogous forms in Sanskrit and Arabic grammar. In particular, Greek and Latin participles are inflected for gender, number and case, but also conjugated for tense and voice and can take prepositional and adverbial modifiers. Cross-linguistically, participles may have a range of functions apart from adjectival modification. In European and Indian languages, the past participle is used to form the passive voice. In English, participles are also associated with periphrastic verb forms ( continuous and perfect) and are widely used in adverbial clauses. In non- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adjective
An adjective (abbreviations, abbreviated ) is a word that describes or defines a noun or noun phrase. Its semantic role is to change information given by the noun. Traditionally, adjectives are considered one of the main part of speech, parts of speech of the English language, although historically they were classed together with Noun, nouns. Nowadays, certain words that usually had been classified as adjectives, including ''the'', ''this'', ''my'', etc., typically are classed separately, as Determiner (class), determiners. Examples: * That's a ''funny'' idea. (Prepositive attributive) * That idea is ''funny''. (Predicate (grammar), Predicative) * * The ''good'', the ''bad'', and the ''funny''. (Substantive adjective, Substantive) * Clara Oswald, completely ''fictional'', died three times. (Apposition, Appositive) Etymology ''Adjective'' comes from Latin ', a calque of (whence also English ''epithet''). In the grammatical tradition of Latin and Greek, because adjectives were I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secondary Predicate
A secondary predicate is a (mostly adjectival) predicative expression that conveys information about the subject or the object but is not the main predicate of the clause. This structure may be analysed in many different ways. These may be resultative, as in (1) and (2) or descriptive (also called "depictive") as in (3). :(1) She painted the town red :(2) The film left me cold :(3) Susan walked around naked. (Depictive over the subject, or "subject-oriented depictive") :(4) John ate the meat raw. (Depictive over the object, or "object-oriented depictive") :(5) All men are created equal. Alternative views Optional depictive secondary predicates are viewed as "predicative adjuncts In brewing, adjuncts are unmalted grains (such as barley, wheat, maize, rice, rye, and oats) or grain products used in brewing beer which supplement the main mash ingredient (such as malted barley). This is often done with the intention of cut ..." by some linguists. (Huddleston & Pullum 2002) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linguistics
Linguistics is the scientific study of language. The areas of linguistic analysis are syntax (rules governing the structure of sentences), semantics (meaning), Morphology (linguistics), morphology (structure of words), phonetics (speech sounds and equivalent gestures in sign languages), phonology (the abstract sound system of a particular language, and analogous systems of sign languages), and pragmatics (how the context of use contributes to meaning). Subdisciplines such as biolinguistics (the study of the biological variables and evolution of language) and psycholinguistics (the study of psychological factors in human language) bridge many of these divisions. Linguistics encompasses Outline of linguistics, many branches and subfields that span both theoretical and practical applications. Theoretical linguistics is concerned with understanding the universal grammar, universal and Philosophy of language#Nature of language, fundamental nature of language and developing a general ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raising (syntax)
In linguistics, raising constructions involve the syntactic movement, movement of an argument (linguistics), argument from an embedded or subordinate clause to a matrix or main clause. A raising predicate (grammar), predicate/verb appears with a syntactic argument that is not its semantic argument but rather the semantic argument of an embedded predicate. In other words, the sentence is expressing something about a phrase taken as a whole. For example, in ''they seem to be trying'', ''"to be trying"'' (the predicand of ''trying'') is the subject of ''seem''. English language, English has raising constructions, unlike some other languages. The term ''raising'' has its origins in the Transformational Grammar, transformational analysis of such constructions; the constituent (linguistics), constituent in question is seen as being "raised" from its initial deep structure position, as the subject of the embedded predicate, to its Deep structure and surface structure, surface structure p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
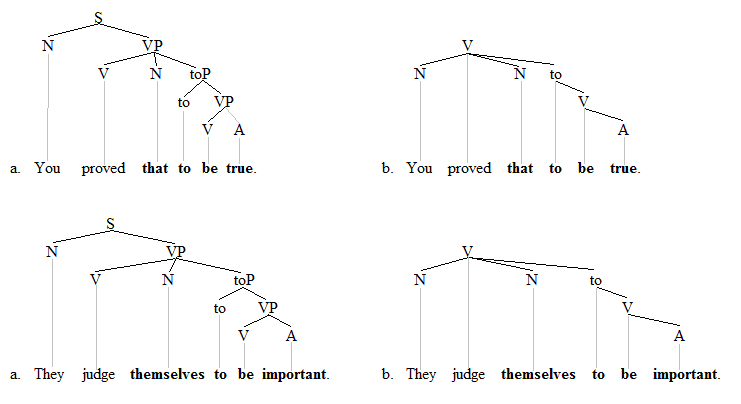
Exceptional Case Marking
Exceptional case-marking (ECM), in linguistics, is a phenomenon in which the subject of an embedded infinitival verb seems to appear in a superordinate clause and, if it is a pronoun, is unexpectedly marked with object case morphology (''him'' not ''he'', ''her'' not ''she'', etc.). The unexpected object case morphology is deemed "exceptional". The term ''ECM'' itself was coined in the Government and Binding grammar framework although the phenomenon is closely related to the accusativus cum infinitivo constructions of Latin. ECM-constructions are also studied within the context of raising. The verbs that license ECM are known as ''raising-to-object'' verbs. Many languages lack ECM-predicates, and even in English, the number of ECM-verbs is small. The structural analysis of ECM-constructions varies in part according to whether one pursues a relatively flat structure or a more layered one. Examples The ECM-construction is licensed by a relatively small number of verbs in English (e.g., ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grammaticality
In linguistics, grammaticality is determined by the conformity to language usage as derived by the grammar of a particular speech variety. The notion of grammaticality rose alongside the theory of generative grammar, the goal of which is to formulate rules that define well-formed, grammatical sentences. These rules of grammaticality also provide explanations of ill-formed, ungrammatical sentences. In theoretical linguistics, a speaker's judgement on the well-formedness of a linguistic 'string'—called a grammaticality judgement—is based on whether the sentence is interpreted in accordance with the rules and constraints of the relevant grammar. If the rules and constraints of the particular lect are followed, then the sentence is judged to be grammatical. In contrast, an ungrammatical sentence is one that violates the rules of the given language variety. Linguists use grammaticality judgements to investigate the syntactic structure of sentences. Generative linguists are larg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noun Phrase
A noun phrase – or NP or nominal (phrase) – is a phrase that usually has a noun or pronoun as its head, and has the same grammatical functions as a noun. Noun phrases are very common cross-linguistically, and they may be the most frequently occurring phrase type. Noun phrases often function as verb subjects and objects, as predicative expressions, and as complements of prepositions. One NP can be embedded inside another NP; for instance, ''some of his constituents'' has as a constituent the shorter NP ''his constituents''. In some theories of grammar, noun phrases with determiners are analyzed as having the determiner as the head of the phrase, see for instance Chomsky (1995) and Hudson (1990) . Identification Some examples of noun phrases are underlined in the sentences below. The head noun appears in bold. ::This election-year's politics are annoying for many people. ::Almost every sentence contains at least one noun phrase. ::Current economic weakness may be a re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infinitive (Ancient Greek)
The Ancient Greek infinitive is a non-finite verb form, sometimes called a verb mood, with no endings for person or number, but it is (unlike in Modern English) inflected for tense and voice (for a general introduction in the grammatical formation and the morphology of the Ancient Greek infinitive see here and for further information see these tables). It is used mainly to express acts, situations and in general "states of affairs" that are depended on another verb form, usually a finite one. It is a non declinable nominal verb form equivalent to a noun, and expresses the verbal notion abstractly; used as a noun in its main uses, it has many properties of it, as it will be seen below, yet it differs from it in some respects: : (a) When used with no article, and in its major uses (subject/object), it can normally only be equivalent to either a nominative or an accusative case; used with the article, it may be in any case (nominative, genitive, dative and accusative). : (b) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coreference
In linguistics, coreference, sometimes written co-reference, occurs when two or more expressions refer to the same person or thing; they have the same referent. For example, in ''Bill said Alice would arrive soon, and she did'', the words ''Alice'' and ''she'' refer to the same person. Co-reference is often non-trivial to determine. For example, in ''Bill said he would come'', the word ''he'' may or may not refer to Bill. Determining which expressions are coreferences is an important part of analyzing or understanding the meaning, and often requires information from the context, real-world knowledge, such as tendencies of some names to be associated with particular species ("Rover"), kinds of artifacts ("Titanic"), grammatical genders, or other properties. Linguists commonly use indices to notate coreference, as in ''Billi said hei would come''. Such expressions are said to be ''coindexed'', indicating that they should be interpreted as coreferential. When expressions are corefer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complement (linguistics)
In grammar, a complement is a word, phrase, or clause that is necessary to complete the meaning of a given expression. Complements are often also arguments (expressions that help complete the meaning of a predicate). Predicative, subject and object complements In many non-theoretical grammars, the terms '' subject complement'' (also called a predicative of the subject) and '' object complement'' are employed to denote the predicative expressions (predicative complements), such as predicative adjectives and nominals (also called a predicative nominative or predicate nominative), that serve to assign a property to a subject or an object: ::Ryan is upset. – Predicative adjective as subject complement ::Rachelle is the boss. – Predicative nominal as subject complement ::That made Michael lazy. – Predicative adjective as object complement ::We call Rachelle the boss. – Predicative nominal as object complement This terminology is used in grammar books: However, this use o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optative (Ancient Greek)
The optative mood ( or ; Ancient Greek , , " nflectionfor wishing", Latin "odefor wishing") is a grammatical mood of the Ancient Greek verb, named for its use as a way to express wishes. The optative mood in Greek is found in four different tenses (present, aorist, perfect and future) and in all three voices (active, middle and passive). It has multiple uses: * To express wishes for the future ("may it happen!") * To talk about a hypothetical future situation ("what would happen if I did this?") * In purpose clauses ("so that it could happen") or clauses expressing fears ("for fear that it might happen") in a past context. (The subjunctive mood can also be used in this type of clause in a past context.) * In subordinate clauses referring to repeated events in a past context ("whenever it happened", "whoever did this" etc.) * To indicate reported speech in a past context ("he said that it had happened", "he asked who they were") * In epic dialects, contrary-to-fact clauses in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |