|
Paris Type
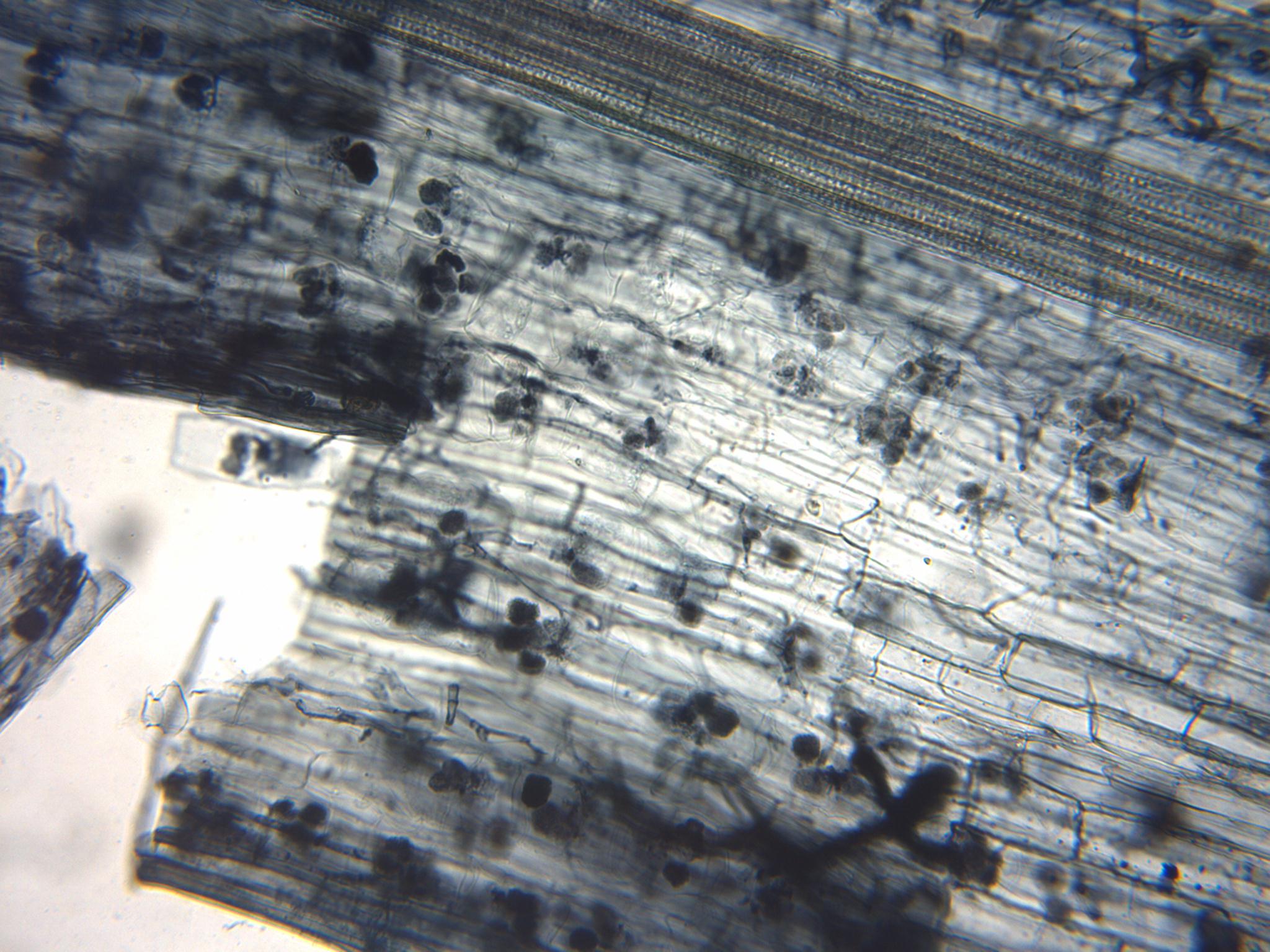
Paris type is a pattern of mycorrhizal infection which is coil-like in morphology. *These have direct intracellular growth to new cells. *The mycoheterotrophic plants use this to their advantage, as well as in many tree species, such as acer. See also *Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi An arbuscular mycorrhiza (AM) (plural ''mycorrhizae'', a.k.a. ''endomycorrhiza'') is a type of mycorrhiza in which the symbiont fungus (''AM fungi'', or AMF) penetrates the cortical cells of the roots of a vascular plant forming arbuscules. (N ... * Arum type References *C.J. Alexopolous, Charles W. Mims, M. Blackwell et al., ''Introductory Mycology, 4th ed.'' (John Wiley and Sons, Hoboken NJ, 2004) Fungal morphology and anatomy {{mycology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mycorrhizal
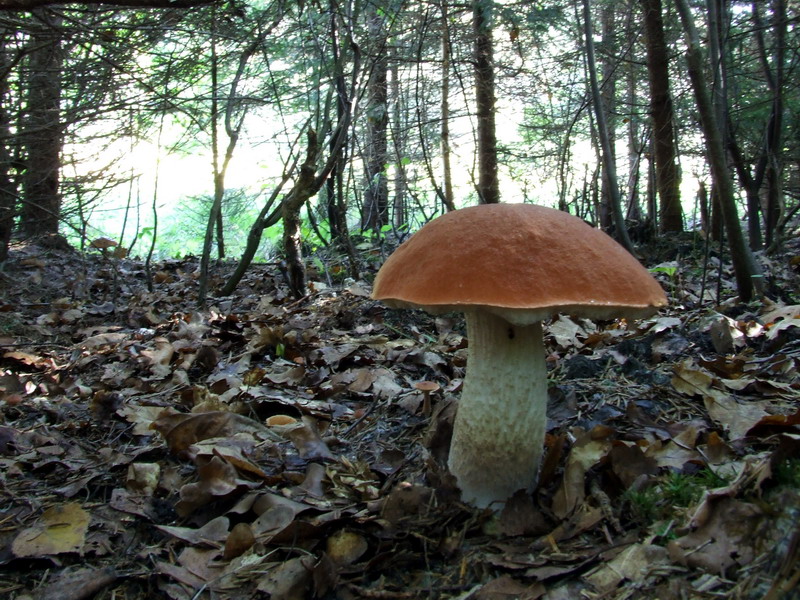
A mycorrhiza (from Greek μύκης ', "fungus", and ῥίζα ', "root"; pl. mycorrhizae, mycorrhiza or mycorrhizas) is a symbiotic association between a fungus and a plant. The term mycorrhiza refers to the role of the fungus in the plant's rhizosphere, its root system. Mycorrhizae play important roles in plant nutrition, soil biology, and soil chemistry. In a mycorrhizal association, the fungus colonizes the host plant's root tissues, either intracellularly as in arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF or AM), or extracellularly as in ectomycorrhizal fungi. The association is sometimes mutualistic. In particular species or in particular circumstances, mycorrhizae may have a parasitic association with host plants. Definition A mycorrhiza is a symbiotic association between a green plant and a fungus. The plant makes organic molecules such as sugars by photosynthesis and supplies them to the fungus, and the fungus supplies to the plant water and mineral nutrients, such as phos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morphology (biology)
Morphology is a branch of biology dealing with the study of the form and structure of organisms and their specific structural features. This includes aspects of the outward appearance (shape, structure, colour, pattern, size), i.e. external morphology (or eidonomy), as well as the form and structure of the internal parts like bones and organs, i.e. internal morphology (or anatomy). This is in contrast to physiology, which deals primarily with function. Morphology is a branch of life science dealing with the study of gross structure of an organism or taxon and its component parts. History The etymology of the word "morphology" is from the Ancient Greek (), meaning "form", and (), meaning "word, study, research". While the concept of form in biology, opposed to function, dates back to Aristotle (see Aristotle's biology), the field of morphology was developed by Johann Wolfgang von Goethe (1790) and independently by the German anatomist and physiologist Karl Friedrich Burdach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intracellular
This glossary of biology terms is a list of definitions of fundamental terms and concepts used in biology, the study of life and of living organisms. It is intended as introductory material for novices; for more specific and technical definitions from sub-disciplines and related fields, see Glossary of genetics, Glossary of evolutionary biology, Glossary of ecology, and Glossary of scientific naming, or any of the organism-specific glossaries in :Glossaries of biology. A B C D E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mycoheterotrophic
Myco-heterotrophy (from Greek μύκης , "fungus", ἕτερος ', "another", "different" and τροφή ', "nutrition") is a symbiotic relationship between certain kinds of plants and fungi, in which the plant gets all or part of its food from parasitism upon fungi rather than from photosynthesis. A myco-heterotroph is the parasitic plant partner in this relationship. Myco-heterotrophy is considered a kind of cheating relationship and myco-heterotrophs are sometimes informally referred to as "mycorrhizal cheaters". This relationship is sometimes referred to as mycotrophy, though this term is also used for plants that engage in mutualistic mycorrhizal relationships. Relationship between myco-heterotrophs and host fungi Full (or obligate) myco-heterotrophy exists when a non-photosynthetic plant (a plant largely lacking in chlorophyll or otherwise lacking a functional photosystem) gets all of its food from the fungi that it parasitizes. Partial (or facultative) myco-heterotr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maple
''Acer'' () is a genus of trees and shrubs commonly known as maples. The genus is placed in the family Sapindaceae.Stevens, P. F. (2001 onwards). Angiosperm Phylogeny Website. Version 9, June 2008 nd more or less continuously updated since http://www.mobot.org/MOBOT/research/APweb/. There are approximately 132 species, most of which are native to Asia, with a number also appearing in Europe, northern Africa, and North America. Only one species, ''Acer laurinum'', extends to the Southern Hemisphere.Gibbs, D. & Chen, Y. (2009The Red List of Maples Botanic Gardens Conservation International (BGCI) The type species of the genus is the sycamore maple, '' Acer pseudoplatanus'', the most common maple species in Europe.van Gelderen, C. J. & van Gelderen, D. M. (1999). ''Maples for Gardens: A Color Encyclopedia'' Maples usually have easily recognizable palmate leaves ('' Acer negundo'' is an exception) and distinctive winged fruits. The closest relatives of the maples are the horse c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi
An arbuscular mycorrhiza (AM) (plural ''mycorrhizae'', a.k.a. ''endomycorrhiza'') is a type of mycorrhiza in which the symbiont fungus (''AM fungi'', or AMF) penetrates the cortical cells of the roots of a vascular plant forming arbuscules. (Not to be confused with ectomycorrhiza or ericoid mycorrhiza.) Arbuscular mycorrhizae are characterized by the formation of unique structures, arbuscules and vesicles, by Glomeromycota and Mucoromycota, sister clades of the more well-known and diverse dikaryan fungi (all three are together called "symbiomycota"). AM fungi help plants to capture nutrients such as phosphorus, sulfur, nitrogen and micronutrients from the soil. It is believed that the development of the arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis played a crucial role in the initial colonisation of land by plants and in the evolution of the vascular plants. It has been said that it is quicker to list the plants that do not form endomycorrhizae than those that do. This symbiosis is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arum Type
Arum-type refers to the morphology of fungal hyphae living in, or around plant root cells. *Forms in arbuscular or tree-like fashion, branching off dichotomously at predetermined junctions. This is a type of mycorrhizal infection whereby the fungus in question invaginates the cell membrane of a plant cell, and branches in arbuscular manner. Arum-type growth of hyphae is used in endomycorrhizal symbiosis with a plant. *Often, but not always, accompanied by intercellular hyphal growth. See also *Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi An arbuscular mycorrhiza (AM) (plural ''mycorrhizae'', a.k.a. ''endomycorrhiza'') is a type of mycorrhiza in which the symbiont fungus (''AM fungi'', or AMF) penetrates the cortical cells of the roots of a vascular plant forming arbuscules. (N ... * Paris type References *C.J. Alexopolous, Charles W. Mims, M. Blackwell et al., ''Introductory Mycology, 4th ed.'' (John Wiley and Sons, Hoboken NJ, 2004) Fungal morphology and anatomy {{mycolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |