|
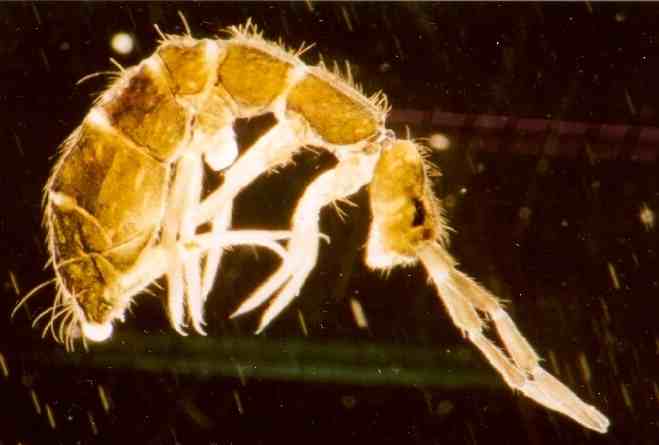
Parakatianna Salmoni
''Parakatianna salmoni'' is a species of springtail belonging to the family Katiannidae. The species was first described by Keith Arthur John Wise in 1964. The species is native to Campbell Island in the New Zealand Subantarctic Islands. Taxonomy The species was first described as ''Longkingia salmoni'' in 1964 by Keith Arthur John Wise Keith Arthur John Wise (1 June 1926 – 31 March 2012), often referred to as K. A. J. Wise, was a New Zealand entomologist. Originally employed at the Department of Scientific and Industrial Research (New Zealand), Department of Scientific and ..., who named this after J. T. Salmon, who first discovered the species. The species has since been placed within the genus '' Parakatianna''. Description ''Parakatianna salmoni'' is dark green and colourless when preserved in alcohol. The species grows up to in length, and has antennae that are twice as long as its head. Distribution The species is known to commonly occur in the Campbell I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Te Papa
The Museum of New Zealand Te Papa Tongarewa is New Zealand's national museum and is located in Wellington. ''Te Papa Tongarewa'' translates literally to "container of treasures" or in full "container of treasured things and people that spring from mother Earth here in New Zealand". Usually known as Te Papa (Māori language, Māori for "Waka huia, the treasure box"), it opened in 1998 after the merging of the National Museum of New Zealand and the National Art Gallery. An average of more than 1.5 million people visit every year, making it the List of most-visited art museums, 17th-most-visited art gallery in the world. Te Papa's philosophy emphasises the living face behind its cultural treasures, many of which retain deep ancestral links to the indigenous Māori people. History Colonial Museum The first predecessor to Te Papa was the ''Colonial Museum'', founded in 1865, with James Hector, Sir James Hector as founding director. The Museum was built on Museum Street, roughly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collembola
Springtails (Collembola) form the largest of the three lineages of modern hexapods that are no longer considered insects (the other two are the Protura and Diplura). Although the three orders are sometimes grouped together in a class called Entognatha because they have internal mouthparts, they do not appear to be any more closely related to one another than they are to all insects, which have external mouthparts. Collembolans are omnivorous, free-living organisms that prefer moist conditions. They do not directly engage in the decomposition of organic matter, but contribute to it indirectly through the fragmentation of organic matter and the control of soil microbial communities. The word ''Collembola'' is from the ancient Greek "glue" and "peg"; this name was given due to the existence of the collophore, which was previously thought to stick to surfaces to stabilize the creature. Some DNA sequence studies suggest that Collembola represent a separate evolutionary line fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Katiannidae
Katiannidae is a family of Collembola Springtails (Collembola) form the largest of the three lineages of modern hexapods that are no longer considered insects (the other two are the Protura and Diplura). Although the three orders are sometimes grouped together in a class called Ento .... Genera of the family include '' Sminthurinus'' and '' Vesicephalus''. References {{Taxonbar, from=Q1942018 Collembola Arthropod families ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keith Arthur John Wise
Keith Arthur John Wise (1 June 1926 – 31 March 2012), often referred to as K. A. J. Wise, was a New Zealand entomologist. Originally employed at the Department of Scientific and Industrial Research (New Zealand), Department of Scientific and Industrial Research, Wise began working with the Bishop Museum in the early 1960s, coordinating field programmes for United States visits to Antarctica and Subantarctic islands. This work led Wise to identify and describe large numbers of novel species, including many species of springtail. In 1965, Wise became the first Curator of Entomology at the Auckland War Memorial Museum, where he was integral in creating the first entomology section within the natural history gallery. Early life Wise was born on 1 June 1926 in Wellington. As his father Victor John Wise worked in insurance, Wise moved around the country often, living in Whangarei, Invercargill and Oamaru, attending Whangarei Boys' High School, Southland Boys' High School and Waitak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Campbell Island, New Zealand
Campbell Island / Motu Ihupuku is an uninhabited subantarctic island of New Zealand, and the main island of the Campbell Island group. It covers of the group's , and is surrounded by numerous stacks, rocks and islets like Dent Island, Folly Island (or Folly Islands), Isle de Jeanette-Marie, and Jacquemart Island, the latter being the southernmost extremity of New Zealand. The island is mountainous, rising to over in the south. A long fiord, Perseverance Harbour, nearly bisects it, opening out to sea on the east coast. The island is listed with the New Zealand Outlying Islands. The island is an immediate part of New Zealand, but not part of any region or district, but instead ''Area Outside Territorial Authority'', like all other outlying islands, other than the Solander Islands. It is the closest piece of land to the antipodal point of the United Kingdom, and Ireland, meaning that the furthest away city is Limerick, Ireland. Campbell Island is a UNESCO World Heritage Site. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand Subantarctic Islands
The New Zealand Subantarctic Islands comprise the five southernmost groups of the New Zealand outlying islands. They are collectively designated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Most of the islands lie near the southeast edge of the largely submerged continent centred on New Zealand called Zealandia, which was riven from Australia 60–85 million years ago, and from Antarctica 85–130 million years ago. They share some features with Australia's Macquarie Island to the west. History Until 1995, scientific research staff were stationed permanently at a meteorological station on Campbell Island. Since then, the islands have been uninhabited, though they are periodically visited by researchers and tourists. Protection of reserves was strengthened in 2014, becoming the largest natural sanctuary in the nation. Islands ; Antipodes Islands: Antipodes Island, Bollons Island, the Windward Islands, Orde Lees Island, Leeward Island, South Islet ; Auckland Islands: Auckland Is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Salmon (entomologist)
John Tenison Salmon (28 June 1910 – 4 May 1999) was a New Zealand photographer, entomologist, academic, conservationist, and author. His primary occupation was as an entomologist; first at the Dominion Museum (which later became Te Papa) and then at Victoria University College (now known as Victoria University of Wellington). Biography Salmon was born in Wellington in 1910. His father, Charles Tenison Salmon, was a surveyor and civil engineer from Palmerston North. His father instilled in him a love for the outdoors and also passed on a passion for photography. Salmon went to primary school in Palmerston North and then boarded at Wellington College. His first job in 1928 was with the Land and Income Tax Department in the capital city and in parallel, he studied science at Victoria University College. His 1934 master's thesis in zoology was on springtails (collembola). That year, he started as an entomologist at the Dominion Museum and he helped with the move to the new buildi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parakatianna
''Parakatianna'' is a genus of springtails in the family Katiannidae. The genus was identified by Herbert Womersley in 1932. Distribution The genus is primarily found in Australia, New Zealand, and on Campbell Island in the New Zealand Subantarctic Islands. Species * '' Parakatianna albirubrafrons'' * '' Parakatianna anomala'' * '' Parakatianna cortica'' * '' Parakatianna diversitata'' * '' Parakatianna hexagona'' * '' Parakatianna homerica'' * '' Parakatianna prospina'' * ''Parakatianna salmoni ''Parakatianna salmoni'' is a species of springtail belonging to the family Katiannidae. The species was first described by Keith Arthur John Wise in 1964. The species is native to Campbell Island in the New Zealand Subantarctic Islands. Tax ...'' * '' Parakatianna spinata'' * '' Parakatianna superba'' References Collembola Springtail genera {{Springtail-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Campbell Islands
The Campbell Islands (or Campbell Island Group) are a group of subantarctic islands, belonging to New Zealand. They lie about 600 km south of Stewart Island. The islands have a total area of , consisting of one big island, Campbell Island (), and several small islets, notably Dent Island (), Isle de Jeanette Marie (), Folly Island (or Folly Islands), Jacquemart Island (), and Monowai Island (also known as Lion Rock, ). Ecologically, they are part of the Antipodes Subantarctic Islands tundra ecoregion. The islands are one of five subantarctic island groups collectively designated as a World Heritage Site by UNESCO. Geography * Campbell Island / Motu Ihupuku () * Dent Island () * Jacquemart Island () * Folly Island or Folly Islands The islands are relatively flat; due to tectonic pressure, however, there are mountains in the centre of each island. A sea stack at the southern tip of Jacquemart Island is – with the exception of the country's Antarctic claims – New Z ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animals Described In 1964
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals consume organic material, breathe oxygen, are able to move, can reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in which their body consists of a hollow sphere of cells, the blastula, during embryonic development. Over 1.5 million living animal species have been described—of which around 1 million are insects—but it has been estimated there are over 7 million animal species in total. Animals range in length from to . They have complex interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology. Most living animal species are in Bilateria, a clade whose members have a bilaterally symmetric body plan. The Bilateria include the protostomes, containing animals such as nematodes, arthropods, flatworms, annelids and molluscs, and the deuterostomes, containing the ec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endemic Arthropods Of New Zealand
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsewhere. For example, the Cape sugarbird is found exclusively in southwestern South Africa and is therefore said to be ''endemic'' to that particular part of the world. An endemic species can be also be referred to as an ''endemism'' or in scientific literature as an ''endemite''. For example ''Cytisus aeolicus'' is an endemite of the Italian flora. '' Adzharia renschi'' was once believed to be an endemite of the Caucasus, but it was later discovered to be a non-indigenous species from South America belonging to a different genus. The extreme opposite of an endemic species is one with a cosmopolitan distribution, having a global or widespread range. A rare alternative term for a species that is endemic is "precinctive", which applies to s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fauna Of The Campbell Islands
Fauna is all of the animal life present in a particular region or time. The corresponding term for plants is ''flora'', and for fungi, it is ''funga''. Flora, fauna, funga and other forms of life are collectively referred to as ''Biota (ecology), biota''. Zoologists and paleontologists use ''fauna'' to refer to a typical collection of animals found in a specific time or place, e.g. the "Sonoran Desert fauna" or the "Burgess Shale fauna". Paleontology, Paleontologists sometimes refer to a sequence of faunal stages, which is a series of rocks all containing similar fossils. The study of animals of a particular region is called faunistics. Etymology ''Fauna of Madagascar, Fauna'' comes from the name Fauna (deity), Fauna, a Roman goddess of earth and fertility, the Roman god Faunus, and the related forest spirits called Fauns. All three words are cognates of the name of the Greek god Pan (god), Pan, and ''panis'' is the Greek language, Greek equivalent of fauna. ''Fauna'' is also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)
