|
Paraechinorhynchus Kalriai
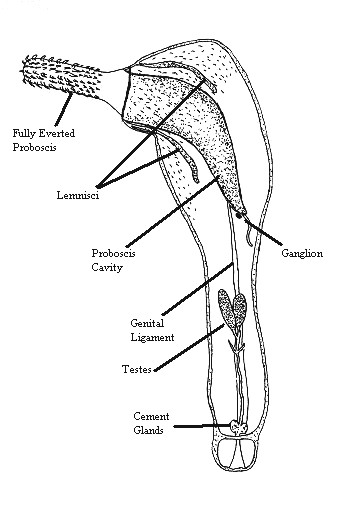
''Paraechinorhynchus'' is a monotypic genus of acanthocephalans (thorny-headed or spiny-headed parasitic worms) containing a single species, ''Paraechinorhynchus kalriai'', that infests the rohu. Taxonomy The species was described by Bilqees and Khan, 1983. The National Center for Biotechnology Information does not indicate that any phylogenetic analysis has been published on ''Paraechinorhynchus'' that would confirm its position as a unique order in the family Neoechinorhynchidae. Description ''P. kalriai'' consists of a proboscis covered in 18 hooks in 3 spiral rows of 4, 6 and 8 hooks respectively, a proboscis receptacle, and a trunk. Distribution The distribution of ''P. kalriai'' is determined by that of its hosts. It was found in Kalri Lake, Sind, Pakistan. Hosts The life cycle of an acanthocephalan consists of three stages beginning when an infective acanthor (development of an egg) is released from the intestines of the definitive host and then ingested by an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monotypic Taxon
In biology, a monotypic taxon is a taxonomic group (taxon) that contains only one immediately subordinate taxon. A monotypic species is one that does not include subspecies or smaller, infraspecific taxa. In the case of genera, the term "unispecific" or "monospecific" is sometimes preferred. In botanical nomenclature, a monotypic genus is a genus in the special case where a genus and a single species are simultaneously described. In contrast, an oligotypic taxon contains more than one but only a very few subordinate taxa. Examples Just as the term ''monotypic'' is used to describe a taxon including only one subdivision, the contained taxon can also be referred to as monotypic within the higher-level taxon, e.g. a genus monotypic within a family. Some examples of monotypic groups are: Plants * In the order Amborellales, there is only one family, Amborellaceae and there is only one genus, '' Amborella'', and in this genus there is only one species, namely ''Amborella trichopoda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acanthocephala
Acanthocephala (Greek , ', thorn + , ', head) is a phylum of parasitic worms known as acanthocephalans, thorny-headed worms, or spiny-headed worms, characterized by the presence of an eversible proboscis, armed with spines, which it uses to pierce and hold the gut wall of its host. Acanthocephalans have complex life cycles, involving at least two hosts, which may include invertebrates, fish, amphibians, birds, and mammals. About 1420 species have been described. The Acanthocephala were thought to be a discrete phylum. Recent genome analysis has shown that they are descended from, and should be considered as, highly modified rotifers. This unified taxon is known as Syndermata. History The earliest recognisable description of Acanthocephala – a worm with a proboscis armed with hooks – was made by Italian author Francesco Redi (1684).Crompton 1985, p. 27 In 1771, Joseph Koelreuter proposed the name Acanthocephala. Philipp Ludwig Statius Müller independently called th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasitism
Parasitism is a Symbiosis, close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the Host (biology), host, causing it some harm, and is Adaptation, adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson has characterised parasites as "predators that eat prey in units of less than one". Parasites include single-celled protozoans such as the agents of malaria, sleeping sickness, and amoebic dysentery; animals such as hookworms, lice, mosquitoes, and vampire bats; fungi such as Armillaria mellea, honey fungus and the agents of ringworm; and plants such as mistletoe, dodder, and the Orobanchaceae, broomrapes. There are six major parasitic Behavioral ecology#Evolutionarily stable strategy, strategies of exploitation of animal hosts, namely parasitic castration, directly transmitted parasitism (by contact), wikt:trophic, trophicallytransmitted parasitism (by being eaten), Disease vector, vector-transmitted paras ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rohu
The rohu, rui, ruhi or roho labeo (''Labeo rohita'') is a species of fish of the carp family, found in rivers in South Asia. It is a large omnivore and extensively used in aquaculture. Description The rohu is a large, silver-colored fish of typical cyprinid shape, with a conspicuously arched head. Adults can reach a maximum weight of and maximum length of , but average around . Distribution and habitat The rohu occurs in rivers throughout much of northern and central and eastern India, Pakistan, Vietnam, Bangladesh, Nepal and Myanmar, and has been introduced into some of the rivers of Peninsular India and Sri Lanka. Ecology The species is an omnivore with specific food preferences at different life stages. During the early stages of its lifecycle, it eats mainly zooplankton, but as it grows, it eats more and more phytoplankton, and as a juvenile or adult is a herbivorous column feeder, eating mainly phytoplankton and submerged vegetation. It has modified, thin hair-like ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Center For Biotechnology Information
The National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) is part of the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM), a branch of the National Institutes of Health (NIH). It is approved and funded by the government of the United States. The NCBI is located in Bethesda, Maryland, and was founded in 1988 through legislation sponsored by US Congressman Claude Pepper. The NCBI houses a series of databases relevant to biotechnology and biomedicine and is an important resource for bioinformatics tools and services. Major databases include GenBank for DNA sequences and PubMed, a bibliographic database for biomedical literature. Other databases include the NCBI Epigenomics database. All these databases are available online through the Entrez search engine. NCBI was directed by David Lipman, one of the original authors of the BLAST sequence alignment program and a widely respected figure in bioinformatics. GenBank NCBI had responsibility for making available the GenBank DNA seque ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phylogenetic
In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek φυλή/ φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups of organisms. These relationships are determined by Computational phylogenetics, phylogenetic inference methods that focus on observed heritable traits, such as DNA sequences, protein amino acid sequences, or morphology. The result of such an analysis is a phylogenetic tree—a diagram containing a hypothesis of relationships that reflects the evolutionary history of a group of organisms. The tips of a phylogenetic tree can be living taxa or fossils, and represent the "end" or the present time in an evolutionary lineage. A phylogenetic diagram can be rooted or unrooted. A rooted tree diagram indicates the hypothetical common ancestor of the tree. An unrooted tree diagram (a network) makes no assumption about the ancestral line, and does ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neoechinorhynchidae
Neoechinorhynchidae is a family of parasitic worms from the order Neoechinorhynchida.Encyclopedia of Life www.eol.org Species Neoechinorhynchidae contains 4 subfamilies: Atactorhynchinae Petrochenko, 1956, Eocollinae Petrochenko, 1956, Gracilisentinae Petrochenko, 1956, Neoechinorhynchinae Ward, 1917. Mayarhynchus The genus Mayarhynchus Pinacho-Pinacho, Hernández-Orts, Sereno-Uribe, Pérez-Ponce de León & García-Varela, 2017 is different from the other 17 genera in Neoechinorhynchidae by having a small proboscis. It has nine longitudinal rows of five hooks each, totaling 45 to 46 relatively weak rooted hooks. *''Mayarhynchus karlae'' Pinacho-Pinacho, Hernández-Orts, Sereno-Uribe, Pérez-Ponce de León & García-Varela, 2017 ''M. karlae'' has a small proboscis with nine longitudinal rows of five hooks each, totaling 45 to 46 relatively weak rooted hooks and a proboscis receptacle is nearly cylindrical and contains a single layered wall. The worm has a short trunk with a bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acanthocephala LifeCycle Lg
Acanthocephala ( Greek , ', thorn + , ', head) is a phylum of parasitic worms known as acanthocephalans, thorny-headed worms, or spiny-headed worms, characterized by the presence of an eversible proboscis, armed with spines, which it uses to pierce and hold the gut wall of its host. Acanthocephalans have complex life cycles, involving at least two hosts, which may include invertebrates, fish, amphibians, birds, and mammals. About 1420 species have been described. The Acanthocephala were thought to be a discrete phylum. Recent genome analysis has shown that they are descended from, and should be considered as, highly modified rotifers. This unified taxon is known as Syndermata. History The earliest recognisable description of Acanthocephala – a worm with a proboscis armed with hooks – was made by Italian author Francesco Redi (1684).Crompton 1985, p. 27 In 1771, Joseph Koelreuter proposed the name Acanthocephala. Philipp Ludwig Statius Müller independently called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Host (biology)
In biology and medicine, a host is a larger organism that harbours a smaller organism; whether a parasite, parasitic, a mutualism (biology), mutualistic, or a commensalism, commensalist ''guest'' (symbiont). The guest is typically provided with nourishment and shelter. Examples include animals playing host to parasitic worms (e.g. nematodes), cell (biology), cells harbouring pathogenic (disease-causing) viruses, a Fabaceae, bean plant hosting mutualistic (helpful) Rhizobia, nitrogen-fixing bacteria. More specifically in botany, a host plant supplies nutrient, food resources to micropredators, which have an evolutionarily stable strategy, evolutionarily stable relationship with their hosts similar to ectoparasitism. The host range is the collection of hosts that an organism can use as a partner. Symbiosis Symbiosis spans a wide variety of possible relationships between organisms, differing in their permanence and their effects on the two parties. If one of the partners in an ass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molt
In biology, moulting (British English), or molting (American English), also known as sloughing, shedding, or in many invertebrates, ecdysis, is the manner in which an animal routinely casts off a part of its body (often, but not always, an outer layer or covering), either at specific times of the year, or at specific points in its life cycle. In medieval times it was also known as "mewing" (from the French verb "muer", to moult), a term that lives on in the name of Britain's Royal Mews where the King's hawks used to be kept during moulting time before becoming horse stables after Tudor times. Moulting can involve shedding the epidermis (skin), pelage (hair, feathers, fur, wool), or other external layer. In some groups, other body parts may be shed, for example, the entire exoskeleton in arthropods, including the wings in some insects. Examples In birds In birds, moulting is the periodic replacement of feathers by shedding old feathers while producing new ones. Feathers are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesenteron
The midgut is the portion of the embryo from which most of the intestines develop. After it bends around the superior mesenteric artery, it is called the "midgut loop". It comprises the portion of the alimentary canal from the end of the foregut at the opening of the bile duct to the hindgut, about two-thirds of the way through the transverse colon. In the embryo During development, the human midgut undergoes a rapid phase of growth in which the loop of midgut herniates outside of the abdominal cavity of the fetus and protrudes into the umbilical cord. This herniation is physiological (occurs normally). Later in development, the fetus's body catches up in size relative to the midgut and creates adequate room in the abdominal cavity for the entirety of the midgut to reside. The midgut loops slip back out of the umbilical cord and the physiological hernia ceases to exist. This change coincides with the termination of the yolk sac and the counterclockwise rotation of the two limb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Larva
A larva (; plural larvae ) is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into adults. Animals with indirect development such as insects, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase of their life cycle. The larva's appearance is generally very different from the adult form (''e.g.'' caterpillars and butterflies) including different unique structures and organs that do not occur in the adult form. Their diet may also be considerably different. Larvae are frequently adapted to different environments than adults. For example, some larvae such as tadpoles live almost exclusively in aquatic environments, but can live outside water as adult frogs. By living in a distinct environment, larvae may be given shelter from predators and reduce competition for resources with the adult population. Animals in the larval stage will consume food to fuel their transition into the adult form. In some organisms like polychaetes and barnacles, adults are immobil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)

