|
Paradox Of The Plankton
In Aquatic ecosystem, aquatic biology, the paradox of the plankton describes the situation in which a limited range of resources supports an unexpectedly wide range of plankton species, apparently flouting the competitive exclusion principle which holds that when two species compete for the same resource, one will be driven to extinction. Ecological paradox The paradox of the plankton results from the clash between the observed biodiversity, diversity of plankton and the competitive exclusion principle, also known as Georgy Gause, Gause's law, which states that, when two species Competition (biology), compete for the same resource, ultimately only one will persist and the other will be driven to extinction. Coexistence between two such species is impossible because the dominant one will inevitably deplete the shared resources, thus decimating the inferior population. Phytoplankton life is diverse at all Phylogenetics, phylogenetic levels despite the limited range of resources (e. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
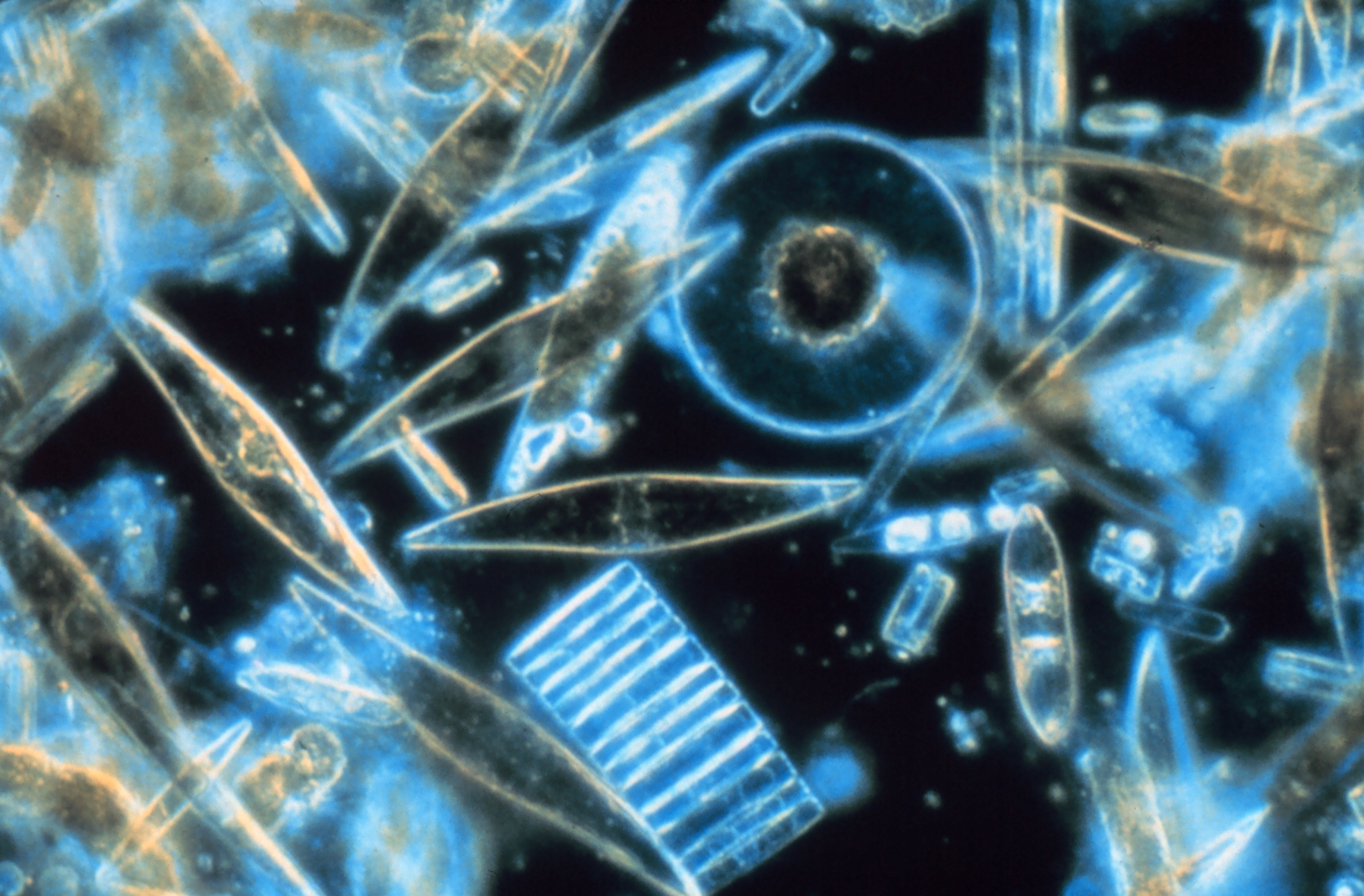
Diatoms Through The Microscope
A diatom (Neo-Latin ''diatoma''), "a cutting through, a severance", from el, διάτομος, diátomos, "cut in half, divided equally" from el, διατέμνω, diatémno, "to cut in twain". is any member of a large group comprising several genera of algae, specifically microalgae, found in the oceans, waterways and soils of the world. Living diatoms make up a significant portion of the Earth's biomass: they generate about 20 to 50 percent of the oxygen produced on the planet each year, take in over 6.7 billion metric tons of silicon each year from the waters in which they live, and constitute nearly half of the organic material found in the oceans. The shells of dead diatoms can reach as much as a half-mile (800 m) deep on the ocean floor, and the entire Amazon basin is fertilized annually by 27 million tons of diatom shell dust transported by transatlantic winds from the African Sahara, much of it from the Bodélé Depression, which was once made up of a system of fres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symbiosis
Symbiosis (from Greek , , "living together", from , , "together", and , bíōsis, "living") is any type of a close and long-term biological interaction between two different biological organisms, be it mutualistic, commensalistic, or parasitic. The organisms, each termed a symbiont, must be of different species. In 1879, Heinrich Anton de Bary defined it as "the living together of unlike organisms". The term was subject to a century-long debate about whether it should specifically denote mutualism, as in lichens. Biologists have now abandoned that restriction. Symbiosis can be obligatory, which means that one or more of the symbionts depend on each other for survival, or facultative (optional), when they can generally live independently. Symbiosis is also classified by physical attachment. When symbionts form a single body it is called conjunctive symbiosis, while all other arrangements are called disjunctive symbiosis."symbiosis." Dorland's Illustrated Medical Dictionary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematical And Theoretical Biology
Mathematical and theoretical biology, or biomathematics, is a branch of biology which employs theoretical analysis, mathematical models and abstractions of the living organisms to investigate the principles that govern the structure, development and behavior of the systems, as opposed to experimental biology which deals with the conduction of experiments to prove and validate the scientific theories. The field is sometimes called mathematical biology or biomathematics to stress the mathematical side, or theoretical biology to stress the biological side. Theoretical biology focuses more on the development of theoretical principles for biology while mathematical biology focuses on the use of mathematical tools to study biological systems, even though the two terms are sometimes interchanged. Mathematical biology aims at the mathematical representation and modeling of biological processes, using techniques and tools of applied mathematics. It can be useful in both theoretical and pra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aquatic Ecology
An aquatic ecosystem is an ecosystem formed by surrounding a body of water, in contrast to land-based terrestrial ecosystems. Aquatic ecosystems contain communities of organisms that are dependent on each other and on their environment. The two main types of aquatic ecosystems are marine ecosystems and freshwater ecosystems. Freshwater ecosystems may be lentic (slow moving water, including pools, ponds, and lakes); lotic (faster moving water, for example streams and rivers); and wetlands (areas where the soil is saturated or inundated for at least part of the time). Types Marine ecosystems Marine coastal ecosystem Marine surface ecosystem Freshwater ecosystems Lentic ecosystem (lakes) Lotic ecosystem (rivers) Wetlands Functions Aquatic ecosystems perform many important environmental functions. For example, they recycle nutrients, purify water, attenuate floods, recharge ground water and provide habitats for wildlife. Aquatic ecosystems are al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biological Oceanography
Biological oceanography is the study of how organisms affect and are affected by the physics, chemistry, and geology of the oceanographic system. Biological oceanography may also be referred to as ocean ecology, in which the root word of ecology is ''Oikos'' (oικoσ), meaning ‘house’ or ‘habitat’ in Greek. With that in mind, it is of no surprise then that the main focus of biological oceanography is on the microorganisms within the ocean; looking at how they are affected by their environment and how that affects larger marine creatures and their ecosystem.Lalli, Carol M., and Timothy R. Parsons. "Introduction." Biological Oceanography: An Introduction. First Edition ed. Tarrytown, New York: Pergamon, 1993. 7-21. Print. Biological oceanography is similar to marine biology, but is different because of the perspective used to study the ocean. Biological oceanography takes a bottom-up approach (in terms of the food web), while marine biology studies the ocean from a top-down ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biological Interactions
In ecology, a biological interaction is the effect that a pair of organisms living together in a community have on each other. They can be either of the same species (intraspecific interactions), or of different species (interspecific interactions). These effects may be short-term, like pollination and predation, or long-term; both often strongly influence the evolution of the species involved. A long-term interaction is called a symbiosis. Symbioses range from mutualism, beneficial to both partners, to competition, harmful to both partners. Interactions can be indirect, through intermediaries such as shared resources or common enemies. This type of relationship can be shown by net effect based on individual effects on both organisms arising out of relationship. Several recent studies have suggested non-trophic species interactions such as habitat modification and mutualisms can be important determinants of food web structures. However, it remains unclear whether these findings ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Klaus Rohde
Klaus Rohde (born 1932 in Brandenburg an der Havel, Germany) is a German biologist at the University of New England (UNE), Australia, known particularly for his work on marine parasitology, evolutionary ecology/zoogeography, and phylogeny/ultrastructure of lower invertebrates. Early life and education Rohde studied zoology, botany, physics, physiological chemistry in Potsdam ( Brandenburgische Landeshochschule, Germany) from 1950–1952, and, after moving from East- to West-Germany, in Münster/Westfalen (Germany) from 1953–1956. He received the degree of Dr.rer.nat. at University of Münster (Germany) in 1956 for a thesis on the behaviour and physiology of Paramecium. Subsequently, (1957–1959), he did scientific work at ASTA-Werke, Brackwede/ Westfalen (pharmaceutical industry) on the development of new tests for screening anthelminthic drugs (filariasis, hookworms, cysticercus). Career From 1960–1967, Rohde was a lecturer at the University of Malaya, Kuala Lump ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unified Neutral Theory Of Biodiversity
The unified neutral theory of biodiversity and biogeography (here "Unified Theory" or "UNTB") is a theory and the title of a monograph by ecologist Stephen P. Hubbell. It aims to explain the diversity and relative abundance of species in ecological communities. Like other neutral theories of ecology, Hubbell assumes that the differences between members of an ecological community of trophically similar species are "neutral", or irrelevant to their success. This implies that niche differences do not influence abundance and the abundance of each species follows a random walk. The theory has sparked controversy, and some authors consider it a more complex version of other null models that fit the data better. "Neutrality" means that at a given trophic level in a food web, species are equivalent in birth rates, death rates, dispersal rates and speciation rates, when measured on a per-capita basis. This can be considered a null hypothesis to niche theory. Hubbell built on earli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Habitat (ecology)
In ecology, the term habitat summarises the array of resources, physical and biotic factors that are present in an area, such as to support the survival and reproduction of a particular species. A species habitat can be seen as the physical manifestation of its ecological niche. Thus "habitat" is a species-specific term, fundamentally different from concepts such as environment or vegetation assemblages, for which the term "habitat-type" is more appropriate. The physical factors may include (for example): soil, moisture, range of temperature, and light intensity. Biotic factors will include the availability of food and the presence or absence of predators. Every species has particular habitat requirements, with habitat generalist species able to thrive in a wide array of environmental conditions while habitat specialist species requiring a very limited set of factors to survive. The habitat of a species is not necessarily found in a geographical area, it can be the interior ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Predation
Predation is a biological interaction In ecology, a biological interaction is the effect that a pair of organisms living together in a community have on each other. They can be either of the same species (intraspecific interactions), or of different species ( interspecific interactio ... where one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not kill the host) and parasitoidism (which always does, eventually). It is distinct from scavenging on dead prey, though many predators also scavenge; it overlaps with herbivory, as seed predators and destructive frugivores are predators. Predators may actively search for or pursue prey or wait for it, often concealed. When prey is detected, the predator assesses whether to attack it. This may involve ambush predation, ambush or pursuit predation, sometimes after stalking the prey. If the attack ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commensalism
Commensalism is a long-term biological interaction ( symbiosis) in which members of one species gain benefits while those of the other species neither benefit nor are harmed. This is in contrast with mutualism, in which both organisms benefit from each other; amensalism, where one is harmed while the other is unaffected; parasitism, where one is harmed and the other benefits, and parasitoidism, which is similar to parasitism but the parasitoid has a free-living state and instead of just harming its host, it eventually ends up killing it. The commensal (the species that benefits from the association) may obtain nutrients, shelter, support, or locomotion from the host species, which is substantially unaffected. The commensal relation is often between a larger host and a smaller commensal; the host organism is unmodified, whereas the commensal species may show great structural adaptation consistent with its habits, as in the remoras that ride attached to sharks and other fish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Column
A water column is a conceptual column of water from the surface of a sea, river or lake to the bottom sediment.Munson, B.H., Axler, R., Hagley C., Host G., Merrick G., Richards C. (2004).Glossary. ''Water on the Web''. University of Minnesota-Duluth. Retrieved 27 May 2014. Descriptively, the deep sea water column is divided into five parts—''pelagic zones'' (from Greek πέλαγος (pélagos), 'open sea')—from the surface to below the floor, as follows: '' epipelagic'', from the surface to 200 meters below the surface; '' mesopelagic'', from 200 to 1000 meters below the surface; ''bathypelagic'', from 1000 to 4000 meters below the surface; '' abyssopelagic'', from 4000 meters below the surface to the level sea floor; '' hadopelagic'', depressions and crevices below the level sea floor. The concept of water column is useful since many aquatic phenomena are explained by the incomplete vertical mixing of waters with discrete chemical, physical or biological characteristics. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_with_its_prey.jpg)
