|
Pacte De Famine
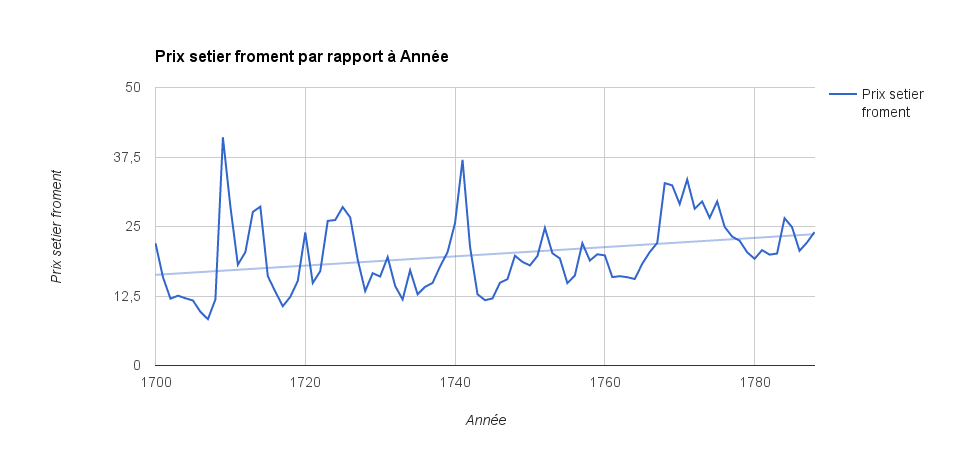
''Pacte de Famine'' (, ''Famine Pact'') was a conspiracy theory adopted by many living in France during the 18th century. The theory held that foods, especially grain, were purposely withheld from them, for the benefit of privileged interest groups. During this period French citizens obtained much of their nourishment from grain.Kaplan 1–2, 52 History The famine plot has roots in pre-revolutionary France, while some of its strongest manifestations were evident during the 1760s and 1770s. The collective mentality surrounding this conspiracy served as a tool for French citizens to make sense of the political environment at the time. Between 1715 and 1789 the population of France increased by 6 million, from 22 million to 28 million. Population growth and demographic changes during the 18th century help to explain the high demand for food, and lack of food supply at the time. Many faced hunger due to scarcity of food, and found it difficult to fend off illness. At times "bad grain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conspiracy Theory
A conspiracy theory is an explanation for an event or situation that invokes a conspiracy by sinister and powerful groups, often political in motivation, when other explanations are more probable.Additional sources: * * * * The term has a negative connotation, implying that the appeal to a conspiracy is based on prejudice or insufficient evidence. A conspiracy theory is not the same as a conspiracy; instead, it refers to a hypothesized conspiracy with specific characteristics, such as an opposition to the mainstream consensus among those people (such as scientists or historians) who are qualified to evaluate its accuracy. Conspiracy theories resist falsification and are reinforced by circular reasoning: both evidence against the conspiracy and an absence of evidence for it are re-interpreted as evidence of its truth, whereby the conspiracy becomes a matter of faith rather than something that can be proven or disproven. Studies have linked belief in conspiracy theories to dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Invisible Hand
The invisible hand is a metaphor used by the British moral philosopher Adam Smith that describes the unintended greater social benefits and public good brought about by individuals acting in their own self-interests. Smith originally mentioned the term in his work ''Theory of Moral Sentiments'' in 1759, but it has actually become known from his main work ''The Wealth of Nations'', where the word itself is mentioned only once, in connection with import restrictions. Similar ideas had already been presented before Smith by other Enlightenment thinkers, such as Anders Chydenius in his work ''The National Gain'' (1765) and Bernard Mandeville. Liberal thinkers wanted to show that society functions without collapsing even without the old hierarchical order of the feudal era. The concept was first introduced by Adam Smith in ''The Theory of Moral Sentiments'', written in 1759. The exact phrase is used just three times in Smith's writings. Smith may have come up with the two mea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Political History Of The Ancien Régime
Politics (from , ) is the set of activities that are associated with making decisions in groups, or other forms of power relations among individuals, such as the distribution of resources or status. The branch of social science that studies politics and government is referred to as political science. It may be used positively in the context of a "political solution" which is compromising and nonviolent, or descriptively as "the art or science of government", but also often carries a negative connotation.. The concept has been defined in various ways, and different approaches have fundamentally differing views on whether it should be used extensively or limitedly, empirically or normatively, and on whether conflict or co-operation is more essential to it. A variety of methods are deployed in politics, which include promoting one's own political views among people, negotiation with other political subjects, making laws, and exercising internal and external force, including w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economic History Of The Ancien Régime
An economy is an area of the production, distribution and trade, as well as consumption of goods and services. In general, it is defined as a social domain that emphasize the practices, discourses, and material expressions associated with the production, use, and management of scarce resources'. A given economy is a set of processes that involves its culture, values, education, technological evolution, history, social organization, political structure, legal systems, and natural resources as main factors. These factors give context, content, and set the conditions and parameters in which an economy functions. In other words, the economic domain is a social domain of interrelated human practices and transactions that does not stand alone. Economic agents can be individuals, businesses, organizations, or governments. Economic transactions occur when two groups or parties agree to the value or price of the transacted good or service, commonly expressed in a certain currency. Howev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambridge University Press
Cambridge University Press is the university press of the University of Cambridge. Granted letters patent by Henry VIII of England, King Henry VIII in 1534, it is the oldest university press A university press is an academic publishing house specializing in monographs and scholarly journals. Most are nonprofit organizations and an integral component of a large research university. They publish work that has been reviewed by schola ... in the world. It is also the King's Printer. Cambridge University Press is a department of the University of Cambridge and is both an academic and educational publisher. It became part of Cambridge University Press & Assessment, following a merger with Cambridge Assessment in 2021. With a global sales presence, publishing hubs, and offices in more than 40 Country, countries, it publishes over 50,000 titles by authors from over 100 countries. Its publishing includes more than 380 academic journals, monographs, reference works, school and uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manchester University Press
Manchester University Press is the university press of the University of Manchester, England and a publisher of academic books and journals. Manchester University Press has developed into an international publisher. It maintains its links with the University. Publishing Manchester University Press publishes monographs and textbooks for academic teaching in higher education. In 2012 it was producing about 145 new books annually and managed a number of journals. Areas of expertise are history, politics and international law, literature and theatre studies, and visual culture. MUP books are marketed and distributed by Oxford University Press in the United States and Canada, and in Australia by Footprint Books; all other global territories are covered from Manchester itself. Some of the press's books were formerly published in the US by Barnes & Noble, Inc., New York. Later the press established an American office in Dover, New Hampshire. Open access Manchester University Pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Just Price
The just price is a theory of ethics in economics that attempts to set standards of fairness in transactions. With intellectual roots in ancient Greek philosophy, it was advanced by Thomas Aquinas based on an argument against usury, which in his time referred to the making of any rate of interest on loans. It gave rise to the contractual principle of '' laesio enormis''. Unjust price: a kind of fraud The argument against usury was that the lender was receiving income for nothing, since nothing was actually lent, rather the money was exchanged. And, a dollar can only be fairly exchanged for a dollar, so asking for more is unfair. Aquinas later expanded his argument to oppose any unfair earnings made in trade, basing the argument on the Golden Rule. The Christian should "do unto others as you would have them do unto you", meaning he should trade value for value. Aquinas believed that it was specifically immoral to raise prices because a particular buyer had an urgent need for what ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flour War Of 1775
The Flour War refers to a wave of riots from April to May 1775, in the northern, eastern, and western parts of the Kingdom of France. It followed an increase in grain prices, and subsequently bread prices; bread was an important source of food among the populace. Contributing factors to the riots include poor weather and harvests, and the withholding by police of public grain supplies from the royal stores in 1773–1774. This large-scale revolt subsided following wheat price controls imposed by Turgot, Louis XVI's Controller-General of Finances (before the supply recovered), and the deploying of military troops. The Flour War was part of a broader social and political crisis during the Ancien Régime. Recent analyses tend to treat this event not only as a revolt caused by hunger, but also as a prelude to the French Revolution. Causes In Ancien Régime France, bread was the main source of food for poor peasants and the king was required to ensure the food supply of his subjects ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guild
A guild ( ) is an association of artisans and merchants who oversee the practice of their craft/trade in a particular area. The earliest types of guild formed as organizations of tradesmen belonging to a professional association. They sometimes depended on grants of letters patent from a monarch or other ruler to enforce the flow of trade to their self-employed members, and to retain ownership of tools and the supply of materials, but were mostly regulated by the city government. A lasting legacy of traditional guilds are the guildhalls constructed and used as guild meeting-places. Guild members found guilty of cheating the public would be fined or banned from the guild. Typically the key "privilege" was that only guild members were allowed to sell their goods or practice their skill within the city. There might be controls on minimum or maximum prices, hours of trading, numbers of apprentices, and many other things. These rules reduced free competition, but sometimes mainta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guild System
A guild ( ) is an association of artisans and merchants who oversee the practice of their craft/trade in a particular area. The earliest types of guild formed as organizations of tradesmen belonging to a professional association. They sometimes depended on grants of letters patent from a monarch or other ruler to enforce the flow of trade to their self-employed members, and to retain ownership of tools and the supply of materials, but were mostly regulated by the city government. A lasting legacy of traditional guilds are the guildhalls constructed and used as guild meeting-places. Guild members found guilty of cheating the public would be fined or banned from the guild. Typically the key "privilege" was that only guild members were allowed to sell their goods or practice their skill within the city. There might be controls on minimum or maximum prices, hours of trading, numbers of apprentices, and many other things. These rules reduced free competition, but sometimes maintained ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laissez-faire
''Laissez-faire'' ( ; from french: laissez faire , ) is an economic system in which transactions between private groups of people are free from any form of economic interventionism (such as subsidies) deriving from special interest groups. As a system of thought, ''laissez-faire'' rests on the following axioms: "the individual is the basic unit in society, i.e. the standard of measurement in social calculus; the individual has a natural right to freedom; and the physical order of nature is a harmonious and self-regulating system." Another basic principle of ''laissez-faire'' holds that markets should naturally be competitive, a rule that the early advocates of ''laissez-faire'' always emphasized. With the aims of maximizing freedom by allowing markets to self-regulate, early advocates of ''laissez-faire'' proposed a ''impôt unique'', a tax on land rent (similar to Georgism) to replace all taxes that they saw as damaging welfare by penalizing production. Proponents of ''l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Market
In economics, a free market is an economic system in which the prices of goods and services are determined by supply and demand expressed by sellers and buyers. Such markets, as modeled, operate without the intervention of government or any other external authority. Proponents of the free market as a normative ideal contrast it with a regulated market, in which a government intervenes in supply and demand by means of various methods such as taxes or regulations. In an idealized free market economy, prices for goods and services are set solely by the bids and offers of the participants. Scholars contrast the concept of a free market with the concept of a coordinated market in fields of study such as political economy, new institutional economics, economic sociology and political science. All of these fields emphasize the importance in currently existing market systems of rule-making institutions external to the simple forces of supply and demand which create space for those ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_per_capita_in_2020.png)





