|
Packard 1A-2500
The Packard 1A-2500 is an American V-12 liquid-cooled aircraft engine designed by Packard in 1924 as a successor to the World War I-era Liberty L-12. Five aero variants were produced, of which the 3A-2500 was the most numerous. Three marine versions, used most prominently in American World War II PT-boats, the 3M-2500, 4M-2500, and 5M-2500, were also derived from it. Applications * Boeing TB *Heinkel HE 8 * Martin T3M * Naval Aircraft Factory PN * Huff-Daland LB-1 * PT boats - marine versions of the 3M/4M/5M-2500 * Packard-Bentley one-off race car *USSR World War II torpedo boats and sub-chasers, which were fitted with 535 4M-2500 engines with W-8 modification under Lend-Lease Variants ;1A-2500:1924, 800 hp. Six built. ;2A-2500 :1925, 800 hp. 75 built. ;2A-2540:? Huff-Daland XHB-1 ;3A-2500:1926, Geared propeller drive option, 800 hp. 175 built. ;4A-2500:1927, fitted with a supercharger, 900 hp. One built. ;5A-2500:1930, experimental use only, 1500 hp. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiProject Aircraft
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is an affinity group for contributors with shared goals within the Wikimedia movement. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within Wikimedia project, sibling projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by ''Smithsonian Magazine, Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outsi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torpedo Boat
A torpedo boat is a relatively small and fast naval ship designed to carry torpedoes into battle. The first designs were steam-powered craft dedicated to ramming enemy ships with explosive spar torpedoes. Later evolutions launched variants of self-propelled Whitehead torpedoes. These were inshore craft created to counter both the threat of battleships and other slow and heavily armed ships by using speed, agility, and powerful torpedoes, and the overwhelming expense of building a like number of capital ships to counter an enemy. A swarm of expendable torpedo boats attacking en masse could overwhelm a larger ship's ability to fight them off using its large but cumbersome guns. A fleet of torpedo boats could pose a similar threat to an adversary's capital ships, albeit only in the coastal areas to which their small size and limited fuel load restricted them. The introduction of fast torpedo boats in the late 19th century was a serious concern to the era's naval strategists, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Packard 1A-1500
The Packard 1A-1500 was an American 12-cylinder liquid-cooled 60-degree Vee piston aircraft engine designed in 1924.Gunston 1989, p.109. Test flown in the second prototype Douglas XO-2, it proved to be unreliable. Only 29 engines were built. Applications * Boeing Model 15 * Boeing XP-4 * Curtiss Falcon * Douglas XO-2 * Loening OL Specifications (1A-1500) See also * Packard 1A-2500 The Packard 1A-2500 is an American V-12 liquid-cooled aircraft engine designed by Packard in 1924 as a successor to the World War I-era Liberty L-12. Five aero variants were produced, of which the 3A-2500 was the most numerous. Three marine v ... References Notes Bibliography * Gunston, Bill. ''World Encyclopedia of Aero Engines''. Cambridge, England. Patrick Stephens Limited, 1989. Aircraft Engine Historical Society {{Packard aeroengines 1920s aircraft piston engines 1A-1500 V12 aircraft engines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fairmile D Motor Torpedo Boat
The Fairmile D motor torpedo boat was a type of United Kingdom, British motor torpedo boat (MTB) and motor gunboat (MGB), conceived by entrepreneur Noel Macklin of Fairmile Marine and designed by naval architect Bill Holt for the Royal Navy. Nicknamed "Dog Boats", they were designed to be assembled in kit form mass-produced by the Fairmile organisation and assembled at dozens of small boatbuilding yards around Britain, to combat the known advantages of the German Schnellboote, E-boats over previous British coastal craft designs. At 115 feet in length, they were bigger than earlier MTB or motor gunboat (MGB) designs (which were typically around 70 feet) but slower, at 30 knots compared to 40 knots. Boats Holt combined a destroyer style bow with a Fairmile style stern, working with Fairmile from 1940 to develop a structure suitable for pre-fabrication. There was a supply of Packard engines due to lend-Lease and these were arranged as two pairs in the engine room expected to give a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petrol
Gasoline (North American English) or petrol ( Commonwealth English) is a petrochemical product characterized as a transparent, yellowish, and flammable liquid normally used as a fuel for spark-ignited internal combustion engines. When formulated as a fuel for engines, gasoline is chemically composed of organic compounds derived from the fractional distillation of petroleum and later chemically enhanced with gasoline additives. It is a high-volume profitable product produced in crude oil refineries. The ability of a particular gasoline blend to resist premature ignition (which causes knocking and reduces efficiency in reciprocating engines) is measured by its octane rating. Tetraethyl lead was once widely used to increase the octane rating but is not used in modern automotive gasoline due to the health hazard. Aviation, off-road motor vehicles, and racing car engines still use leaded gasolines. Other substances are frequently added to gasoline to improve chemical stabilit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overhead Camshaft
An overhead camshaft (OHC) engine is a piston engine in which the camshaft is located in the cylinder head above the combustion chamber. This contrasts with earlier overhead valve engines (OHV), where the camshaft is located below the combustion chamber in the engine block. ''Single overhead camshaft'' (SOHC) engines have one camshaft per cylinder bank, bank of cylinders. ''Dual overhead camshaft'' (DOHC, also known as "twin-cam") engines have two camshafts per bank. The first production car to use a DOHC engine was built in 1910. Use of DOHC engines slowly increased from the 1940s, leading to many automobiles by the early 2000s using DOHC engines. Design In an OHC engine, the camshaft is located at the top of the engine, above the combustion chamber. This contrasts the earlier overhead valve engine (OHV) and flathead engine configurations, where the camshaft is located down in the engine block. The valves in both OHC and OHV engines are located above the combustion chamber; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
V Engine
A V engine, sometimes called a Vee engine, is a common configuration for internal combustion engines. It consists of two cylinder banks—usually with the same number of cylinders in each bank—connected to a common crankshaft. These cylinder banks are arranged at an angle to each other, so that the banks form a "V" shape when viewed from the front of the engine. V engines typically have a shorter length than equivalent inline engines, however the trade-off is a larger width. V6, V8 and V12 engines are the most common layout for automobile engines with 6, 8 or 12 cylinders respectively. History The first V engine, a two-cylinder V-twin, was designed by Wilhelm Maybach and used in the 1889 Daimler Stahlradwagen automobile. The first V8 engine was produced in 1903, in the form of the Antoinette engine designed by Léon Levavasseur for racing boats and airplanes. The first V12 engine was produced the following year by Putney Motor Works in London, again for use in raci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patrol Torpedo Boat PT-658
Motor torpedo boat ''PT-658'' is a ''PT-625''-class Higgins PT boat, built for the United States Navy during World War II. ''PT-658'' is a prime example of US Navy motor torpedo boat development during World War II. ''PT-658'' was in the last group of four boats delivered from the 36-boat contract NObs-1680, October 1944 for ''PT-625'' to ''PT-660''. Delivered and accepted on 31 July 1945, she was fitted with all of the latest armaments and design modifications as a result of lessons learned from previous contracts and battlefield experience. In this way, ''PT-658'' is a showcase of the final form that motor torpedo boats would take by the end of World War II. ''PT-658'' was listed on the National Register of Historic Places on 4 September 2012. Of three PT boats listed on the National Register, she is one of 2 maintained in operating condition. PT-305, at The National WWII Museum in New Orleans, has been restored to operating condition as of March 2017, but it not (yet) listed i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Packard Proving Grounds
The Packard Proving Grounds (the remains of which are now called the Packard Proving Grounds Gateway Complex), was a proving ground established in Shelby Charter Township, Michigan in 1927 by the Packard Motor Car Company of Detroit. It is listed in the National Register of Historic Places. History Packard had been founded in Warren, Ohio in 1899 by brothers James Ward Packard and William Doud Packard. The company attracted several investors from Detroit, and by 1903 the Michigan investors had convinced the Packard brothers to let them relocate the young business to the emerging motor capital of Detroit. The Packard automobile quickly evolved into a superbly engineered prestige vehicle. To maintain and advance their product position, Packard's general manager, Henry Bourne Joy, sought to establish a dedicated testing facility. Testing on local streets and roads was risky due to traffic, and could potentially expose Packard's future product developments to curious competitors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New England Air Museum
The New England Air Museum (NEAM) is an American aerospace museum located adjacent to Bradley International Airport in Windsor Locks, Connecticut. The museum consists of three display hangars with additional storage and restoration hangars. Its collections include aircraft ranging from early flying machines to supersonic jets, as well as engines, and other pieces of flight-related equipment. Significant aircraft include * the Silas Brooks balloon basket - the oldest surviving American-built aircraft * the Sikorsky VS-44A - the sole remaining American-built commercial trans-oceanic four-engine flying boat * the Goodyear ZNPK-28 Blimp Control Car - one of only two surviving K-class control cars in the world. The museum library has approximately 6,000 aviation books, approximately 20,000 periodicals, approximately 10,000 technical manuals, approximately 21,000 photographs, nearly 8,000 slides, over 200 pieces of artwork, over 1,200 prints, and approximately 500 engineering drawin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
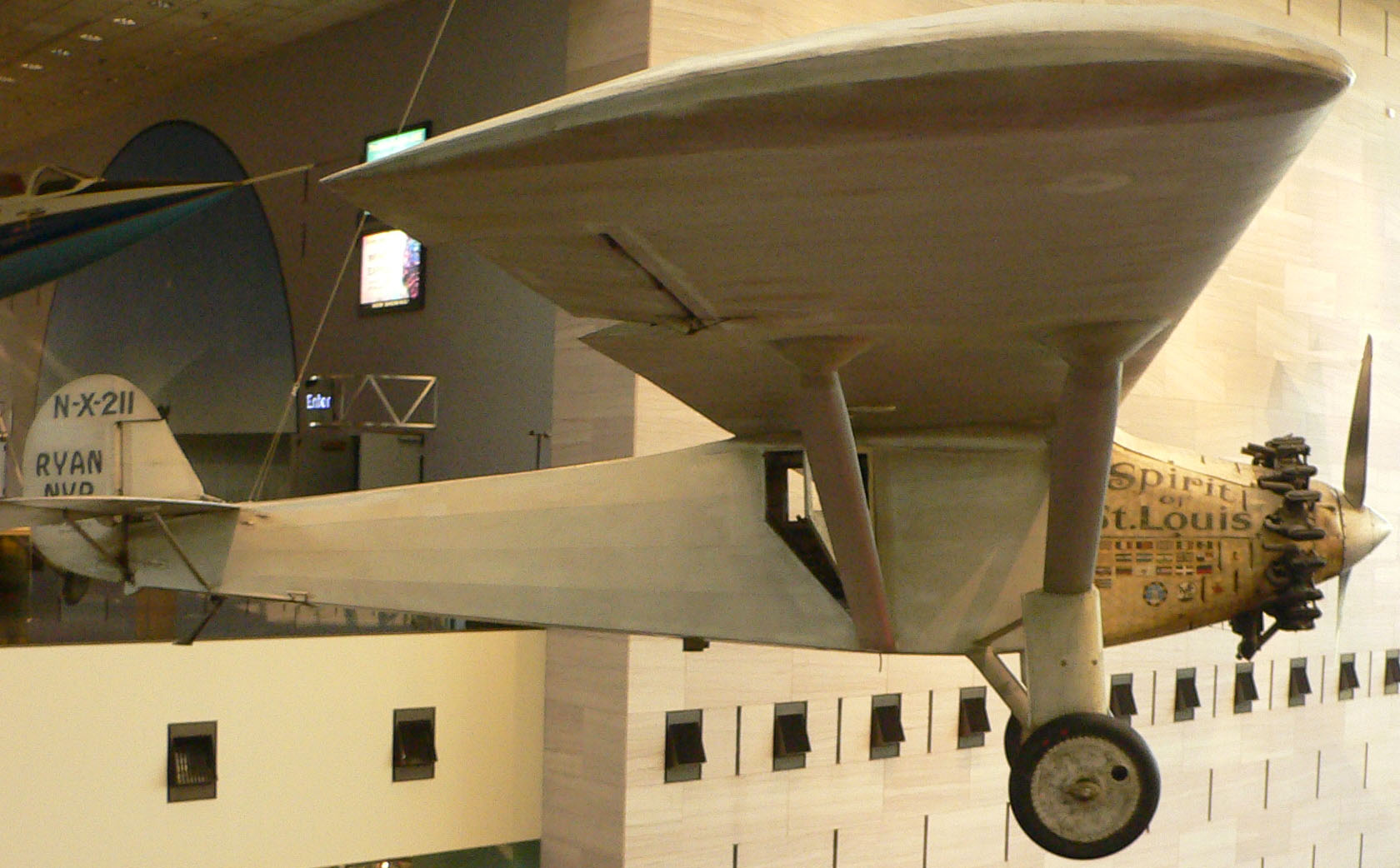
National Air And Space Museum
The National Air and Space Museum (NASM) of the Smithsonian Institution is a museum in Washington, D.C., in the United States, dedicated to history of aviation, human flight and space exploration. Established in 1946 as the National Air Museum, its main building opened on the National Mall near L'Enfant Plaza in 1976. In 2023, the museum welcomed 3.1 million visitors, making it the list of most-visited museums in the United States, fourth-most visited museum in the United States and List of most-visited museums, eleventh-most in the world. The museum is a center for research into the history and science of aviation and spaceflight, as well as planetary science and terrestrial geology and geophysics. Almost all of its spacecraft and aircraft on display are original primary or backup craft (rather than facsimiles). Its collection includes the Apollo 11 Command module Columbia, Command Module ''Columbia'', the Mercury-Atlas 6, ''Friendship 7'' capsule which was flown by John Glenn, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supercharger
In an internal combustion engine, a supercharger compresses the intake gas, forcing more air into the engine in order to produce more power for a given displacement (engine), displacement. It is a form of forced induction that is mechanically powered (usually by a belt from the engine's crankshaft), as opposed to a turbocharger, which is powered by the kinetic energy of the exhaust gases. However, up until the mid-20th century, a turbocharger was called a "turbosupercharger" and was considered a type of supercharger. The first supercharged engine was built in 1878, with usage in aircraft engines beginning in the 1910s and usage in car engines beginning in the 1920s. In piston engines used by aircraft, supercharging was often used to compensate for the lower air density at high altitudes. Supercharging is less commonly used in the 21st century, as manufacturers have shifted to turbochargers to reduce fuel consumption and increase power outputs, especially with reduced engine dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |