|
Pacemaker (other)
An artificial cardiac pacemaker is a medical device that regulates the beating of the heart. Pacemaker may also refer to: Medicine * Biological pacemaker, the use of specialized cells to improve the regulation of the heart * Brain pacemaker, a device to treat movement disorders, epilepsy, depression, or other conditions * Cardiac pacemaker, cells within the heart that initiate contractions and set the pace of beating * Diaphragmatic pacemaker, a device used to help patients breathe through pacing of the diaphragm Other uses * Pacemaker (running), a runner who enters a race to set a fast pace for other competitors * ''Pacemaker'' (film), a 2012 South Korean film * The Pacemaker, a pocket-sized DJ system * National Pacemaker Awards, American awards for excellence in student journalism * Pacemaker (software), a high-availability cluster resource manager * ''Pacemaker'' (train), an American passenger train * Pacemaker Entertainment, a Canadian record label, part of the Canadian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
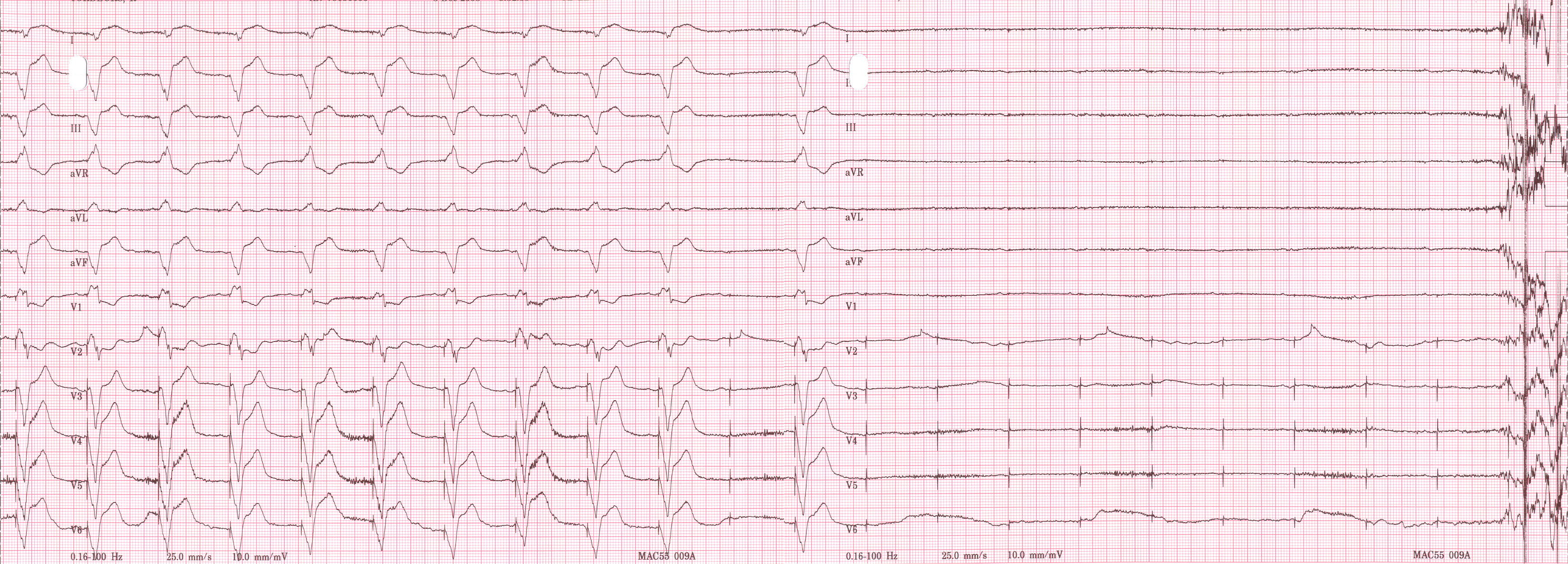
Artificial Cardiac Pacemaker
An artificial cardiac pacemaker (or artificial pacemaker, so as not to be confused with the natural cardiac pacemaker) or pacemaker is a medical device that generates electrical impulses delivered by electrodes to the chambers of the heart either the upper atria, or lower ventricles to cause the targeted chambers to contract and pump blood. By doing so, the pacemaker regulates the function of the electrical conduction system of the heart. The primary purpose of a pacemaker is to maintain an adequate heart rate, either because the heart's natural pacemaker is not fast enough, or because there is a block in the heart's electrical conduction system. Modern pacemakers are externally programmable and allow a cardiologist, particularly a cardiac electrophysiologist, to select the optimal pacing modes for individual patients. Most pacemakers are on demand, in which the stimulation of the heart is based on the dynamic demand of the circulatory system. Others send out a fixed rate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biological Pacemaker
A biological pacemaker is one or more types of cellular components that, when "implanted or injected into certain regions of the heart," produce specific electrical stimuli that mimic that of the body's natural pacemaker cells. Biological pacemakers are indicated for issues such as heart block, slow heart rate, and asynchronous heart ventricle contractions. The biological pacemaker is intended as an alternative to the artificial cardiac pacemaker that has been in human use since the late 1950s. Despite their success, several limitations and problems with artificial pacemakers have emerged during the past decades such as electrode fracture or damage to insulation, infection, re-operations for battery exchange, and venous thrombosis. The need for an alternative is most obvious in children, including premature newborn babies, where size mismatch and the fact that pacemaker leads do not grow with children are a problem. A more biological approach has been taken in order to mitigate ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurostimulator
Neurostimulation is the purposeful modulation of the nervous system's activity using invasive (e.g. microelectrodes) or non-invasive means (e.g. transcranial magnetic stimulation or transcranial electric stimulation, tES, such as tDCS or transcranial alternating current stimulation, tACS). Neurostimulation usually refers to the electromagnetic approaches to neuromodulation. Neurostimulation technology can improve the life quality of those who are severely paralyzed or have profound losses to various sense organs, as well as for permanent reduction of severe, chronic pain which would otherwise require constant (around-the-clock), high-dose opioid therapy (such as neuropathic pain and spinal-cord injury). It serves as the key part of neural prosthetics for hearing aids, artificial vision, artificial limbs, and brain-machine interfaces. In the case of neural stimulation, mostly an electrical stimulation is utilized and charge-balanced biphasic constant current waveforms or capacit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiac Pacemaker
350px, Image showing the cardiac pacemaker or SA node, the primary pacemaker within the electrical_conduction_system_of_the_heart">SA_node,_the_primary_pacemaker_within_the_electrical_conduction_system_of_the_heart. The_muscle_contraction.html" "title="electrical conduction system of the heart.">electrical conduction system of the heart">SA node, the primary pacemaker within the electrical conduction system of the heart. The muscle contraction">contraction of cardiac muscle (heart muscle) in all animals is initiated by electrical impulses known as action potentials that in the heart are known as cardiac action potentials. The rate at which these impulses fire controls the rate of cardiac contraction, that is, the heart rate. The cells that create these rhythmic impulses, setting the pace for blood pumping, are called pacemaker cells, and they directly control the heart rate. They make up the cardiac pacemaker, that is, the natural pacemaker of the heart. In most humans, the h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diaphragmatic Pacemaker
Diaphragm pacing (and even earlier as electrophrenic respiration) is the rhythmic application of electrical impulses to the diaphragm to provide artificial ventilatory support for respiratory failure or sleep apnea. Historically, this has been accomplished through the electrical stimulation of a phrenic nerve by an implanted receiver/electrode, though today an alternative option of attaching percutaneous wires to the diaphragm exists. History The idea of stimulating the diaphragm through the phrenic nerve was first firmly postulated by German physician Christoph Wilhelm Hufeland, who in 1783 proposed that such a technique could be applied as a treatment for asphyxia. French neurologist Duchenne de Boulogne made a similar proposal in 1855, though neither of them tested it. It was not until a year later that Hugo Wilhelm von Ziemssen demonstrated diaphragm pacing on a 27-year-old woman asphyxiated on charcoal fumes by rhythmically faradizing her phrenic nerves, saving her life. Duch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacemaker (running)
A pacemaker or pacesetter, sometimes informally called a rabbit, is a runner who leads a middle- or long-distance running event for the first section to ensure a fast time and avoid excessive tactical racing. Pacemakers are frequently employed by race organisers for world record attempts with specific instructions for lap times. Some athletes have essentially become professional pacemakers. A competitor who chooses the tactic of leading in order to win is called a front-runner rather than a pacemaker. Pacemakers may be used to avoid the tactics of deception that are possible in competition by those who, for example, race away from the start line (and are likely to subsequently slow down), giving the other runners the impression that they are far behind. A trusted team of pacemakers who are paid to keep the runners at a speed that they can manage for the rest of the race become useful in such a situation. Pacemakers are also used on world record attempts in order to make sur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacemaker (film)
''Pacemaker'' () is a 2012 South Korean sports drama film. This was director Kim Dal-joong's feature film debut; he had previously directed stage musicals. ''Pacemaker'' received three nominations at the 49th Grand Bell Awards (Best Actor, Best New Director, and Best New Actress). Plot Joo Man-ho, a boy from an impoverished family, has a talent for long-distance running but always finishes second place in a race — on purpose, in order to win the box of instant noodles given to runners-up. He grows up to become a national marathoner, but because of an injury, he never becomes a premier athlete and instead hold himself back as he did in his childhood. He is relegated to the role of "pacemaker" – someone who runs alongside the star athletes for three-quarters of the marathon (30 of 42.195 kilometers), making sure they stay on winning pace, but then letting them finish the race alone. Later in life, a cold-hearted marathon coach scouts Joo to run again, this time pacing for Korea's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Pacemaker
The Pacemaker is a pocket-size DJ system invented by Jonas Norberg. The device features include a 120 GB hard drive, a signal-to-noise ratio of 103, and many basic DJ audio tools, including line out and headphone crossfaders and jacks, bend, pitch, DJ pause, cue points, loop, equalisation, filter, sound effects, and a USB 2.0 connector. History As of 2008-10-02, the Pacemaker supports MP3, variable bitrate, AAC, OGG Vorbis, FLAC, AIFF, SND (file) and WAV. In 2007 the physical device was showcased at the Sónar Festival in Barcelona in June, on Ibiza in July and at IFA Berlin and PLASA trade shows. It was also at the Amsterdam dance event. Originally scheduled for release in February 2008, slight delays pushed it back to March 2008 when the first units were shipped. The first release of the device was to the first 2000 people who pre-ordered (all of whom received the "Premier Edition" of the device). Using his Tonium Pacemaker, DJ JMS made history in 2009 being the fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Pacemaker Awards
The National Pacemaker Awards are awards for excellence in American student journalism, given annually since 1927. The awards are generally considered to be the highest national honors in their field, and are unofficially known as the "Pulitzer Prizes of student journalism". The National Scholastic Press Association administers the contest for high school programs, while the Associated Collegiate Press administers the college and university contests. Pacemakers are awarded annually at the JEA/NSPA National Conference (for high schools) and the ACP/CMA National College Media Convention (for colleges) in the following categories: Newspaper, Online, Yearbook/Magazine, and Broadcast. Newspaper Pacemakers ACP, NSPA and the Newspaper Association of America Foundation have co-sponsored the Pacemaker competition since 1961. NSPA began the awards in 1927. The Pacemaker competition was discontinued in 1948–49, then resumed in 1961. The awards, which are considered by many to be the hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacemaker (software)
Pacemaker is an open-source high availability resource manager software used on computer clusters since 2004. Until about 2007, it was part of the Linux-HA project, then was split out to be its own project. It implements several APIs for controlling resources, but its preferred API for this purpose is the Open Cluster Framework resource agent API. Related software Pacemaker is generally used with Corosync Cluster engine or Linux-HA Heartbeat. See also *High-availability cluster High-availability clusters (also known as HA clusters, fail-over clusters) are groups of computers that support server applications that can be reliably utilized with a minimum amount of down-time. They operate by using high availability softwa ... * Red Hat cluster suite References {{Reflist External linksClusterLabs the home of Pacemaker. Cluster computing Free software programmed in C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacemaker (train)
An artificial cardiac pacemaker (or artificial pacemaker, so as not to be confused with the natural cardiac pacemaker) or pacemaker is a medical device that generates electrical impulses delivered by electrodes to the chambers of the heart either the upper atria, or lower ventricles to cause the targeted chambers to contract and pump blood. By doing so, the pacemaker regulates the function of the electrical conduction system of the heart. The primary purpose of a pacemaker is to maintain an adequate heart rate, either because the heart's natural pacemaker is not fast enough, or because there is a block in the heart's electrical conduction system. Modern pacemakers are externally programmable and allow a cardiologist, particularly a cardiac electrophysiologist, to select the optimal pacing modes for individual patients. Most pacemakers are on demand, in which the stimulation of the heart is based on the dynamic demand of the circulatory system. Others send out a fixed rate of i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_is_a_technique_for_noninvasive_stimulation_of_the_adult_brain.jpg)