|
Pa'u Riders
Pa'u riders (pronounced pah-oo riders), (sometimes written as ''pa-u riders''), are ''wahine'' () horseback riders who wear long, colorful skirts ( haw, pāʻū) and characteristically ride astride, rather than sidesaddle. This equestrian tradition's roots are from the early 19th century, when horses were introduced to Hawaii and aliʻi women dressed up to ride for formal occasions. It declined after the overthrow of the Kingdom of Hawaii, but was revitalized in the early 20th century with the establishment of formal riding organizations called Pa'u Riders. Today, they participate in Kamehameha Day floral parades and other parades and festivals throughout the islands. History The pa'u riding tradition began just after Captain Richard J. Cleveland introduced horses to Hawaii in 1803. Kamehameha disliked the creatures, partially on account of the amount of food they required, so western sailors began riding them along the beaches to demonstrate their capabilities. Hawaiian men and wom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pa'u Queen
Pa'u riders (pronounced pah-oo riders), (sometimes written as ''pa-u riders''), are ''wahine'' () equestrianism, horseback riders who wear long, colorful skirts ( haw, pāʻū) and characteristically ride astride, rather than sidesaddle. This equestrian tradition's roots are from the early 19th century, when horses were introduced to Hawaii and aliʻi women dressed up to ride for formal occasions. It declined after the overthrow of the Kingdom of Hawaii, but was revitalized in the early 20th century with the establishment of formal riding organizations called Pa'u Riders. Today, they participate in Kamehameha Day floral parades and other parades and festivals throughout the islands. History The pa'u riding tradition began just after Captain Richard J. Cleveland introduced horses to Hawaii in 1803. Kamehameha I, Kamehameha disliked the creatures, partially on account of the amount of food they required, so western sailors began riding them along the beaches to demonstrate their capab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isabella Bird
Isabella Lucy Bird, married name Bishop (15 October 1831 – 7 October 1904), was a nineteenth-century British explorer, writer, photographer, and naturalist. With Fanny Jane Butler she founded the John Bishop Memorial Hospital in Srinagar in today’s Kashmir. She was the first woman to be elected Fellow of the Royal Geographical Society. Early life Isabella Bird was born on 15 October 1831 in Boroughbridge Hall, Yorkshire, the home of her maternal grandmother and her father's first curacy after taking orders in 1821. Her parents were Rev Edward Bird and his second wife, Dora Lawson (1803–1866). Her paternal grandparents were Lucy Wilberforce Bird and Bird, Savage & Bird#Robert Bird, Robert Bird (cousins). Bird moved several times during her childhood. In 1832, Reverend Bird was appointed curate in Maidenhead. Because of her father's ill health, Bird's family moved again in 1834 to Tattenhall in Cheshire, a living presented to him by his cousin Dr John Bird Sumner, Bish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hawaii Culture
Hawaii ( ; haw, Hawaii or ) is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, Western United States, located in the Pacific Ocean about from the U.S. mainland. It is the only U.S. state outside North America, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only state geographically located within the tropics. Hawaii comprises Midway Atoll, nearly the entire Hawaiian Islands, Hawaiian archipelago, 137 High island, volcanic islands spanning that are physiography, physiographically and Ethnography, ethnologically part of the Polynesian subregion of Oceania. The state's ocean coastline is consequently the list of U.S. states and territories by coastline, fourth-longest in the U.S., at about . The eight main islands, from northwest to southeast, are Niihau, Niihau, Kauai, Kauai, Oahu, Oahu, Molokai, Molokai, Lanai, Lānai, Kahoolawe, Kahoolawe, Maui, and Hawaii (island), Hawaii—the last of these, after which the state is named, is often called the "Big Island" or "Hawa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hawaiiana
Hawaiiana is a popular term of academia used in reference to history and various aspects of the culture of Hawai'i, currently a region and state of the United States. The term is used especially in reflection of the periods of antiquity and the Kingdom of Hawai'i era. Hawaiiana has become increasingly popular among students of history and sociology throughout the world. The principal repository of Hawaiiana is the Princess Bernice Pauahi Bishop Museum in Honolulu on the island of O'ahu. The institution is also called the Hawai'i State Museum of Natural and Cultural History and often shares artifacts and information with other institutions globally for the sake of research and study. The term "Hawaiiana" has been in use since 1915, perhaps even earlier, despite the widespread belief Hawaiian entertainer and cultural expert, Nona Beamer, coined the term in 1948. See also *Americana Americana may refer to: *Americana (music), a genre or style of American music *Americana (culture ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Cruise Of The Snark
''The Cruise of the Snark'' (1911) is a non-fictional, illustrated book by Jack London chronicling his sailing adventure in 1907 across the south Pacific in his ketch the ''Snark''. Accompanying London on this voyage was his wife Charmian London and a small crew. London taught himself celestial navigation and the basics of sailing and of boats during the course of this adventure and describes these details to the reader. He visits exotic locations including the Solomon Islands and Hawaii, and his first-person accounts and photographs provide insight into these remote places at the beginning of the 20th century. About the ''Snark'' In 1906, Jack London began to build a 45-foot yacht on which he planned a round-the-world voyage, to last seven years. The ''Snark'' was named after Lewis Carroll's 1876 poem ''The Hunting of the Snark''. She had two masts and was 45 feet long at the waterline and 55 feet on deck, and London claimed to have spent thirty thousand dollars on her const ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jack London
John Griffith Chaney (January 12, 1876 – November 22, 1916), better known as Jack London, was an American novelist, journalist and activist. A pioneer of commercial fiction and American magazines, he was one of the first American authors to become an international celebrity and earn a large fortune from writing. He was also an innovator in the genre that would later become known as science fiction. London was part of the radical literary group "The Crowd" in San Francisco and a passionate advocate of animal rights, workers’ rights and socialism.Swift, John N. "Jack London's ‘The Unparalleled Invasion’: Germ Warfare, Eugenics, and Cultural Hygiene." American Literary Realism, vol. 35, no. 1, 2002, pp. 59–71. .Hensley, John R. "Eugenics and Social Darwinism in Stanley Waterloo's ‘The Story of Ab’ and Jack London's ‘Before Adam.’" Studies in Popular Culture, vol. 25, no. 1, 2002, pp. 23–37. . London wrote several works dealing with these topics, such as his dy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glottal Stop
The glottal plosive or stop is a type of consonantal sound used in many spoken languages, produced by obstructing airflow in the vocal tract or, more precisely, the glottis. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is . As a result of the obstruction of the airflow in the glottis, the glottal vibration either stops or becomes irregular with a low rate and sudden drop in intensity. Features Features of the glottal stop: * It has no phonation, as there is no airflow through the glottis. It is voiceless, however, in the sense that it is produced without vibration of the vocal cords. Writing In the traditional Romanization of many languages, such as Arabic, the glottal stop is transcribed with the apostrophe or the symbol ʾ, which is the source of the IPA character . In many Polynesian languages that use the Latin alphabet, however, the glottal stop is written with a rotated apostrophe, (called '' ‘okina'' in Hawaiian and Sam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theresa Wilcox
Teresa (also Theresa, Therese; french: Thérèse) is a feminine given name. It originates in the Iberian Peninsula in late antiquity. Its derivation is uncertain, it may be derived from Greek θερίζω (''therízō'') "to harvest or reap", or from θέρος (''theros'') "summer". It is first recorded in the form ''Therasia'', the name of Therasia of Nola, an aristocrat of the 4th century. Its popularity outside of Iberia increased because of saint Teresa of Ávila, and more recently Thérèse of Lisieux and Mother Teresa. In the United States it was ranked as the 852nd most popular name for girls born in 2008, down from 226th in 1992 (it ranked 65th in 1950, and 102nd in 1900). Spelled "Teresa," it was the 580th most popular name for girls born in 2008, down from 206th in 1992 (it ranked 81st in 1950, and 220th in 1900). People In aristocracy: *Teresa of Portugal (other) ** Theresa, Countess of Portugal (1080–1130), mother of Afonso Henriques, the first K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
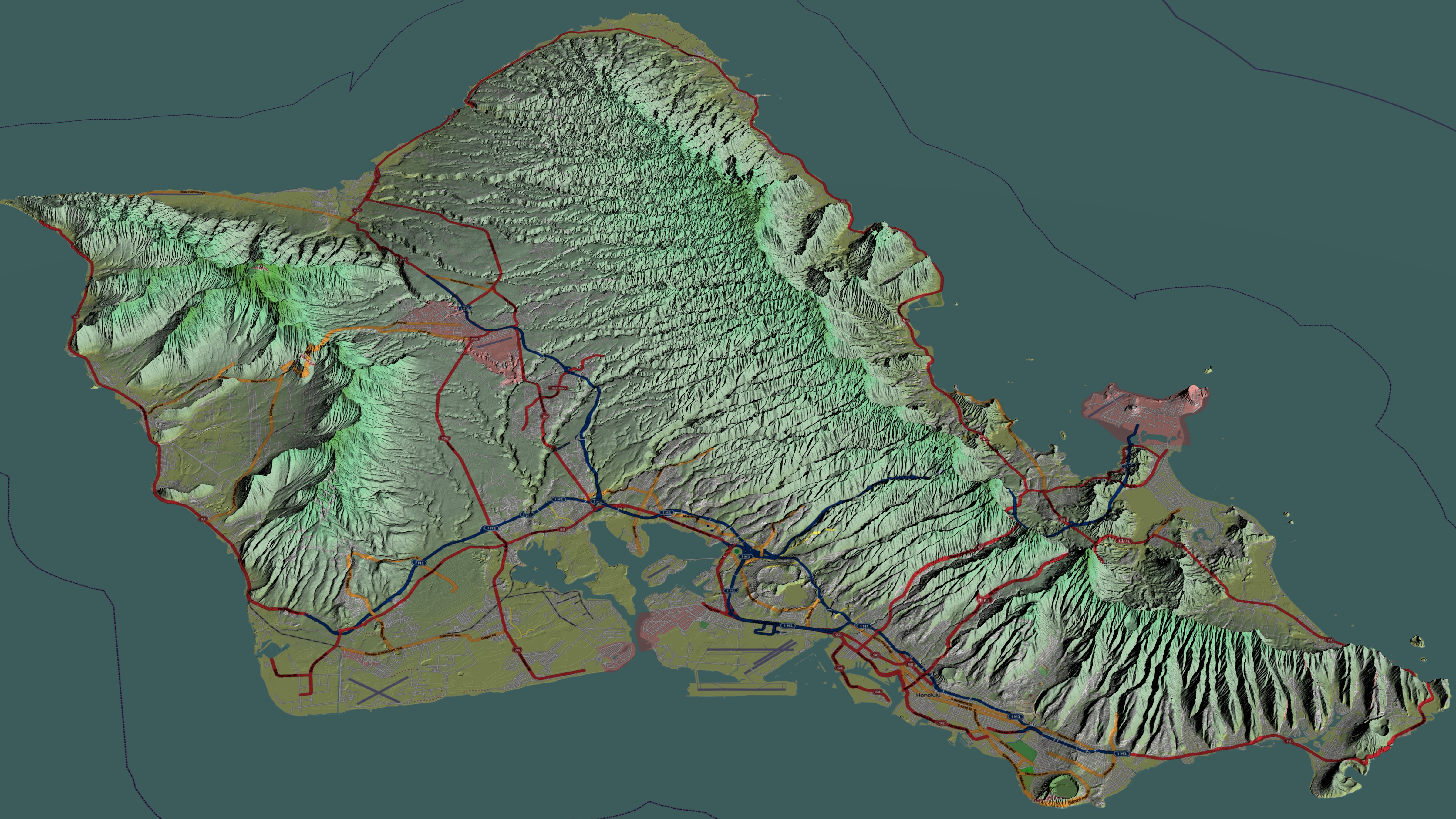
Oahu
Oahu () (Hawaiian language, Hawaiian: ''Oʻahu'' ()), also known as "The Gathering place#Island of Oʻahu as The Gathering Place, Gathering Place", is the third-largest of the Hawaiian Islands. It is home to roughly one million people—over two-thirds of the population of the U.S. state of Hawaii. The island of O’ahu and the Northwestern Hawaiian Islands constitute the City and County of Honolulu, Hawaii, City and County of Honolulu. The state capital, Honolulu, is on Oʻahu's southeast coast. Oʻahu had a population of 1,016,508 according to the 2020 U.S. Census, up from 953,207 people in 2010 (approximately 70% of the total 1,455,271 population of the State of Hawaii, with approximately 81% of those living in or near the Honolulu urban area). Name The Island of O{{okinaahu in Hawaii is often nicknamed (or translated as) ''"The Gathering Place"''. It appears that O{{okinaahu grew into this nickname; it is currently the most populated Hawaiian islands, Hawaiian Island, how ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waikiki
Waikiki (; haw, Waikīkī; ; also known as Waikiki Beach) is a neighborhood of Honolulu on the south shore of the island of Oahu in the U.S. state of Hawaii. Waikiki is most famous for Waikiki Beach, which is one of six beaches in the district, along with Queen's Beach, Kuhio Beach, Gray's Beach, Fort DeRussy Beach and Kahanamoku Beach. Waikiki Beach is almost entirely man-made. There are beaches called Waikiki in other parts of the world, such as Tarragona (Spain), Western Australia (Australia), or Lima ( Peru). Waikiki (Hawaii) is home to public places including Kapiolani Park, Fort DeRussy, Kahanamoku Lagoon, Kūhiō Beach Park and Ala Wai Harbor. Waikiki was the first capital of the Kingdom of Hawaii from 1795 to 1796. Etymology The Hawaiian language name means ''spouting fresh water'', for springs and streams that fed wetlands that once separated Waikiki from the interior. History The area was a retreat for Hawaiian royalty in the 1800s who enjoyed surfing there ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hawaiian Language
Hawaiian (', ) is a Polynesian language of the Austronesian language family that takes its name from Hawaii, the largest island in the tropical North Pacific archipelago where it developed. Hawaiian, along with English, is an official language of the US state of Hawaii. King Kamehameha III established the first Hawaiian-language constitution in 1839 and 1840. For various reasons, including territorial legislation establishing English as the official language in schools, the number of native speakers of Hawaiian gradually decreased during the period from the 1830s to the 1950s. Hawaiian was essentially displaced by English on six of seven inhabited islands. In 2001, native speakers of Hawaiian amounted to less than 0.1% of the statewide population. Linguists were unsure if Hawaiian and other endangered languages would survive. Nevertheless, from around 1949 to the present day, there has been a gradual increase in attention to and promotion of the language. Public Hawaiian-langua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |