|
P-class Cruiser
The P class was a planned group of twelve heavy cruisers of Nazi Germany's '' Kriegsmarine''; they were the successor to the s. Design work began in 1937 and continued until 1939; at least twenty designs were submitted with nine of them being considered. There were three designs that were selected as the final contenders. One design was armed with six 283mm main guns in one triple turret forward and one more turret aft. It had two 150mm double secondary gun turrets as secondary armament with one being positioned above and just fore of the aft of the main 283mm main turret, and the other being in front and lower of the front main gun turret. This design had more beam than the other 2 designs. It also mounted 2 seaplanes on its fantail instead of the mid ship area. The final design was armed with six quick-firing guns in two triple turrets, as in the preceding ''Deutschland'' class. The ships were designated as ''Panzerschiff'' (armored ship), and given the preliminary names P1–P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
D-class Cruiser (Germany)
The D-class cruisers were a pair of German heavy cruisers, classified as ("armored ships") by the (Navy of the Realm). The ships were improved versions of the preceding s, authorized by Adolf Hitler in 1933. They were intended to counter a new French naval construction program. Displacement increased to , but Hitler allowed only increases to armor, prohibiting additions to the ships' main battery armament. Only one of the two ships was laid down, but work was canceled less than five months after the keel was laid. It was determined that the designs should be enlarged to counter the new French . The construction contracts for both ships were superseded by the s. Design The ships were designed as follow-ons to the s. In 1933, the rise of the Nazi Party brought Adolf Hitler to power in Germany. At the time, he opposed a large-scale naval rearmament program, but decided to allow limited construction to counter French naval expansion. He therefore authorized the (Navy of the Real ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against France. The modern Royal Navy traces its origins to the early 16th century; the oldest of the UK's armed services, it is consequently known as the Senior Service. From the middle decades of the 17th century, and through the 18th century, the Royal Navy vied with the Dutch Navy and later with the French Navy for maritime supremacy. From the mid 18th century, it was the world's most powerful navy until the Second World War. The Royal Navy played a key part in establishing and defending the British Empire, and four Imperial fortress colonies and a string of imperial bases and coaling stations secured the Royal Navy's ability to assert naval superiority globally. Owing to this historical prominence, it is common, even among non-Britons, to ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamburg
(male), (female) en, Hamburger(s), Hamburgian(s) , timezone1 = Central (CET) , utc_offset1 = +1 , timezone1_DST = Central (CEST) , utc_offset1_DST = +2 , postal_code_type = Postal code(s) , postal_code = 20001–21149, 22001–22769 , area_code_type = Area code(s) , area_code = 040 , registration_plate = , blank_name_sec1 = GRP (nominal) , blank_info_sec1 = €123 billion (2019) , blank1_name_sec1 = GRP per capita , blank1_info_sec1 = €67,000 (2019) , blank1_name_sec2 = HDI (2018) , blank1_info_sec2 = 0.976 · 1st of 16 , iso_code = DE-HH , blank_name_sec2 = NUTS Region , blank_info_sec2 = DE6 , website = , footnotes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blohm & Voss
Blohm+Voss (B+V), also written historically as Blohm & Voss, Blohm und Voß etc., is a German shipbuilding and engineering company. Founded in Hamburg in 1877 to specialise in steel-hulled ships, its most famous product was the World War II battleship '' Bismarck''. In the 1930s, its owners established the Hamburger Flugzeugbau aircraft manufacturer which, shortly before the outbreak of World War II, adopted the name of its parent company. Following a difficult period after the war, B+V was revived, changing ownership among several owners, as Thyssen Group and Star Capital. In 2016, it became a subsidiary of Lürssen and continues to supply both the military and civilian markets. It serves two areas – new construction of warships as NVL B.V. & Co. KG, and new construction and refitting of megayachts.Meyer, Kristian"Erste Bilanz nach Übernahme Alles neu bei Traditionswerft Blohm+Voss" ''Hamburger Morgenpost'', 27 April 2018. The company has been in operation, building ships and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kiel
Kiel () is the capital and most populous city in the northern Germany, German state of Schleswig-Holstein, with a population of 246,243 (2021). Kiel lies approximately north of Hamburg. Due to its geographic location in the southeast of the Jutland peninsula on the southwestern shore of the Baltic Sea, Kiel has become one of Germany's major maritime centres, known for a variety of international sailing events, including the annual Kiel Week, which is the biggest sailing event in the world. Kiel is also known for the Kiel mutiny, Kiel Mutiny, when sailors refused to board their vessels in protest against Germany's further participation in World War I, resulting in the abdication of the Wilhelm II, German Emperor, Kaiser and the formation of the Weimar Republic. The Olympic sailing competitions of the 1936 Summer Olympics, 1936 and the 1972 Summer Olympics#Venues, 1972 Summer Olympics were held in the Bay of Kiel. Kiel has also been one of the traditional homes of the German Nav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deutsche Werke
Deutsche Werke was a German shipbuilding company that was founded in 1925 when Kaiserliche Werft Kiel and other shipyards were merged. It came as a result of the Treaty of Versailles after World War I that forced the German defense industry to shrink. The company was owned by the government of the Weimar Republic and its headquarters was in Berlin while the manufacturing location was in Kiel. Deutsche Werke started building merchant ships, but when the Nazi Party gained power in 1933 the production was changed to naval ships. Besides shipbuilding, Deutsche Werke also produced firearms. Especially well-known are the so-called Ortgies pistols, which were particularly popular in the United States. The pistols were developed by Heinrich Ortgies. During World War II the company expanded to Gdynia, establishing ''Deutsche Werke Gotenhafen''. Deutsche Werke facilities and infrastructure were destroyed during World War II by bombing raids. Parts of the works were reorganised as Maschi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hull (watercraft)
A hull is the watertight body of a ship, boat, or flying boat. The hull may open at the top (such as a dinghy), or it may be fully or partially covered with a deck. Atop the deck may be a deckhouse and other superstructures, such as a funnel, derrick, or mast. The line where the hull meets the water surface is called the waterline. General features There is a wide variety of hull types that are chosen for suitability for different usages, the hull shape being dependent upon the needs of the design. Shapes range from a nearly perfect box in the case of scow barges to a needle-sharp surface of revolution in the case of a racing multihull sailboat. The shape is chosen to strike a balance between cost, hydrostatic considerations (accommodation, load carrying, and stability), hydrodynamics (speed, power requirements, and motion and behavior in a seaway) and special considerations for the ship's role, such as the rounded bow of an icebreaker or the flat bottom of a landing craft. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beam (nautical)
The beam of a ship is its width at its widest point. The maximum beam (BMAX) is the distance between planes passing through the outer extremities of the ship, beam of the hull (BH) only includes permanently fixed parts of the hull, and beam at waterline (BWL) is the maximum width where the hull intersects the surface of the water. Generally speaking, the wider the beam of a ship (or boat), the more initial stability it has, at the expense of secondary stability in the event of a capsize, where more energy is required to right the vessel from its inverted position. A ship that heels on her ''beam ends'' has her deck beams nearly vertical. Typical values Typical length-to-beam ratios ( aspect ratios) for small sailboats are from 2:1 (dinghies to trailerable sailboats around ) to 5:1 (racing sailboats over ). Large ships have widely varying beam ratios, some as large as 20:1. Rowing shells designed for flatwater racing may have length to beam ratios as high as 30:1, while a cor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Length Overall
__NOTOC__ Length overall (LOA, o/a, o.a. or oa) is the maximum length of a vessel's hull measured parallel to the waterline. This length is important while docking the ship. It is the most commonly used way of expressing the size of a ship, and is also used for calculating the cost of a marina berth (for example, £2.50 per metre LOA). LOA is usually measured on the hull alone. For sailing ships, this may ''exclude'' the bowsprit and other fittings added to the hull. This is how some racing boats and tall ships use the term LOA. However, other sources may include bowsprits in LOA. Confusingly, LOA has different meanings. "Sparred length", "Total length including bowsprit", "Mooring length" and "LOA including bowsprit" are other expressions that might indicate the full length of a sailing ship. LOD Often used to distinguish between the length of a vessel including projections (e.g. bow sprits, etc.) from the length of the hull itself, the Length on Deck or LOD is often repor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plan Z
Plan Z was the name given to the planned re-equipment and expansion of the ''Kriegsmarine'' (German navy) ordered by Adolf Hitler in early 1939. The fleet was meant to challenge the naval power of the United Kingdom, and was to be completed by 1948. Development of the plan began in 1938, but it reflected the evolution of the strategic thinking of the ''Oberkommando der Marine'' (Naval High Command) over the two decades following World War I. The plan called for a fleet centered on ten battleships and four aircraft carriers which were intended to battle the Royal Navy. This force would be supplemented with numerous long-range cruisers that would attack British shipping. A relatively small force of U-boats was also stipulated. When World War II broke out in September 1939, almost no work had been done on the new ships ordered under Plan Z. The need to shift manufacturing capacity to more pressing requirements forced the ''Kriegsmarine'' to abandon the construction program, and only a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erich Raeder
Erich Johann Albert Raeder (24 April 1876 – 6 November 1960) was a German admiral who played a major role in the naval history of World War II. Raeder attained the highest possible naval rank, that of grand admiral, in 1939, becoming the first person to hold that rank since Henning von Holtzendorff in 1918. Raeder led the ''Kriegsmarine'' for the first half of the war; he resigned in January 1943 and was replaced by Karl Dönitz. At the Nuremberg Trials he was sentenced to life imprisonment but was released early owing to failing health. Early career Early years Raeder was born in Wandsbek in the Prussian province of Schleswig-Holstein in the German Empire. His father was a headmaster, who as a teacher and a father was noted for his marked authoritarian views, and who impressed upon his son the values of hard work, thrift, faith and obedience – all values that Raeder preached throughout his life.Bird ''Erich Raeder'' pp. 1–2. Hans Raeder also warned his children that if ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
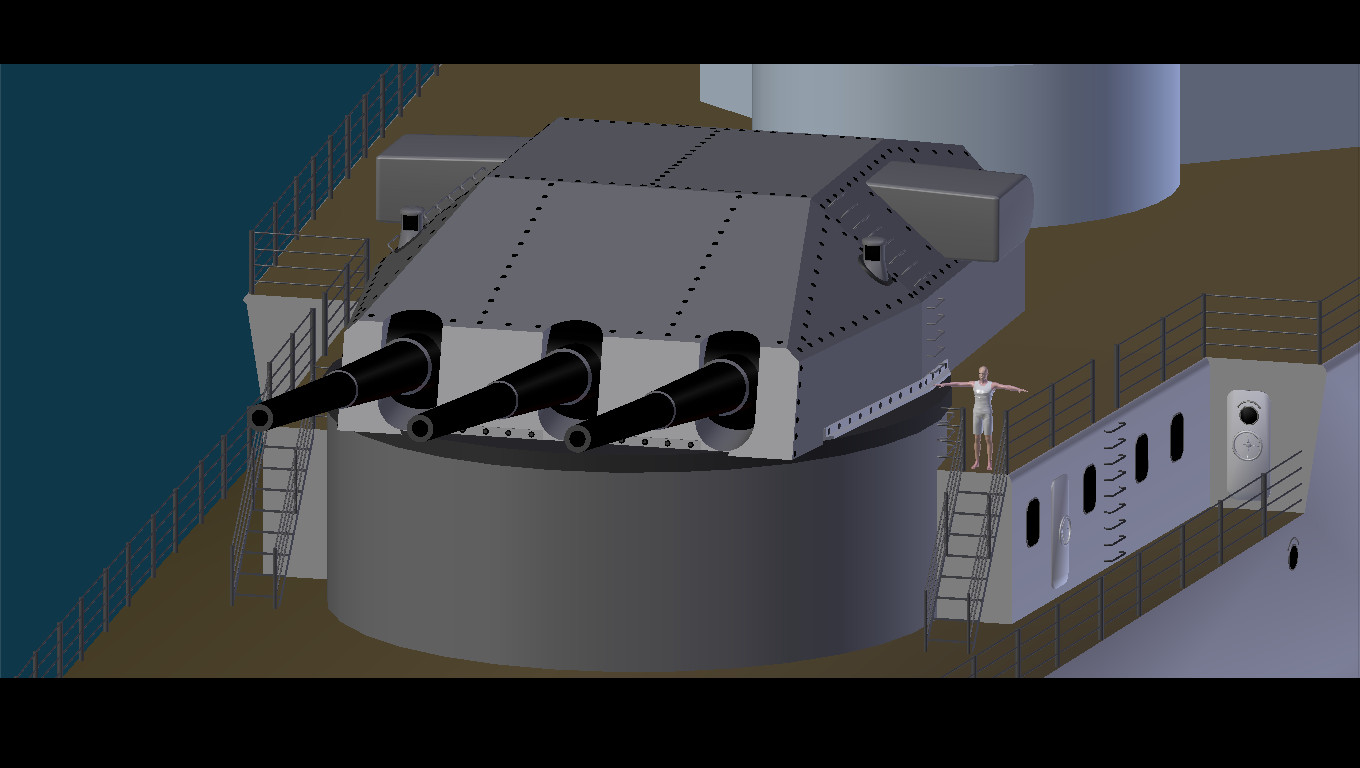
Gun Turret
A gun turret (or simply turret) is a mounting platform from which weapons can be fired that affords protection, visibility and ability to turn and aim. A modern gun turret is generally a rotatable weapon mount that houses the crew or mechanism of a projectile-firing weapon and at the same time lets the weapon be aimed and fired in some degree of azimuth and elevation (cone of fire). Description Rotating gun turrets protect the weapon and its crew as they rotate. When this meaning of the word "turret" started being used at the beginning of the 1860s, turrets were normally cylindrical. Barbettes were an alternative to turrets; with a barbette the protection was fixed, and the weapon and crew were on a rotating platform inside the barbette. In the 1890s, armoured hoods (also known as "gun houses") were added to barbettes; these rotated with the platform (hence the term "hooded barbette"). By the early 20th Century, these hoods were known as turrets. Modern warships have gu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |